We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox 167
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(→Luciferase Reaction) |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Luciferase Reaction == | == Luciferase Reaction == | ||
| - | + | Typically, luciferases produce light through a high energy complex with a luciferin cofactor, and ATP. In L. polyedrum, the process is pH specific, requiring an optimal pH of about | |
Revision as of 17:46, 8 March 2010
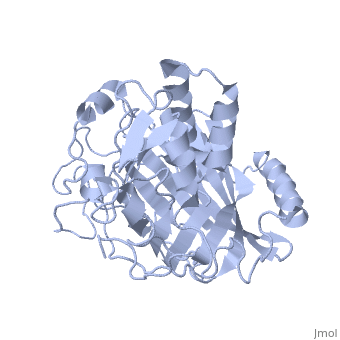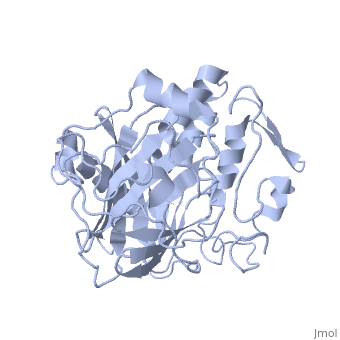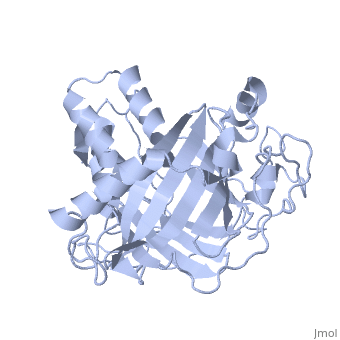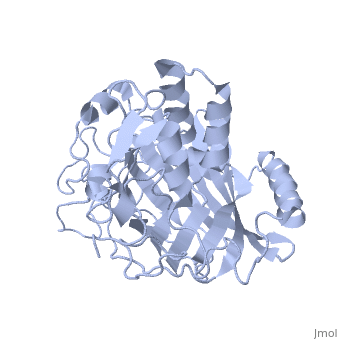
Lingulodinium polyedrum dinoflagellate luciferase
|
Lingulodinium polyedrum, a marine dinoflagellate often responsible for red tide, posesses a unique-domain luciferase enyzme. When mechanically stimulated, the organism uses this enzyme to produce a blue light, likely for use in quorum sensing.
Introduction
In L. polyedrum, the luciferase enzyme is a single polypeptide chain folded into 3 similiar domains. Each domain participates in its own reaction with luciferin, allowing for simultaneous luciferase reactions to take place on the same protein.
Luciferase Reaction
Typically, luciferases produce light through a high energy complex with a luciferin cofactor, and ATP. In L. polyedrum, the process is pH specific, requiring an optimal pH of about