Tropomyosin
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:1c1g.png|left|150px|thumb|Crystal Structure of Pig Tropomyosin, [[1c1g]]]] | [[Image:1c1g.png|left|150px|thumb|Crystal Structure of Pig Tropomyosin, [[1c1g]]]] | ||
| - | {{STRUCTURE_1c1g| PDB=1c1g | SIZE=300| SCENE=Tropomyosin/Cv/ | + | {{STRUCTURE_1c1g| PDB=1c1g | SIZE=300| SCENE=Tropomyosin/Cv/1 |right|CAPTION=Tropomyosin from pig, [[1c1g]] }} |
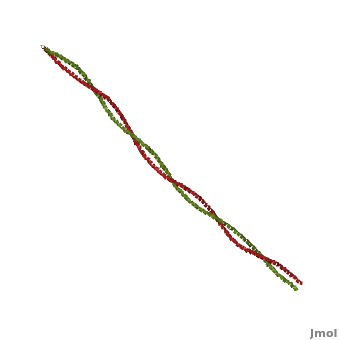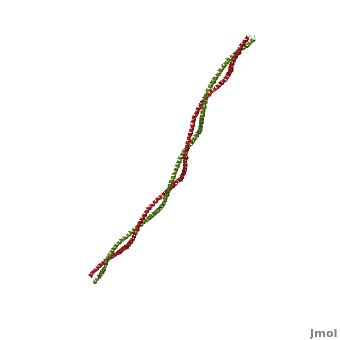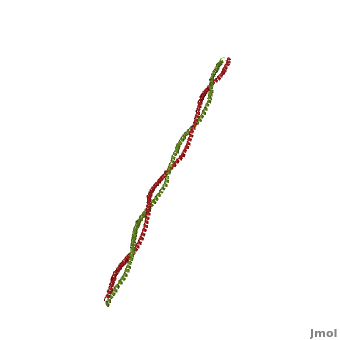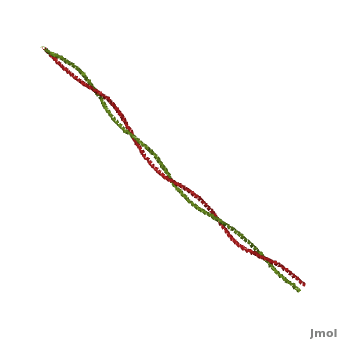
| - | '''Tropomyosin (TPM)''' has a 4-helix coiled dimer structure. It regulates the binding of myosin thus regulating muscle contraction. <ref>PMID:9108196</ref> In its locked conformation it binds troponin T (TnnT) and prevents the binding of myosin to actin. When Ca++ ions bind to TnnT, the TPM assumes an open conformation and myosin can bind to actin. The images at the top and at the right correspond to one representative TPM structure, ''i.e.'' Tropomyosin from pig ([[1c1g]]). You can <scene name='Tropomyosin/Cv/ | + | '''Tropomyosin (TPM)''' has a 4-helix coiled dimer structure. It regulates the binding of myosin thus regulating muscle contraction. <ref>PMID:9108196</ref> In its locked conformation it binds troponin T (TnnT) and prevents the binding of myosin to actin. When Ca++ ions bind to TnnT, the TPM assumes an open conformation and myosin can bind to actin. The images at the top and at the right correspond to one representative TPM structure, ''i.e.'' Tropomyosin from pig ([[1c1g]]). You can <scene name='Tropomyosin/Cv/2'>enlarge the image</scene> at the right for clarity. |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 09:09, 26 July 2010
| |||||||||
| Tropomyosin from pig, 1c1g | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Tropomyosin (TPM) has a 4-helix coiled dimer structure. It regulates the binding of myosin thus regulating muscle contraction. [1] In its locked conformation it binds troponin T (TnnT) and prevents the binding of myosin to actin. When Ca++ ions bind to TnnT, the TPM assumes an open conformation and myosin can bind to actin. The images at the top and at the right correspond to one representative TPM structure, i.e. Tropomyosin from pig (1c1g). You can at the right for clarity.
3D Structures of Tropomyosin
3mtu, 3mud – cTPM alpha-1 – chicken
1ic2 - cTPM alpha-1 (mutant)
2w49 – cTnnC+cTnnT+cTnnI+cTPM alpha-1+cActin
2z5h – yTPM alpha-1 N-terminal+C-terminal+GNC4 leucine zipper+TnnT – yeast
2z5i - yTPM alpha-1 N-terminal+C-terminal+GNC4 leucine zipper
2efr, 2efs, 2d3e - rTPM alpha-1 C-terminal+GNC4 leucine zipper – rabbit
1kql - TPM alpha-1 C-terminal+GNC4 leucine zipper - rat
2b9c – TPM mid region – rat
1c1g – TPM – pig
2tma – TPM - model
References
- ↑ Gunning P, Weinberger R, Jeffrey P. Actin and tropomyosin isoforms in morphogenesis. Anat Embryol (Berl). 1997 Apr;195(4):311-5. PMID:9108196
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Gregory Hoeprich, Jaime Prilusky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman