Glutamate receptor (GluA2)
From Proteopedia
m (made capitalization consistent in captions David Canner added) |
m (fixing parts removed by David Canner and making better segues) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Structure of the Glutamate Receptor (GluA2)== | ==Structure of the Glutamate Receptor (GluA2)== | ||
<StructureSection load='3kg2' size='500' side='right' scene='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Default3kg2/1' caption='Glutamate Receptor ([[3kg2]])'> | <StructureSection load='3kg2' size='500' side='right' scene='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Default3kg2/1' caption='Glutamate Receptor ([[3kg2]])'> | ||
| + | ===Overview=== | ||
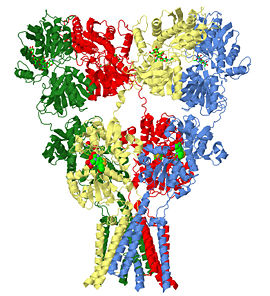
The homomeric rat GluA2 receptor <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Default3kg2/1'>has four subunits</scene> arranged in a 'Y'-shape with the <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Meas3kg2/1'>'top' being about three times the width of the 'bottom'</scene><ref name="main" />. This structure is a functional homotetramer of the AMPA-subtype; native ionotropic glutamate receptors are almost exclusively heterotetramers. {{Link Toggle FancyCartoonHighQualityView}}. | The homomeric rat GluA2 receptor <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Default3kg2/1'>has four subunits</scene> arranged in a 'Y'-shape with the <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Meas3kg2/1'>'top' being about three times the width of the 'bottom'</scene><ref name="main" />. This structure is a functional homotetramer of the AMPA-subtype; native ionotropic glutamate receptors are almost exclusively heterotetramers. {{Link Toggle FancyCartoonHighQualityView}}. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 35: | ||
*As explored further in [[#Transmembrane domain architecture and the occluded pore|a later section below]] , the <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Tmd_domain_4fold/2'>symmetry is an overall four-fold for the TMD</scene>. Thus, remarkably, the symmetry switches from an overall two-fold symmetry for the ATD and LBD to four-fold for the TMD. | *As explored further in [[#Transmembrane domain architecture and the occluded pore|a later section below]] , the <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Tmd_domain_4fold/2'>symmetry is an overall four-fold for the TMD</scene>. Thus, remarkably, the symmetry switches from an overall two-fold symmetry for the ATD and LBD to four-fold for the TMD. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | ===Subunit Non-Equivalence, Transmembrane domain Architecture and the Occluded Pore=== | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='3kg2' size='500' side='left' scene ='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Default3kg2/1' caption='Glutamate Receptor Structure' name='main2NDwindow'> | ||
===Subunit non-equivalence=== | ===Subunit non-equivalence=== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='3kg2' size='500' side='left' scene ='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Default3kg2/1' caption='Glutamate Receptor Structure'> | ||
As a result of the swapping and symmetry mismatch, there is subunit non-equivalence; even though all the chains are the same chemically, there are two distinct conformations of the subunits. This means there are two matching pairs of subunits. The pairs are illustrated on the left and the morphs referred to below will show on the right: | As a result of the swapping and symmetry mismatch, there is subunit non-equivalence; even though all the chains are the same chemically, there are two distinct conformations of the subunits. This means there are two matching pairs of subunits. The pairs are illustrated on the left and the morphs referred to below will show on the right: | ||
| - | + | <table width='140' align='left' cellpadding='2'><tr><td bgcolor='#eeeeee'><applet load='3kg2' size='140' frame='true' align='left' scene='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Ac3kg2letter/1' caption='A is equivalent to C'/></td><td bgcolor='#eeeeee'><applet load='3kg2' size='140' frame='true' align='left' scene='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Bd3kg2letter/2' caption='B is equivalent to D'/></td></tr></table> | |
