User:Nicole Maille/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | Looking at the structure of HIV-1 protease, we see that the protein is composed of <scene name='HIV-1_protease/2nmz_symmetric/2'>two symmetrically related subunits</scene>, shown here in [[cartoon backbone representation]] to highlight [[secondary structure]]. Each subunit | + | Looking at the structure of HIV-1 protease, we see that the protein is composed of <scene name='HIV-1_protease/2nmz_symmetric/2'>two symmetrically related subunits</scene>, shown here in [[cartoon backbone representation]] to highlight [[secondary structure]]. Each subunit of the homodimer consists of a small 99 amino acid chain. The subunits come together in such as way as to <scene name='HIV-1_protease/2nmz_tunnel/1'>form a tunnel where they meet</scene>, shown here in [[spacefilling representation]] to showcase the physical surface of the protein. The protein to be cleaved sits in this tunnel. In the middle of the tunnel is the <scene name='HIV-1_protease/2nmz_triads/1'>active site</scene> of the protease: <scene name='HIV-1_protease/2nmz_triadslabeled/2'>two Asp-Thr-Gly catalytic triads</scene> (residue numbers 25, 26, and 27 on one chain and 125, 126, and 127 on the second). <scene name='HIV-1_protease/2nmz_aspslabeled/1'>The two Asp's</scene> act as the main catalytic residues in the active site and use a water molecule to help break the protein chain that binds in the tunnel. You may be wondering how a protein to be cleaved makes its way into the active-site tunnel to begin with -- after all, the tunnel does not seem so accessible. The key is the two flexible flaps on the top of the tunnel that can <scene name='HIV-1_protease/Hiv1_protease_morph/4'>move</scene> (large scene, takes a while to load) to allow proteins to enter the tunnel. A <scene name='HIV-1_protease/Hiv1_p_morph_sp/2'>spacefill view of the flexible flaps</scene> is also illuminating, as the change in the accessibility of the tunnel becomes more obvious. This movement of the flexible flaps is simulated by morphing between two crystal structures, the first being the native HIV-1 protease structure with no inhibitor bound (PDB entry [[1hhp]]) and the second being the HIV-1 protease complexed with Saquinavir. |
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Inhibitors== | ==Inhibitors== | ||
| - | Saquinavir was the the first protease inhibitor approved by the FDA for the treatment of HIV. It inhibits HIV-1 protease by <scene name='HIV-1_protease/2nmz_saquinavir_spacefill/1'>binding tightly to the active site tunnel</scene>, thus preventing the protease from cleaving any protein chains | + | Saquinavir was the the first protease inhibitor approved by the FDA for the treatment of HIV. It inhibits HIV-1 protease by <scene name='HIV-1_protease/2nmz_saquinavir_spacefill/1'>binding tightly to the active site tunnel</scene>, thus preventing the protease from cleaving any protein chains. |
Other drugs used to treat patients infected with the HIV virus include Indinavir (PDB entry [[1hsg]]), Ritonavir (PDB entry [[1hxw]]), and Nelfinavir (PDB entry [[1ohr]]). | Other drugs used to treat patients infected with the HIV virus include Indinavir (PDB entry [[1hsg]]), Ritonavir (PDB entry [[1hxw]]), and Nelfinavir (PDB entry [[1ohr]]). | ||
Revision as of 02:50, 2 May 2010
| |||||||||
| 2nmz, resolution 0.97Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , | ||||||||
| Gene: | gag (Human immunodeficiency virus 1) | ||||||||
| Activity: | HIV-1 retropepsin, with EC number 3.4.23.16 | ||||||||
| Related: | 2nmw, 2nmy, 2nnk, 2nnp | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Contents |
Introduction
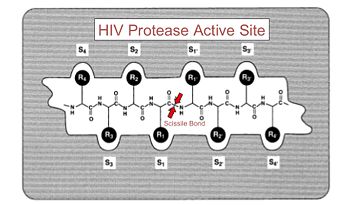
HIV is a notoriously lethal retrovirus that is known to cause AIDS[1]. There currently is no cure or vaccine, but, scientists have discovered treatments that can slow progression of the HIV virus, thanks in large part to our understanding of the structure of HIV-1 protease (EC.3.4.23.16), seen here on the right in complex with a potent drug used for slowing the progression of HIV, (PDB entry 2nmz).
HIV-1 protease is a protein made by the HIV virus that is crucial to the virus's infectious capacity. The virus makes certain proteins that need to be cleaved, or cut, in order to transform into mature, fully-functional proteins that can allow the virus to infect new cells. HIV-1 protease is responsible for cleaving these nascent proteins into their mature form.
