Copper, Zinc Superoxide Dismutase
From Proteopedia
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==The Reaction of Dismutase== | ==The Reaction of Dismutase== | ||
| - | + | In mammals there are three known isomers of superoxide dismutase (SOD). Copper and Zinc containing SOD1 is located in the cytoplasm. Manganese containing SOD2 is located in the mitochondria while a second Copper and Zinc containing SOD3 is located in the extracellular space. SOD3 and SOD2 are tetramers whereas SOD1 is a dimer. These enzymes perform the dismutation reaction by a similar mechanism. The oxidized form of the enzyme is reduced by superoxide to form oxygen. The reduced form of the enzyme, formed in this reaction, then reacts with a second superoxide ion to form peroxide, which takes up two protons along the reaction path to yield hydrogen peroxide. | |
The hydrogen peroxide formed by superoxide dismutase and by other processes is scavenged by catalase, a ubiquitous heme protein that catalyzes the dismutation of hydrogen peroxide into water and molecular oxygen. | The hydrogen peroxide formed by superoxide dismutase and by other processes is scavenged by catalase, a ubiquitous heme protein that catalyzes the dismutation of hydrogen peroxide into water and molecular oxygen. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
One of the long-term benefits of exercise may be to increase the amount of superoxide dismutase in the cell. The elevated aerobic metabolism during exercise causes more ROS to be generated. In response, the cell synthesizes more protective enzymes. The net effect is one of protection, because the increase in superoxide dismutase more effectively protects the cell during periods of rest. | One of the long-term benefits of exercise may be to increase the amount of superoxide dismutase in the cell. The elevated aerobic metabolism during exercise causes more ROS to be generated. In response, the cell synthesizes more protective enzymes. The net effect is one of protection, because the increase in superoxide dismutase more effectively protects the cell during periods of rest. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Superoxide_dismutase.png|alt text]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
texttext<ref>PMID:#(specific#)</ref> | texttext<ref>PMID:#(specific#)</ref> | ||
Revision as of 20:49, 23 March 2010
Cu/Zn Superoxide Dismutase Cu/Zn Superoxide (SODc) dismutase is an oxidoreductase enzyme, catalyzing the dismutation of superoxide into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide.
Contents |
Introduction
Cu/Zn Superoxide dismutase is an important antioxidant defense in nearly all cells exposed to oxygen. Cu2+ Zn Superoxide Dismutase belongs to the superfamily of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on superoxide as acceptor.
Dismutation is a term that refers to a special type of reaction, where two equal but opposite reactions occur on two separate molecules. SOD takes two molecules of superoxide, strips the extra electron off of one, and places it on the other. So, one ends up with an electron less, forming normal oxygen, and the other ends up with an extra electron. The one with the extra electron then rapidly picks up two hydrogen ions to form hydrogen peroxide. Of course, hydrogen peroxide is also a dangerous compound, so the cell must use the enzyme catalase to detoxify it.
The Reaction of Dismutase
In mammals there are three known isomers of superoxide dismutase (SOD). Copper and Zinc containing SOD1 is located in the cytoplasm. Manganese containing SOD2 is located in the mitochondria while a second Copper and Zinc containing SOD3 is located in the extracellular space. SOD3 and SOD2 are tetramers whereas SOD1 is a dimer. These enzymes perform the dismutation reaction by a similar mechanism. The oxidized form of the enzyme is reduced by superoxide to form oxygen. The reduced form of the enzyme, formed in this reaction, then reacts with a second superoxide ion to form peroxide, which takes up two protons along the reaction path to yield hydrogen peroxide.
The hydrogen peroxide formed by superoxide dismutase and by other processes is scavenged by catalase, a ubiquitous heme protein that catalyzes the dismutation of hydrogen peroxide into water and molecular oxygen.
