Ketosteroid Isomerase
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
<applet load='1ISK' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='Ketosteroid Isomerase (KSI; PDB 1ISK)' scene='User:Laura_M._Haynes/Sandbox_1/Ksi/4' /> | <applet load='1ISK' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='Ketosteroid Isomerase (KSI; PDB 1ISK)' scene='User:Laura_M._Haynes/Sandbox_1/Ksi/4' /> | ||
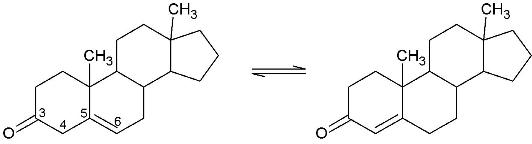
| - | Ketosteroid isomerase (KSI, EC#5.3.3.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of 3-oxo-Δ<sup>5</sup> ketosteroids to their hormonally active Δ<sup>4</sup>-conjugated isomers.<ref>PMID:15381400</ref> | + | Ketosteroid isomerase (KSI, EC#5.3.3.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of 3-oxo-Δ<sup>5</sup> ketosteroids to their hormonally active Δ<sup>4</sup>-conjugated isomers, as illustrated below with the isomerization of .<ref name="Pollack">PMID:15381400</ref> |
[[Image:Reaction.jpg]] | [[Image:Reaction.jpg]] | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
==Enzyme Mechanism== | ==Enzyme Mechanism== | ||
| + | The hydrophobic active site of ketosteroid isomerase contains an aspartate residue at position 99 and a tyrosine residue at position 14 (according to the numbering for the ''Commamonas tetosteroni'' protein, which will be used throughout) that are capable of binding the 3-position carbonyl of the steroid. Additionally, the active site contains an aspartate residue at position 38 that is participates in the catalytic activity of KSI.<ref name="Pollack" /> | ||
==Related Proteins== | ==Related Proteins== | ||
Revision as of 20:12, 2 April 2010
Contents |
Ketosteroid Isomerase
Introduction
|
Ketosteroid isomerase (KSI, EC#5.3.3.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of 3-oxo-Δ5 ketosteroids to their hormonally active Δ4-conjugated isomers, as illustrated below with the isomerization of .[1]
This reaction is essential in the biosynthesis of steroids in mammals where KSI is a membrane-bound complex.[2] In bacteria, however, KSI exists as a soluble protein is involves in catabolism of steroids.[2] It is one of the most proficient known enzymes with an essentially diffusion limited rate of catalysis. An NMR solution phase structure of KSI was solved in 1997 by Wu et al.[3]
Structure
Ketosteroid isomerase exits as a 28 kDa homodimeric protein, in which the two dimers related to each other via hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions.[3]
The catalytic site of KSI is extremely hydrophobic.
Enzyme Mechanism
The hydrophobic active site of ketosteroid isomerase contains an aspartate residue at position 99 and a tyrosine residue at position 14 (according to the numbering for the Commamonas tetosteroni protein, which will be used throughout) that are capable of binding the 3-position carbonyl of the steroid. Additionally, the active site contains an aspartate residue at position 38 that is participates in the catalytic activity of KSI.[1]
Related Proteins
Available Structures
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Pollack RM. Enzymatic mechanisms for catalysis of enolization: ketosteroid isomerase. Bioorg Chem. 2004 Oct;32(5):341-53. PMID:15381400 doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2004.06.005
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Ha NC, Choi G, Choi KY, Oh BH. Structure and enzymology of Delta5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001 Dec;11(6):674-8. PMID:11751047
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Wu ZR, Ebrahimian S, Zawrotny ME, Thornburg LD, Perez-Alvarado GC, Brothers P, Pollack RM, Summers MF. Solution structure of 3-oxo-delta5-steroid isomerase. Science. 1997 Apr 18;276(5311):415-8. PMID:9103200
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Laura M. Haynes, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky