User:Ankit Vahia/sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(→Ligand-binding domain) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:intactModelLargeText.jpg|frame| | + | [[Image:intactModelLargeText.jpg|frame|T7 RNA polymerase in the late initiation phase]] |
A [[CBI Molecule]] being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org/ Molecular Playground]. | A [[CBI Molecule]] being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org/ Molecular Playground]. | ||
| - | + | T7 RNA Polymerase is a single sub-unit DNA dependent RNA polymerase. | |
| - | + | === 7 base DNA-RNA hybrid === | |
| - | {{Clear}} | ||
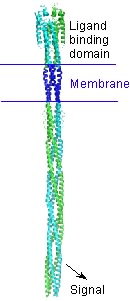
| - | <applet load='1wat' size='[450,338]' frame='true' align='right' | ||
| - | caption='Aspartate receptor ligand binding domain (1wat)' scene='User:Lynmarie_K_Thompson/Sandbox_1/Loadedfrompdb/4'/> | ||
| - | === Ligand-binding domain === | ||
| - | + | The spinning protein (<scene name='User:Ankit_Vahia/sandbox1/T7-7mer_rna_scene_1/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene>) ) shows a 7 mer DNA-RNA hybrid as the enzyme is about to loose promoter contacts and transition into the more stable elongation phase. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | The spinning protein (<scene name='User:Ankit_Vahia/sandbox1/T7-7mer_rna_scene_1/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene>) ) is the | + | |
Molecular Playground banner: A receptor protein used by bacteria to "smell" their environment. | Molecular Playground banner: A receptor protein used by bacteria to "smell" their environment. | ||
Revision as of 19:32, 28 April 2010
A CBI Molecule being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst and on display at the Molecular Playground.
T7 RNA Polymerase is a single sub-unit DNA dependent RNA polymerase.
7 base DNA-RNA hybrid
The spinning protein () ) shows a 7 mer DNA-RNA hybrid as the enzyme is about to loose promoter contacts and transition into the more stable elongation phase.
Molecular Playground banner: A receptor protein used by bacteria to "smell" their environment.