| - | * <span style="color:forestgreen">Subunit '''A</span>''' is equivalent to <span style="color:cornflowerblue">Subunit '''C'''</span> (ABOVE). On the | + | * <span style="color:forestgreen">Subunit '''A</span>''' is equivalent to <span style="color:cornflowerblue">Subunit '''C'''</span> (ABOVE). On the left in the main window, a <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Atocmorph/5' target='main2NDwindow'>morph showing the equivalency of the two subunits by rotating around the axis of their symmetry</scene>. |
| - | * <span style="color:red">Subunit '''B</span>''' is equivalent to Subunit '''D''' (ABOVE). <!--<span style="color:#FFFF80">Subunit '''D'''</span>(<--says 'Subunit D' in hard-to-read gold color matching the structure)--> On the | + | * <span style="color:red">Subunit '''B</span>''' is equivalent to Subunit '''D''' (ABOVE). <!--<span style="color:#FFFF80">Subunit '''D'''</span>(<--says 'Subunit D' in hard-to-read gold color matching the structure)--> On the left, a <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Btodmorph/5' target='main2NDwindow'>morph showing the equivalency of the two subunits by rotating around the axis of their symmetry</scene>. |
However, each of the subunit '''<span style="color:forestgreen">A</span>'''/<span style="color:cornflowerblue">'''C'''</span> group though is distinct from those of the <span style="color:red">'''B</span>'''/'''D''' group. Having established the two equivalent groups we can simplify the discussion of the relationship between the two pairs by focusing solely on comparing <span style="color:forestgreen">Subunit '''A'</span>''' and <span style="color:red">Subunit '''B</span>'''.<br> | However, each of the subunit '''<span style="color:forestgreen">A</span>'''/<span style="color:cornflowerblue">'''C'''</span> group though is distinct from those of the <span style="color:red">'''B</span>'''/'''D''' group. Having established the two equivalent groups we can simplify the discussion of the relationship between the two pairs by focusing solely on comparing <span style="color:forestgreen">Subunit '''A'</span>''' and <span style="color:red">Subunit '''B</span>'''.<br> | ||
The domains themselves stay relatively static between the two conformational forms, with the linkers in between and the resulting arrangement changing. This is best illustrated by superposition of the individual domains of <span style="color:forestgreen">Subunit '''A</span>''' and <span style="color:red">Subunit '''B</span>''': | The domains themselves stay relatively static between the two conformational forms, with the linkers in between and the resulting arrangement changing. This is best illustrated by superposition of the individual domains of <span style="color:forestgreen">Subunit '''A</span>''' and <span style="color:red">Subunit '''B</span>''': | ||
| - | *<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Atdatobsuper/4'>Superposition of the ATD</scene>. | + | *<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Atdatobsuper/4' target='main2NDwindow'>Superposition of the ATD</scene>. |
| - | *<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Lbdatobsuper/2'>Superposition of the LBD</scene>. | + | *<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Lbdatobsuper/2' target='main2NDwindow'>Superposition of the LBD</scene>. |
| - | *<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Tmdatobsuper/1'>Superposition of the TMD</scene>. | + | *<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Tmdatobsuper/1' target='main2NDwindow'>Superposition of the TMD</scene>. |
| - | <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Atobmorph/2'>Subunit A morphing into Subunit B best illustrates how portions, especially the linkers, of the protein change</scene> between the two conformational forms.<br> | + | <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Atobmorph/2' target='main2NDwindow'>Subunit A morphing into Subunit B best illustrates how portions, especially the linkers, of the protein change</scene> between the two conformational forms.<br> |
{{Button Toggle AnimationOnPause}} | {{Button Toggle AnimationOnPause}} | ||
:The linkers are key; besides playing roles in domain swapping and resolving the symmetry mismatch, they are also responsible for relaying the modulation signals from the ATD to the other domains and signaling the conformational change of the LBD to control the opening and closing of the pore. Beyond the two conformations seen here though this particular structure ([[3kg2]]) of the receptor does not shed light on the transduction process. | :The linkers are key; besides playing roles in domain swapping and resolving the symmetry mismatch, they are also responsible for relaying the modulation signals from the ATD to the other domains and signaling the conformational change of the LBD to control the opening and closing of the pore. Beyond the two conformations seen here though this particular structure ([[3kg2]]) of the receptor does not shed light on the transduction process. | ||
