This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Grace Natalie
From Proteopedia
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
<font size=2>Glutamine synthetase (GS) catalyzes the ATP-dependent condensation of ammonia and | <font size=2>Glutamine synthetase (GS) catalyzes the ATP-dependent condensation of ammonia and | ||
glutamate to yield glutamine, ADP, and inorganic phosphate in the presence of divalent cations | glutamate to yield glutamine, ADP, and inorganic phosphate in the presence of divalent cations | ||
| - | <applet load='1lgr' size='350' color='white' frame='true' align='right' caption='Glutamine Synthetase from Salmonella typhimurium'/> | ||
<ref name="Liaw">Liaw, S-H, et.al.,Discovery of the ammonium substrate site on glutamine synthetase, a third cation binding site Protein Sci. 1995 4: 2358-2365</ref> . | <ref name="Liaw">Liaw, S-H, et.al.,Discovery of the ammonium substrate site on glutamine synthetase, a third cation binding site Protein Sci. 1995 4: 2358-2365</ref> . | ||
The reaction occurs in two steps with γ-glutamyl phosphate as an intermediate and is used by | The reaction occurs in two steps with γ-glutamyl phosphate as an intermediate and is used by | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
<center><font size=2>Glutamate + NH<SUB>4</SUB><SUP>+</SUP> + ATP --> glutamine + ADP + P<SUB>i</SUB></font></center> | <center><font size=2>Glutamate + NH<SUB>4</SUB><SUP>+</SUP> + ATP --> glutamine + ADP + P<SUB>i</SUB></font></center> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | <applet load='1lgr' size='350' color='white' frame='true' align='right' caption='Glutamine Synthetase from Salmonella typhimurium'> | ||
<font size=4 face ="Arial">Overall Mechanism</font> | <font size=4 face ="Arial">Overall Mechanism</font> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 04:16, 22 December 2008
Background
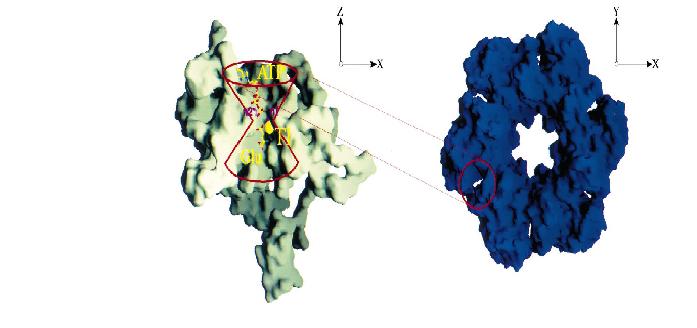
Glutamine synthetase (GS) catalyzes the ATP-dependent condensation of ammonia and
glutamate to yield glutamine, ADP, and inorganic phosphate in the presence of divalent cations
[1] .
The reaction occurs in two steps with γ-glutamyl phosphate as an intermediate and is used by
bacteria to introduce reduced nitrogen into cellular metabolism. GS is a dodecamer formed from
two face-to-face hexameric rings of subunits, with 12 active sites formed between monomers
[2] .
| |||||||||||