User:Eran Hodis/Sandbox3
From Proteopedia
(→Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')) |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
==Regulation of HMG-CoA Reductase== | ==Regulation of HMG-CoA Reductase== | ||
| - | As stated before, HMGR is among the most highly regulated enzymes in the human body. <ref name="Meigs">PMID:8626470</ref> | + | As stated before, HMGR is among the most highly regulated enzymes in the human body.<ref name="Meigs">PMID:8626470</ref> Regulation of HMG-CoA reductase occurs at 4 different levels of feedback regulation. First by regulation of transcription of the reductase gene, which is activated by sterol regulatory element binding protein, a protein that binds to the promoter of the HMGR gene when cholesterol levels fall. The second level of regulation is at the translation of the HMGR mRNA, which is inhibited by Farnesol, a derivative of the mevalonate pathway.<ref name="Meigs"/> |
| - | The third level of HMGR regulation involves the degradation of intact reductase. As the level of sterols increases, HMGR reductase becomes more susceptible to ER-associated degradation. Helices 2-6 of the HMGR transmembrane domain, called the sterol-sensing domain, sense the increased levels of sterols. Degradation of HMGR is initiated when a membrane-bound cysteine protease cleaves residues within the transmembrane region of HMGR. Additionally, as sterol levels increase, the helices can expose Lysine 248 which can be ubiquitinated and subsequently trigger proteolytic degradation. <ref name="Roitelman"/> <ref>PMID:16168377</ref> | + | The third level of HMGR regulation involves the degradation of intact reductase. As the level of sterols increases, HMGR reductase becomes more susceptible to ER-associated degradation. Helices 2-6 of the HMGR transmembrane domain, called the sterol-sensing domain, sense the increased levels of sterols. Degradation of HMGR is initiated when a membrane-bound cysteine protease cleaves residues within the transmembrane region of HMGR. Additionally, as sterol levels increase, the helices can expose Lysine 248 which can be ubiquitinated and subsequently trigger proteolytic degradation.<ref name="Roitelman"/><ref>PMID:16168377</ref> |
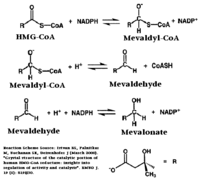
| - | A final level of HMGR regulation is achieved by inhibition via <scene name='HMG-CoA_Reductase/1dqa_phosphorylation_871/1'>phosphorylation of Serine 872</scene>. HMGR is phosphorylated and inactivated by an AMP-activated protein kinase, when the energy charge of the cell is low and AMP concentrations are high. Since Serine 872 is in the vicinity of the pohsphate of NADP, phosphorylation likely results in a decreased affinity for NADPH, halting the formation of Mevaldyl-CoA from HMG-CoA. | + | A final level of HMGR regulation is achieved by inhibition via <scene name='HMG-CoA_Reductase/1dqa_phosphorylation_871/1'>phosphorylation of Serine 872</scene>. HMGR is phosphorylated and inactivated by an AMP-activated protein kinase, when the energy charge of the cell is low and AMP concentrations are high. Since Serine 872 is in the vicinity of the pohsphate of NADP, phosphorylation likely results in a decreased affinity for NADPH, halting the formation of Mevaldyl-CoA from HMG-CoA.<ref>PMID:1967820</ref> |
| - | <ref>PMID:1967820</ref> | + | |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 18:03, 31 October 2010
Contents |
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||
|
Nucleosome Structure
|
IntroductionThe nucleosome core particle contains two copies of each histone protein (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) and 146 basepairs (bp) of superhelical DNA wrapped around this histone octamer. It represents the first order of DNA packaging in the nucleus and as such is the principal structure that determines DNA accessibility. The Histone Octamer
alpha1-loop1-alpha2-loop2-alpha3 |
References
- ↑ Istvan ES, Deisenhofer J. Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science. 2001 May 11;292(5519):1160-4. PMID:11349148 doi:10.1126/science.1059344
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Roitelman J, Olender EH, Bar-Nun S, Dunn WA Jr, Simoni RD. Immunological evidence for eight spans in the membrane domain of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase: implications for enzyme degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):959-73. PMID:1374417
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Meigs TE, Roseman DS, Simoni RD. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase degradation by the nonsterol mevalonate metabolite farnesol in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 5;271(14):7916-22. PMID:8626470
- ↑ Song BL, Sever N, DeBose-Boyd RA. Gp78, a membrane-anchored ubiquitin ligase, associates with Insig-1 and couples sterol-regulated ubiquitination to degradation of HMG CoA reductase. Mol Cell. 2005 Sep 16;19(6):829-40. PMID:16168377 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.08.009
- ↑ Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):425-30. PMID:1967820 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/343425a0