Structure
Looking at the structure of HIV-1 protease, we see that the protein is composed of , shown here in cartoon backbone representation to highlight secondary structure. Each subunit of the homodimer consists of a small 99 amino acid chain. The subunits come together in such as way as to , shown here in spacefilling representation to showcase the physical surface of the protein. The protein to be cleaved sits in this tunnel. In the middle of the tunnel is the of the protease: (residue numbers 25, 26, and 27 on one chain and 125, 126, and 127 on the second). act as the main catalytic residues in the active site and use a water molecule to help break the protein chain that binds in the tunnel. You may be wondering how a protein to be cleaved makes its way into the active-site tunnel to begin with -- after all, the tunnel does not seem so accessible. The key is the two flexible flaps on the top of the tunnel that can (large scene, takes a while to load) to allow proteins to enter the tunnel. A is also illuminating, as the change in the accessibility of the tunnel becomes more obvious. This movement of the flexible flaps is simulated by morphing between two crystal structures, the first being the native HIV-1 protease structure with no inhibitor bound (PDB entry 1hhp) and the second being the HIV-1 protease complexed with Saquinavir.
Mechanism
HIV protease is classified as an aspartic protease. Evidence for this classification is listed below:
1) The Asp-Thr-Gly in the active site of HIV protease is highly conserved in aspartic protease enzymes[2].
2) Mutational analysis studies have shown that mutation of one of these essential Asp-25 groups to Asn, Thr, or Ala resulted in complete loss of proteolytic activity[3][4][5][6].
3) HIV protease is inhibited in vitro by pepstatin, a known inhibitor of aspartic proteases[4][5][7].
4) The 3-dimensional Homodimeric structure is characteristic of aspartic proteases[8][9][10].
Proposed mechanism by Northrop
Inhibitors
Saquinavir was the the first protease inhibitor approved by the FDA for the treatment of HIV. It inhibits HIV-1 protease by , thus preventing the protease from cleaving any protein chains.
Other drugs used to treat patients infected with the HIV virus include Indinavir (PDB entry 1hsg), Ritonavir (PDB entry 1hxw), and Nelfinavir (PDB entry 1ohr).
References
- ↑ Gallo RC, Montagnier L. AIDS in 1988. Sci Am. 1988 Oct;259(4):41-8. PMID:3072672
- ↑ Cairns J, Overbaugh J, Miller S. The origin of mutants. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):142-5. PMID:3045565 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/335142a0
- ↑ Kohl NE, Emini EA, Schleif WA, Davis LJ, Heimbach JC, Dixon RA, Scolnick EM, Sigal IS. Active human immunodeficiency virus protease is required for viral infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4686-90. PMID:3290901
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Darke PL, Leu CT, Davis LJ, Heimbach JC, Diehl RE, Hill WS, Dixon RA, Sigal IS. Human immunodeficiency virus protease. Bacterial expression and characterization of the purified aspartic protease. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2307-12. PMID:2644259
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Blusch JH, Seelmeir S, von der Helm K. Molecular and enzymatic characterization of the porcine endogenous retrovirus protease. J Virol. 2002 Aug;76(15):7913-7. PMID:12097607
- ↑ Mous J, Heimer EP, Le Grice SF. Processing protease and reverse transcriptase from human immunodeficiency virus type I polyprotein in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1433-6. PMID:2450209
- ↑ Hansen J, Billich S, Schulze T, Sukrow S, Moelling K. Partial purification and substrate analysis of bacterially expressed HIV protease by means of monoclonal antibody. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1785-91. PMID:3049075
- ↑ Navia MA, Fitzgerald PM, McKeever BM, Leu CT, Heimbach JC, Herber WK, Sigal IS, Darke PL, Springer JP. Three-dimensional structure of aspartyl protease from human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):615-20. PMID:2645523 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/337615a0
- ↑ Miller M, Schneider J, Sathyanarayana BK, Toth MV, Marshall GR, Clawson L, Selk L, Kent SB, Wlodawer A. Structure of complex of synthetic HIV-1 protease with a substrate-based inhibitor at 2.3 A resolution. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1149-52. PMID:2686029
- ↑ Lapatto R, Blundell T, Hemmings A, Overington J, Wilderspin A, Wood S, Merson JR, Whittle PJ, Danley DE, Geoghegan KF, et al.. X-ray analysis of HIV-1 proteinase at 2.7 A resolution confirms structural homology among retroviral enzymes. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):299-302. PMID:2682266 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/342299a0
- Atomic resolution crystal structures of HIV-1 protease and mutants V82A and I84V with saquinavir., Tie Y, Kovalevsky AY, Boross P, Wang YF, Ghosh AK, Tozser J, Harrison RW, Weber IT, Proteins. 2007 Apr 1;67(1):232-42. PMID:17243183
- The three-dimensional structure of the aspartyl protease from the HIV-1 isolate BRU., Spinelli S, Liu QZ, Alzari PM, Hirel PH, Poljak RJ, Biochimie. 1991 Nov;73(11):1391-6. PMID:1799632
Links
- HIV-1 Protease featured in David S. Goodsell's Molecule of the Month
- HIV-1 Protease in Wikipedia