User:Jaime Prilusky/Sandbox Animated Gif
From Proteopedia
< User:Jaime Prilusky(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:small_wh_ray0001.gif]] | + | [[Image:small_wh_ray0001.gif]]<br /> |
| + | <applet load="1ea5_rot.pdb" size="300" color="white" frame="true" spin="on" caption="AChE" align="right" script="Acetylcholinesterase/New_down_gorge/1" /> | ||
| + | '''3D structure of acetylcholinesterase'''<br /> | ||
| + | {{TOC limit|limit=2}} | ||
| + | == Key Enzyme in the Nervous System == | ||
| + | |||
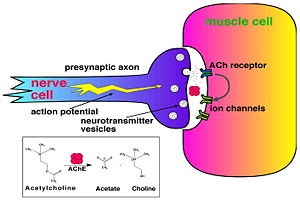
| + | '''Acetylcholinesterase''' (AChE) is key enzyme in the nervous system of animals. By rapid hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter, '''acetylcholine''' (ACh), AChE terminates neurotransmission at cholinergic synapses. It is a very fast enzyme, especially for a serine hydrolase, functioning at a rate approaching that of a diffusion-controlled reaction. AChE inhibitors are among the key drugs approved by the FDA for management of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The powerful toxicity of organophosphorus (OP) poisons is attributed primarily to their potent AChE inhibitors. | ||
| + | [[Image:Synapse_Schematic.jpg|thumb|Cholinergic Synapse|300px|left]] | ||
Current revision
|
3D structure of acetylcholinesterase
Contents |
Key Enzyme in the Nervous System
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is key enzyme in the nervous system of animals. By rapid hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine (ACh), AChE terminates neurotransmission at cholinergic synapses. It is a very fast enzyme, especially for a serine hydrolase, functioning at a rate approaching that of a diffusion-controlled reaction. AChE inhibitors are among the key drugs approved by the FDA for management of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The powerful toxicity of organophosphorus (OP) poisons is attributed primarily to their potent AChE inhibitors.