We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox caroldavila
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=[Image:Opening 1igt.png|450px|left|thumb| Intact Immunoglobulin, [[1igt]]]] | =[Image:Opening 1igt.png|450px|left|thumb| Intact Immunoglobulin, [[1igt]]]] | ||
| - | {{STRUCTURE_1hzh| right| PDB=1hzh | SCENE= Antibody/1hzh_starting_scene/3 |CAPTION= | + | {{STRUCTURE_1hzh| right| PDB=1hzh | SCENE=Antibody/1hzh_starting_scene/3 |CAPTION= Crystal Structure of the Intact Human IGG B12: A Template for a Potential HIV Vaccine, [[1hzh]] }} |
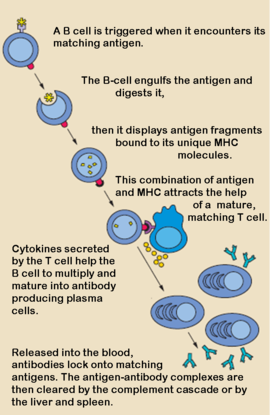
'''Antibodies''', also known as Immunoglobulins (Ig) are gamma globulin proteins, primarily found in the blood of vertebrates. These [[glycoproteins]] serve as a critical component of the immune system when the host fails to activate alternative compliment pathways or phagocytic cells in response to invading microorganisms or other [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antigen antigens]. The incredible specificity with which immunoglobulins bind to an antigen is based upon structural complementarity between the antigen and antibody <scene name='Antibody/1hzh_heavy_chains/1'>heavy </scene>and <scene name='Antibody/1hzh_light_chains/1'>light chains </scene>. It is this specificity that has made <scene name='Antibody/1hzh_starting_scene/3'>antibodies</scene> a critical component in laboratory and medical research. | '''Antibodies''', also known as Immunoglobulins (Ig) are gamma globulin proteins, primarily found in the blood of vertebrates. These [[glycoproteins]] serve as a critical component of the immune system when the host fails to activate alternative compliment pathways or phagocytic cells in response to invading microorganisms or other [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antigen antigens]. The incredible specificity with which immunoglobulins bind to an antigen is based upon structural complementarity between the antigen and antibody <scene name='Antibody/1hzh_heavy_chains/1'>heavy </scene>and <scene name='Antibody/1hzh_light_chains/1'>light chains </scene>. It is this specificity that has made <scene name='Antibody/1hzh_starting_scene/3'>antibodies</scene> a critical component in laboratory and medical research. | ||
Revision as of 07:16, 20 October 2010
=[Image:Opening 1igt.png|450px|left|thumb| Intact Immunoglobulin, 1igt]]
| |||||||||
| Crystal Structure of the Intact Human IGG B12: A Template for a Potential HIV Vaccine, 1hzh | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , , , | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Antibodies, also known as Immunoglobulins (Ig) are gamma globulin proteins, primarily found in the blood of vertebrates. These glycoproteins serve as a critical component of the immune system when the host fails to activate alternative compliment pathways or phagocytic cells in response to invading microorganisms or other antigens. The incredible specificity with which immunoglobulins bind to an antigen is based upon structural complementarity between the antigen and antibody and . It is this specificity that has made a critical component in laboratory and medical research.