Phosphoglucoisomerase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Phosphoglucoisomerase is also know for a list of activities outside the cells: | Phosphoglucoisomerase is also know for a list of activities outside the cells: | ||
| - | * Neuroleukin (NLK)- nerve growth factor secreted by T cells, also used to stimulate the production of immunoglobulin. | + | * Neuroleukin (NLK)- nerve growth factor secreted by T cells, also used to stimulate the production of immunoglobulin <ref>PMID:3764429</ref>. |
* Autocrine motility factor (AMF)- product of tumor cells, it promotes cell migration and viewed as a possible cause in cancer metastasis<ref>PMID:12054796</ref>. | * Autocrine motility factor (AMF)- product of tumor cells, it promotes cell migration and viewed as a possible cause in cancer metastasis<ref>PMID:12054796</ref>. | ||
| - | * Maturation factor(MF) | + | * Maturation factor(MF) <ref>PMID:8639816</ref> |
| - | * Myofibril-bound serine protese inhibitor (MBSPI) | + | * Myofibril-bound serine protese inhibitor (MBSPI)<ref>PMID:10833440</ref> |
=='''Structure'''== | =='''Structure'''== | ||
Revision as of 22:41, 28 February 2010
|
Phosphoglucoisomerase (alternatively known as phosphoglucose isomerase or Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase) are a group of enzymes of the isomerase family (EC 5.3.1.9), so named for their main function in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. In both these pathways phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI) is used to inter-convert glucose-6-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate, reaction driven by the relative concentrations of these sugars in the cytoplasmic matrix of the cell.
Phosphoglucoisomerase is also know for a list of activities outside the cells:
- Neuroleukin (NLK)- nerve growth factor secreted by T cells, also used to stimulate the production of immunoglobulin [1].
- Autocrine motility factor (AMF)- product of tumor cells, it promotes cell migration and viewed as a possible cause in cancer metastasis[2].
- Maturation factor(MF) [3]
- Myofibril-bound serine protese inhibitor (MBSPI)[4]
Contents |
Structure
|
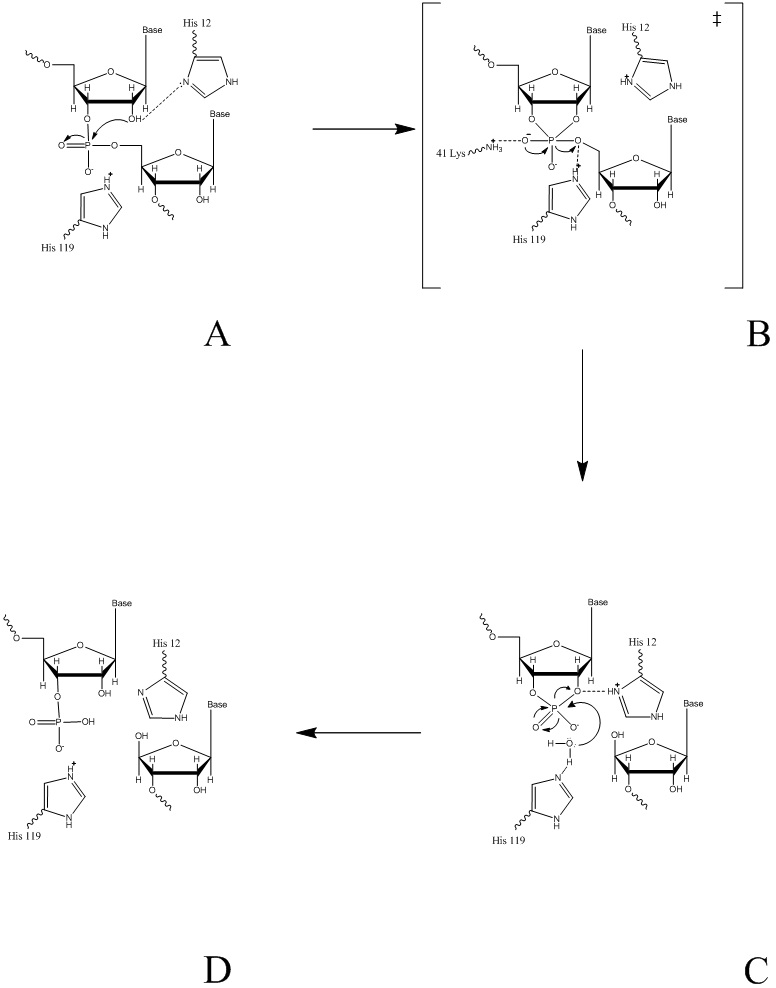
Mechanism
Links
References
- ↑ Gurney ME, Heinrich SP, Lee MR, Yin HS. Molecular cloning and expression of neuroleukin, a neurotrophic factor for spinal and sensory neurons. Science. 1986 Oct 31;234(4776):566-74. PMID:3764429
- ↑ Tanaka N, Haga A, Uemura H, Akiyama H, Funasaka T, Nagase H, Raz A, Nakamura KT. Inhibition mechanism of cytokine activity of human autocrine motility factor examined by crystal structure analyses and site-directed mutagenesis studies. J Mol Biol. 2002 May 10;318(4):985-97. PMID:12054796 doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00186-9
- ↑ Xu W, Seiter K, Feldman E, Ahmed T, Chiao JW. The differentiation and maturation mediator for human myeloid leukemia cells shares homology with neuroleukin or phosphoglucose isomerase. Blood. 1996 Jun 1;87(11):4502-6. PMID:8639816
- ↑ Cao MJ, Osatomi K, Matsuda R, Ohkubo M, Hara K, Ishihara T. Purification of a novel serine proteinase inhibitor from the skeletal muscle of white croaker (Argyrosomus argentatus). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Jun 7;272(2):485-9. PMID:10833440 doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.2803
- ↑ Read J, Pearce J, Li X, Muirhead H, Chirgwin J, Davies C. The crystal structure of human phosphoglucose isomerase at 1.6 A resolution: implications for catalytic mechanism, cytokine activity and haemolytic anaemia. J Mol Biol. 2001 Jun 1;309(2):447-63. PMID:11371164 doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4680
- ↑ Lee JH, Chang KZ, Patel V, Jeffery CJ. Crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with its substrate D-fructose 6-phosphate. Biochemistry. 2001 Jul 3;40(26):7799-805. PMID:11425306
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Joel L. Sussman, Bogdan Stancu, Michal Harel, Andrew Gilman, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner