103d
From Proteopedia
OCA (Talk | contribs)
(New page: 200px<br /> <applet load="103d" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="103d" /> '''THE UNUSUAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN CENTROME...)
Next diff →
Revision as of 13:33, 29 October 2007
|
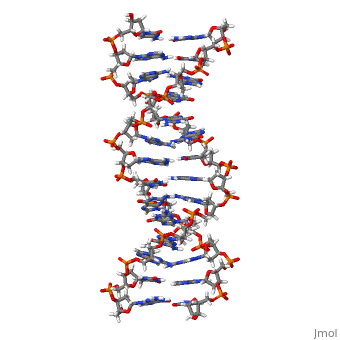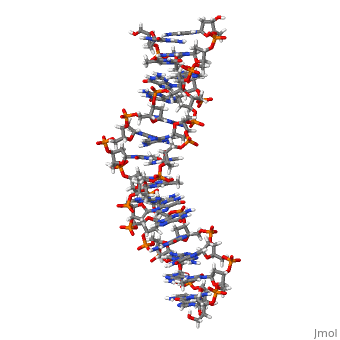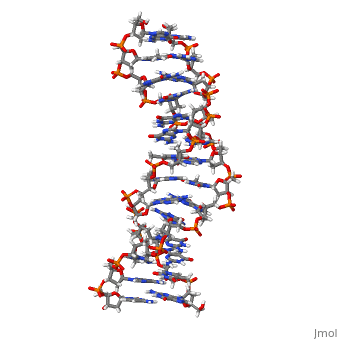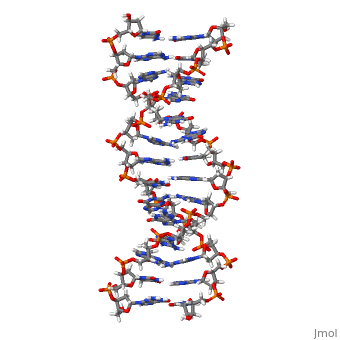
THE UNUSUAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN CENTROMERE (GGA)2 MOTIF: UNPAIRED GUANOSINE RESIDUES STACKED BETWEEN SHEARED G(DOT)A PAIRS
Overview
The centromere of human chromosomes contains multiple repeats of the DNA, sequence d(TGGAA)n. This sequence has the interesting property of pairing, with itself to form stable duplexes. We have determined the solution, structure of the unusual DNA duplex 5'-TGGAATGGAA:TGGAATGGAA-3' at atomic, resolution. The duplex contains unpaired staggered guanosine residues, which co-stack by intercalation between sheared G.A and A.G base-pairs to, form an interesting new structural motif, the GA-bracketed G-stack. The, TGGAA repeat unit contains six "steps", four of which are not Watson-Crick, base-pairs.
About this Structure
103D is a [Protein complex] structure of sequences from [[1]]. Full crystallographic information is available from [OCA].
Reference
The unusual structure of the human centromere (GGA)2 motif. Unpaired guanosine residues stacked between sheared G.A pairs., Chou SH, Zhu L, Reid BR, J Mol Biol. 1994 Dec 2;244(3):259-68. PMID:7966337
Page seeded by OCA on Mon Oct 29 15:37:57 2007