===Transmembrane domain architecture and the occluded pore=== | ===Transmembrane domain architecture and the occluded pore=== | ||
| - | *<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Transmemlabeled/1'>Transmembrane segments M1 to M4 depicted in different colors to show the approximate 4-fold rotational symmetry of the entire ion channel domain.</scene> | + | *<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Transmemlabeled/1' target='main2NDwindow'>Transmembrane segments M1 to M4 depicted in different colors to show the approximate 4-fold rotational symmetry of the entire ion channel domain.</scene> |
::* '''<span style="color:coral">M1</span>''' | ::* '''<span style="color:coral">M1</span>''' | ||
::* '''<span style="color:lightgreen">M2</span>''' | ::* '''<span style="color:lightgreen">M2</span>''' | ||
| Line 58: | Line 60: | ||
::* '''<span style="color:lightskyblue">M4</span>''' | ::* '''<span style="color:lightskyblue">M4</span>''' | ||
| - | *The segments shown again, <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Transmem/4'>this time parallel to the four-fold axis</scene>. | + | *The segments shown again, <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Transmem/4' target='main2NDwindow'>this time parallel to the four-fold axis</scene>. |
::There is <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Transmemclosed/1'>no pore visible in the center</scene> consistent with the channel being in a closed state with the antagonist (ZK200775) bound to the LBD. | ::There is <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Transmemclosed/1'>no pore visible in the center</scene> consistent with the channel being in a closed state with the antagonist (ZK200775) bound to the LBD. | ||
| - | ::It is <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/M3_closed/3'>the tight helix crossing of specifically the M3 helices</scene> that occludes the channel. [BE PATIENT as a small surface is generated.] | + | ::It is <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/M3_closed/3' target='main2NDwindow'>the tight helix crossing of specifically the M3 helices</scene> that occludes the channel. [BE PATIENT as a small surface is generated.] |
| - | ::Note <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/M3_closed_top/1'>the differences between the conformations of the carboxy-termini ('top') of the subunit A/C and B/D M3 segments</scene>. This is in part is why the symmetry is only approximately four-fold and is one of the several intriguing observations in regard to symmetry for this macromolecule. In fact, the location of two-fold symmetry at the ends of M3 is just above the portion that spans the membrane and is close to the last region of the structure that doesn't show four-fold symmetry as abruptly below this point everything is four-fold symmetric. | + | ::Note <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/M3_closed_top/1' target='main2NDwindow'>the differences between the conformations of the carboxy-termini ('top') of the subunit A/C and B/D M3 segments</scene>. This is in part is why the symmetry is only approximately four-fold and is one of the several intriguing observations in regard to symmetry for this macromolecule. In fact, the location of two-fold symmetry at the ends of M3 is just above the portion that spans the membrane and is close to the last region of the structure that doesn't show four-fold symmetry as abruptly below this point everything is four-fold symmetric. |
| - | *To better observe the contributions of each of the membrane segments to the subunit-subunit interactions, <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Trans_surf/4'>the transmembrane domains of three subunits are shown in a surface representation with the segments M1-M4 of the fourth subunit shown as green cylinders</scene>. <nowiki>[</nowiki>Note: this scene generates a substantial surface which may take about a minute to calculate. Be patient.<nowiki>]</nowiki> | + | *To better observe the contributions of each of the membrane segments to the subunit-subunit interactions, <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Trans_surf/4' target='main2NDwindow'>the transmembrane domains of three subunits are shown in a surface representation with the segments M1-M4 of the fourth subunit shown as green cylinders</scene>. <nowiki>[</nowiki>Note: this scene generates a substantial surface which may take about a minute to calculate. Be patient.<nowiki>]</nowiki> |