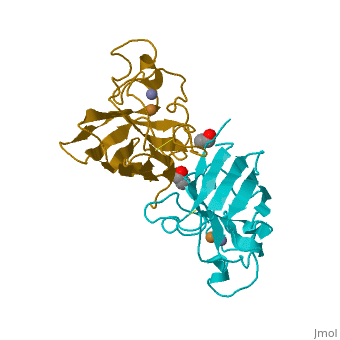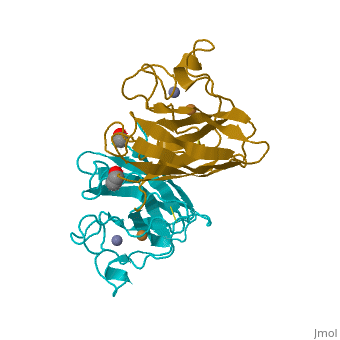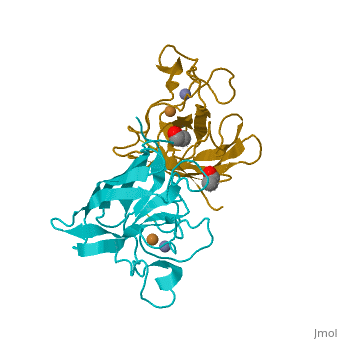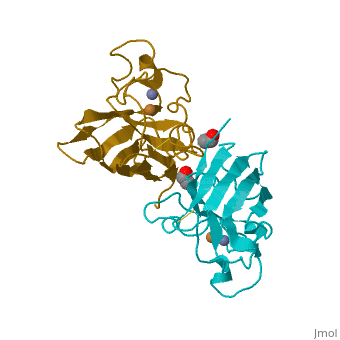
General Structure
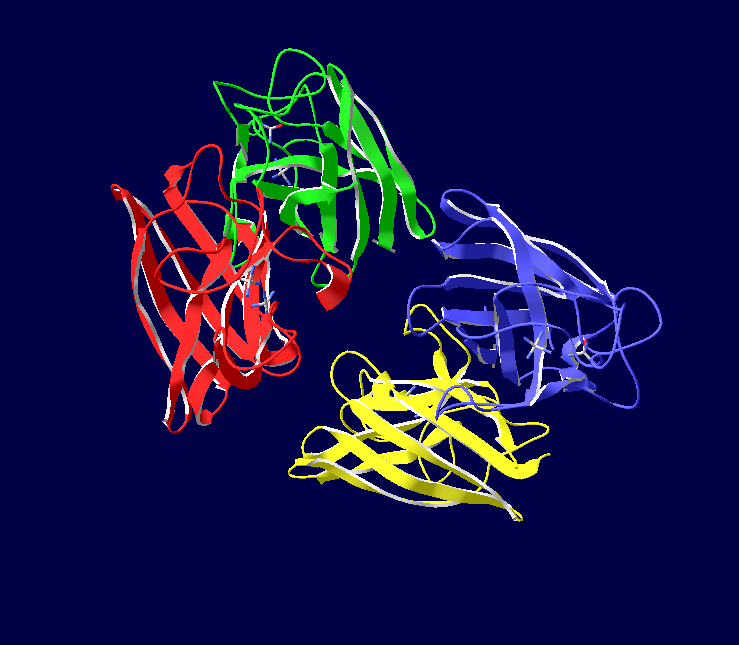
Cu/Zn Superoxide dismutase contains four polypeptide chains (B,O,G,Y). Each chain contains one alpha-helix and 12-14 beta-sheets.
|
Importance of Vitamins
Superoxide dismutase and catalase are remarkably efficiently, performing their reactions at or near the diffusion-limited rate. Glutathione peroxide also plays a role in scavenging H2O2. Other cellular defences against oxidative damage include the antioxidant vitamins, vitamins E and C. Because it is lipophilic, vitamin E is especially useful in protecting membranes from lipid peroxidation.
One of the long-term benefits of exercise may be to increase the amount of superoxide dismutase in the cell. The elevated aerobic metabolism during exercise causes more ROS to be generated. In response, the cell synthesizes more protective enzymes. The net effect is one of protection, because the increase in superoxide dismutase more effectively protects the cell during periods of rest.
References
texttext[1]
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Jordan Schibli, Jane S. Richardson, David Canner, Michal Harel, Andrea Gorrell