User:Grace Natalie
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<font size=4 face ="Arial">Background</font> | <font size=4 face ="Arial">Background</font> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
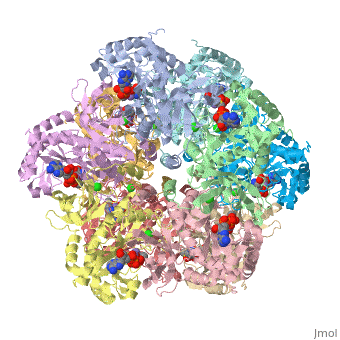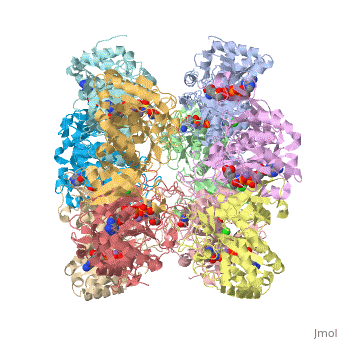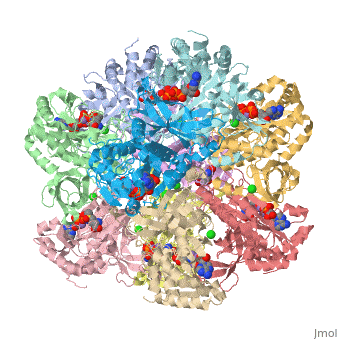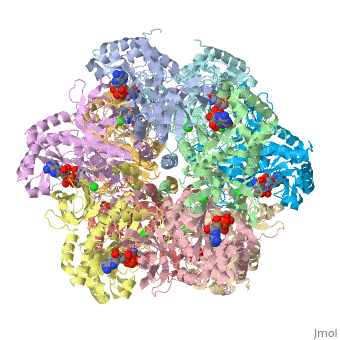
| - | <font size=3> | + | <font size=3>Glutamine synthetase (GS) catalyzes the ATP-dependent condensation of ammonia and |
| - | + | glutamate to yield glutamine, ADP, and inorganic phosphate in the presence of divalent cations. | |
| - | + | The reaction occurs in two steps with γ-glutamyl phosphate as an intermediate and is used by | |
| - | </font> | + | bacteria to introduce reduced nitrogen into cellular metabolism. GS is an enzyme of 12 identical |
| + | subunits, arranged in two rings of 6, with the active site between each pair of subunits in a ring. | ||
| + | GS contains two divalent cation sites (n1,n2) and one monovalent cation site per subunit.</font> | ||
Revision as of 08:47, 7 December 2008
The Glutamine Synthetase Project
Goals
- To map the ATP binding site
- Indicate which residues stabilize ATP binding
- Indicate which residues are important for activity and how they contribute to catalysis
Background
Glutamine synthetase (GS) catalyzes the ATP-dependent condensation of ammonia and
glutamate to yield glutamine, ADP, and inorganic phosphate in the presence of divalent cations.
The reaction occurs in two steps with γ-glutamyl phosphate as an intermediate and is used by
bacteria to introduce reduced nitrogen into cellular metabolism. GS is an enzyme of 12 identical
subunits, arranged in two rings of 6, with the active site between each pair of subunits in a ring.
GS contains two divalent cation sites (n1,n2) and one monovalent cation site per subunit.
University of Maryland Baltimore County - BioChemistry
|