::Note that the M4 segment associates with the ion-channel core of an adjacent subunit. | ::Note that the M4 segment associates with the ion-channel core of an adjacent subunit. | ||
:{{Link Toggle FancyCartoonHighQualityView}}. | :{{Link Toggle FancyCartoonHighQualityView}}. | ||
| - | *The TMD domain of the GluA2 receptor shares structural and sequence similarity with the pore region of the potassium (K+), as hinted at by earlier work<ref name ="pot1">PMID: 7539962</ref><ref name ="pot2">PMID: 7761417</ref><ref name ="pot3">PMID: 9525859</ref>. Here the pore region of ''Streptomyces lividans'' potassium channel ([[1bl8]])<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Gluvspottmd/4'> superposed with the TMD domain of GluA2</scene>, specifically the <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Gluvspottmdm3/1'>inner helix of the K+ channel aligned with the M3 segment</scene>. The <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Gluvspottmdm1/2'>M1 segment of GluA2 also overlays well with the outer helix</scene> of the K+ channel even though these portions weren't even included in the calculation of the alignment seen here. | + | *The TMD domain of the GluA2 receptor shares structural and sequence similarity with the pore region of the potassium (K+), as hinted at by earlier work<ref name ="pot1">PMID: 7539962</ref><ref name ="pot2">PMID: 7761417</ref><ref name ="pot3">PMID: 9525859</ref>. Here the pore region of ''Streptomyces lividans'' potassium channel ([[1bl8]])<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Gluvspottmd/4' target='main2NDwindow'> superposed with the TMD domain of GluA2</scene>, specifically the <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Gluvspottmdm3/1' target='main2NDwindow'>inner helix of the K+ channel aligned with the M3 segment</scene>. The <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Gluvspottmdm1/2' target='main2NDwindow'>M1 segment of GluA2 also overlays well with the outer helix</scene> of the K+ channel even though these portions weren't even included in the calculation of the alignment seen here. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==Details of Structure Featured== | ==Details of Structure Featured== | ||
Revision as of 22:41, 28 November 2010
The glutamate receptor is the ion channel opened by glutamate that keeps neurons in touch by mediating fast cell-to-cell information transfer in the nervous system. Several studies have revealed structures for portions of the glutamate receptor [1][2][3][4]. Groundbreaking work elucidated the structure of a complete functional, homomeric glutamate receptor[5][6] and that structure, 3kg2, is the subject of this page.
Contents |
Structure of the Glutamate Receptor (GluA2)
| |||||||||||
Subunit Non-Equivalence, Transmembrane domain Architecture and the Occluded Pore
| |||||||||||
Details of Structure Featured
3kg2 is a 4 chains structure of sequences from Rattus norvegicus. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. Although it is billed as the first structure of a full-length glutamate receptor, the carboxy-terminal domain is not present in the structure.
Reference for the structure
- Sobolevsky AI, Rosconi MP, Gouaux E. X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature. 2009 Dec 10;462(7274):745-56. Epub . PMID:19946266 doi:10.1038/nature08624
See Also
- 3kgc – GluA2 ligand-binding core complex bound with glutamate
- 2a5t – GluN1-GluN2A ligand-binding domain heterodimer
- 2a5s – GluN2A ligand-binding domain bound with glutamate
- 3h5w and 3h5v – Crystal structure of the GluR2 amino-terminal domain[1]
- 1gr2 – Structure of a glutamate-receptor ligand-binding core in complex with kainate[13]
- 3jpy and 3jpw – Structure of the zinc-bound amino-terminal domain of the NMDA receptor NR2B subunit[3]
- 1iiw and 1iit and 1ii5 – Prokaryotic glutamte receptor (Glur0) Apo structure and with various ligands bound, including glutmate [14]. This helped cement the notion the glutamate and potassium receptors share structural similarity and possibly evolutionary ancestry [10][11].
- 3hgh and 3hgh – The N-terminal domain of a GluR6-subtype glutamate receptor[2]
- 1bl8 and 1jq1 and 1jq2 – Streptomyces lividans KcsA potassium channel[12][15]: The M1, M2 and M3 segments of GluA2's ion channel overlap remarkably well with the structurally equivalent portions KcsA.
