Sandbox 154
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
= F-Actin = | = F-Actin = | ||
'''Filamentous actin''' ('''F-actin''') is also referred to as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/microfilaments/ microfilament] <ref> Microfilament - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microfilaments. Date accessed: March 16th, 2010. </ref> and is a highly conserved proteinous component found near ubiquitously in eukaryotic cytoskeletons. F-actin and other [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/actin/ actin] proteins generally provide a structural role to the cell. | '''Filamentous actin''' ('''F-actin''') is also referred to as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/microfilaments/ microfilament] <ref> Microfilament - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microfilaments. Date accessed: March 16th, 2010. </ref> and is a highly conserved proteinous component found near ubiquitously in eukaryotic cytoskeletons. F-actin and other [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/actin/ actin] proteins generally provide a structural role to the cell. | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| Line 11: | Line 10: | ||
<applet load='2zwh' size='175' color='white' frame='true' align='left' caption='Filamentous Actin (F-actin)'/> | <applet load='2zwh' size='175' color='white' frame='true' align='left' caption='Filamentous Actin (F-actin)'/> | ||
<scene name='Sandbox_154/Thing_in_the_middle/1'>This thing in the middle</scene> | <scene name='Sandbox_154/Thing_in_the_middle/1'>This thing in the middle</scene> | ||
| + | == History of the structure == | ||
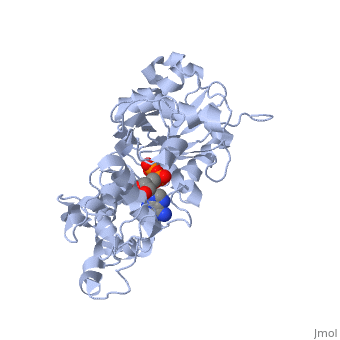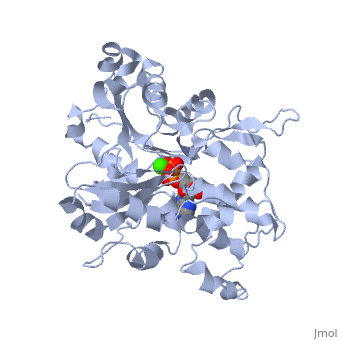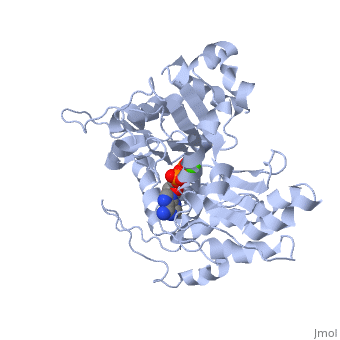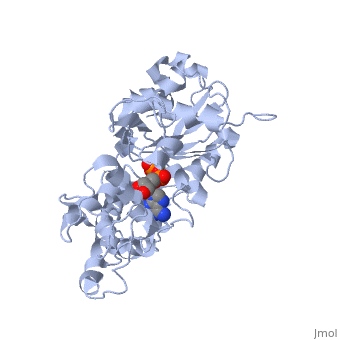
| + | The F-actin structure was discovered by Straub in 1942. The structure was speculated based on a low-resolution x-ray crystallograph found in 1990 by Holmes et al. The structure was deposited in the PDB databank in Decemeber 2008 by Oda et al. <ref> Oda T, Iwasa M, Aihara T, Maéda Y, and Narita A. 2009. The nature of the globular-to fibrous actin transition. Nature,457(7228):441-445. PMID: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19158791/ 19158791]</ref>. | ||
Structurally, F-actin appears like a double right-handed helix. It is actually composed of 13 actin units for every 6 left-handed turns, which each have 166° rotations, occurring over 350 Å . <ref> Holmes, K.C., Popp, D., Gebhard, W. and Kabsch, W. 1990. Atomic model of the actin filament. Nature,347(6288):44-49. PMID: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2395461/ 2395461]</ref>. | Structurally, F-actin appears like a double right-handed helix. It is actually composed of 13 actin units for every 6 left-handed turns, which each have 166° rotations, occurring over 350 Å . <ref> Holmes, K.C., Popp, D., Gebhard, W. and Kabsch, W. 1990. Atomic model of the actin filament. Nature,347(6288):44-49. PMID: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2395461/ 2395461]</ref>. | ||
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa | aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa | ||
Revision as of 00:49, 26 March 2010
| |||||||
| 2zwh, resolution 3.30Å () | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , | ||||||
| Non-Standard Residues: | |||||||
| |||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
Contents |
F-Actin
Filamentous actin (F-actin) is also referred to as microfilament [1] and is a highly conserved proteinous component found near ubiquitously in eukaryotic cytoskeletons. F-actin and other actin proteins generally provide a structural role to the cell.
Introduction
Assembly
Structure of F-actin
|
History of the structure
The F-actin structure was discovered by Straub in 1942. The structure was speculated based on a low-resolution x-ray crystallograph found in 1990 by Holmes et al. The structure was deposited in the PDB databank in Decemeber 2008 by Oda et al. [2]. Structurally, F-actin appears like a double right-handed helix. It is actually composed of 13 actin units for every 6 left-handed turns, which each have 166° rotations, occurring over 350 Å . [3]. aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Monomeric Unit - G-actin
|
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Domains
Function
Enzymatic Role
Active Site
Ligand
Structural Role
References
- ↑ Microfilament - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microfilaments. Date accessed: March 16th, 2010.
- ↑ Oda T, Iwasa M, Aihara T, Maéda Y, and Narita A. 2009. The nature of the globular-to fibrous actin transition. Nature,457(7228):441-445. PMID: 19158791
- ↑ Holmes, K.C., Popp, D., Gebhard, W. and Kabsch, W. 1990. Atomic model of the actin filament. Nature,347(6288):44-49. PMID: 2395461
| Please do NOT make changes to this Sandbox until after April 23, 2010. Sandboxes 151-200 are reserved until then for use by the Chemistry 307 class at UNBC taught by Prof. Andrea Gorrell. |