Sandbox Aryan 20221057 BI3323-Aug2025
From Proteopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| | ||
| - | ''' | + | === Key Interactions === |
| + | Cas9's PI domain (residues ~1100-1368) mediates multiple contacts: electrostatic histone tail interactions (non-essential for binding), PI edge lysine '''K1155''' stabilizing the post-cleavage complex, and core DNA loops ('''H1264, R1298, K1300''') causing inhibitory non-specific binding. Mutants disrupting PI-core DNA contacts (H1264A/R1298Q) enhance both in vitro cleavage efficiency and rice genome editing.[attached_file:1] | ||
| - | Cas9 | + | === Biological Insights === |
| - | + | Nucleosomes inhibit Cas9 via two mechanisms: (1) DNA end inflexibility blocks access; (2) PI domain trapping restricts domain motions needed for cleavage. Entry-exit asymmetry arises from Widom601 sequence-dependent flexibility, explaining variable editing efficiency across chromatin contexts.[web:14] | |
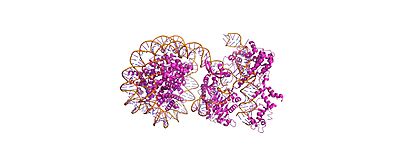
| - | + | [[Image:8YNYOverall.jpg|400px|thumb|Scene 1: Overall complex - DNA unwrapping]] | |
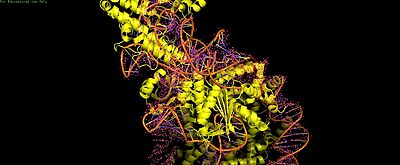
| - | + | [[Image:8YNYPI.jpg|400px|thumb|Scene 2: PI domain contacts]] | |
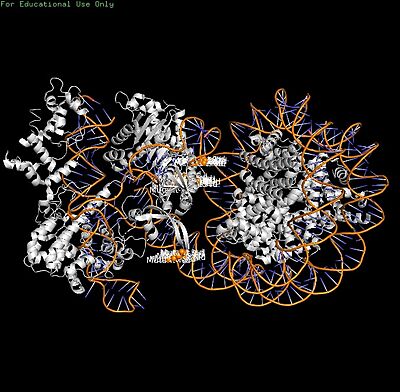
| - | + | [[Image:8YNYMutant.jpg|400px|thumb|Scene 3: Mutant sites (orange)]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | Scene 3: Mutant sites | + | |
| - | + | ||
BI3323-Aug2025 | BI3323-Aug2025 | ||
Revision as of 17:56, 30 November 2025
Cas9-Nucleosome Complex (PDB: 8YNY)
Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoprotein targets linker DNA (PAM1/PAM28) and entry-exit regions (SHL6) of nucleosomes, avoiding tightly wrapped core DNA (SHL0-5), as revealed by native-PAGE on Widom 601 nucleosomes. The cryo-EM structure (PDB: 8YNY, 4.52 Å, EMDB: EMD-39431) captures the post-cleavage ternary complex at PAM1, showing ~15 bp DNA peeled from the histone octamer, exposing H3 N-terminus—mimicking eukaryotic nucleosome unwrapping.
Key Interactions
Cas9's PI domain (residues ~1100-1368) mediates multiple contacts: electrostatic histone tail interactions (non-essential for binding), PI edge lysine K1155 stabilizing the post-cleavage complex, and core DNA loops (H1264, R1298, K1300) causing inhibitory non-specific binding. Mutants disrupting PI-core DNA contacts (H1264A/R1298Q) enhance both in vitro cleavage efficiency and rice genome editing.[attached_file:1]
Biological Insights
Nucleosomes inhibit Cas9 via two mechanisms: (1) DNA end inflexibility blocks access; (2) PI domain trapping restricts domain motions needed for cleavage. Entry-exit asymmetry arises from Widom601 sequence-dependent flexibility, explaining variable editing efficiency across chromatin contexts.[web:14]
BI3323-Aug2025