We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Monkeypox DNA Polymerase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
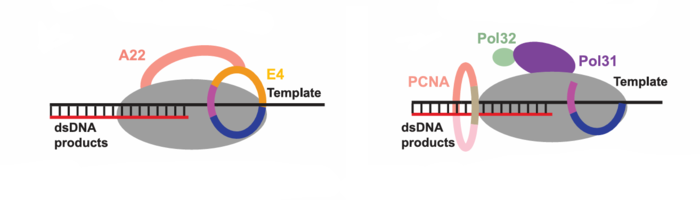
'''Supporting biochemistry:''' Primer-extension assays show F8 alone is distributive (incorporates <14 nt), while addition/assembly with A22–E4 yields full-length extension (60 nt template) in a concentration-dependent manner; alanine scanning of E4 residues (e.g., W36, R39, N165) confirms residues critical for processivity. | '''Supporting biochemistry:''' Primer-extension assays show F8 alone is distributive (incorporates <14 nt), while addition/assembly with A22–E4 yields full-length extension (60 nt template) in a concentration-dependent manner; alanine scanning of E4 residues (e.g., W36, R39, N165) confirms residues critical for processivity. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | [[Image:MPXV.png|700px]] | ||
| Line 59: | Line 60: | ||
47 F8 residues directly contact DNA (29 to template strand, 18 to primer strand), mostly interacting with phosphodiester backbone rather than bases — explains sequence-independent elongation. | 47 F8 residues directly contact DNA (29 to template strand, 18 to primer strand), mostly interacting with phosphodiester backbone rather than bases — explains sequence-independent elongation. | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Refernces== | ||
| + | Peng, X., Zhang, Y., Sun, L., Peng, R., Zhao, Y., Chen, Y., Lu, X., Yang, H., & Rao, Z. (2023). Structure of the monkeypox virus DNA polymerase holoenzyme. Science, 380(6652), 703–709. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.ade6360 | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 01:12, 30 November 2025
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Yana Fedotova, Eric Martz, Silky Srivastava, Alicia Daeden, Jaime Prilusky, Susana Retamal, Eran Hodis, Wayne Decatur