This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Michael nobbe sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(→'''Structure:''') |
(→'''Structure:''') |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Isocitrate dehydrogenase is SCOP classified as an alpha beta structure. Its secondary composition consists of mainly alpha helices and beta sheets which are arranged into three layer alpha beta alpha sandwich structures. The entire protein consists of two side by side sandwich structures that face opposite directions. This then causes the proteins two active sites to face opposite directions as well. These two groups make up the A and B subunits of isocitrate dehydrogenase. | Isocitrate dehydrogenase is SCOP classified as an alpha beta structure. Its secondary composition consists of mainly alpha helices and beta sheets which are arranged into three layer alpha beta alpha sandwich structures. The entire protein consists of two side by side sandwich structures that face opposite directions. This then causes the proteins two active sites to face opposite directions as well. These two groups make up the A and B subunits of isocitrate dehydrogenase. | ||
| - | [[Image:Human isocitrate]] | + | [[Image:Human isocitrate.jpeg]] |
Human Isocitrate Dehydrogenase bound by NADH and CA2+ | Human Isocitrate Dehydrogenase bound by NADH and CA2+ | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
Image made using JMOL | Image made using JMOL | ||
| - | [[Image:Chemicals isocitrate]] | + | [[Image:Chemicals isocitrate.jpeg]] |
Citric Acid is converted to alpha-ketoglutarate | Citric Acid is converted to alpha-ketoglutarate | ||
Revision as of 20:27, 1 March 2010
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Structure:
Isocitrate dehydrogenase is SCOP classified as an alpha beta structure. Its secondary composition consists of mainly alpha helices and beta sheets which are arranged into three layer alpha beta alpha sandwich structures. The entire protein consists of two side by side sandwich structures that face opposite directions. This then causes the proteins two active sites to face opposite directions as well. These two groups make up the A and B subunits of isocitrate dehydrogenase.
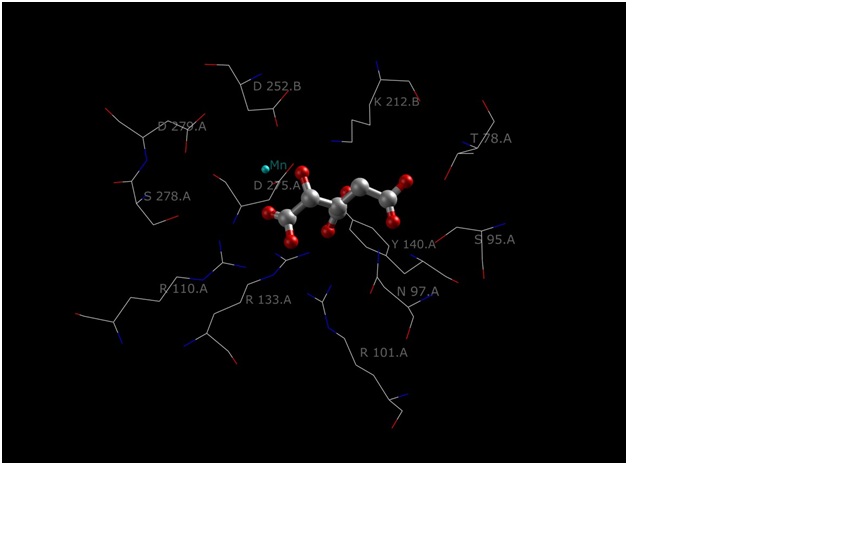
Human Isocitrate Dehydrogenase bound by NADH and CA2+ and Citrate Image made using JMOL
Image:Chemicals isocitrate.jpeg
Citric Acid is converted to alpha-ketoglutarate
Image from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isocitrate_dehydrogenase
Function:
Isocitrate dehydrogenase is a digestive enzyme that is used in the citric acid cycle. Its main function is to catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate into alpha-ketoglutarate. Human isocitrate dehydrogenase is regulation is not fully understood however, it is known that NADP and Ca2+ bind in the active site to create three different conformations. These conformations form in the active site and are as follows: a loop is form in the inactive enzyme, a partially unraveled alpha helix in the semi open form, and a alpha helix in the active form (PDB). Bacterial isocitrate dehydrogenase uses phosphorylation for regulation. The Ser94 residue undergoes reversible phosphorylation causing structural changes in the active site which hinders the catalytic function of the enzyme (PBD).
Image from:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isocitrate_dehydrogenase Image:C:/.jpg