- Molecular Playground/Glutamate Receptor
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Jin R, Singh SK, Gu S, Furukawa H, Sobolevsky AI, Zhou J, Jin Y, Gouaux E. Crystal structure and association behaviour of the GluR2 amino-terminal domain. EMBO J. 2009 Jun 17;28(12):1812-23. Epub 2009 May 21. PMID:19461580 doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.140
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Kumar J, Schuck P, Jin R, Mayer ML. The N-terminal domain of GluR6-subtype glutamate receptor ion channels. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Jun;16(6):631-8. Epub 2009 May 24. PMID:19465914 doi:10.1038/nsmb.1613
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Karakas E, Simorowski N, Furukawa H. Structure of the zinc-bound amino-terminal domain of the NMDA receptor NR2B subunit. EMBO J. 2009 Dec 16;28(24):3910-20. Epub . PMID:19910922 doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.338
- ↑ Armstrong N, Sun Y, Chen GQ, Gouaux E. Structure of a glutamate-receptor ligand-binding core in complex with kainate. Nature. 1998 Oct 29;395(6705):913-7. PMID:9804426 doi:10.1038/27692
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Sobolevsky AI, Rosconi MP, Gouaux E. X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature. 2009 Dec 10;462(7274):745-56. Epub . PMID:19946266 doi:10.1038/nature08624
- ↑ Wollmuth LP, Traynelis SF. Neuroscience: Excitatory view of a receptor. Nature. 2009 Dec 10;462(7274):729-31. PMID:20010675 doi:10.1038/462729a
- ↑ Wo ZG, Oswald RE. Unraveling the modular design of glutamate-gated ion channels. Trends Neurosci. 1995 Apr;18(4):161-8. PMID:7539962
- ↑ Turski L, Huth A, Sheardown M, McDonald F, Neuhaus R, Schneider HH, Dirnagl U, Wiegand F, Jacobsen P, Ottow E. ZK200775: a phosphonate quinoxalinedione AMPA antagonist for neuroprotection in stroke and trauma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Sep 1;95(18):10960-5. PMID:9724812
- ↑ Walters MR, Kaste M, Lees KR, Diener HC, Hommel M, De Keyser J, Steiner H, Versavel M. The AMPA antagonist ZK 200775 in patients with acute ischaemic stroke: a double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled safety and tolerability study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2005;20(5):304-9. Epub 2005 Aug 30. PMID:16131799 doi:10.1159/000087929
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Wo ZG, Oswald RE. Unraveling the modular design of glutamate-gated ion channels. Trends Neurosci. 1995 Apr;18(4):161-8. PMID:7539962
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Wood MW, VanDongen HM, VanDongen AM. Structural conservation of ion conduction pathways in K channels and glutamate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):4882-6. PMID:7761417
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Doyle DA, Morais Cabral J, Pfuetzner RA, Kuo A, Gulbis JM, Cohen SL, Chait BT, MacKinnon R. The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science. 1998 Apr 3;280(5360):69-77. PMID:9525859
- ↑ Armstrong N, Sun Y, Chen GQ, Gouaux E. Structure of a glutamate-receptor ligand-binding core in complex with kainate. Nature. 1998 Oct 29;395(6705):913-7. PMID:9804426 doi:10.1038/27692
- ↑ Chen GQ, Cui C, Mayer ML, Gouaux E. Functional characterization of a potassium-selective prokaryotic glutamate receptor. Nature. 1999 Dec 16;402(6763):817-21. PMID:10617203 doi:10.1038/45568
- ↑ Liu YS, Sompornpisut P, Perozo E. Structure of the KcsA channel intracellular gate in the open state. Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Oct;8(10):883-7. PMID:11573095 doi:10.1038/nsb1001-883
Additional Literature and Resources
- For additional information, see: Alzheimer's Disease
- For additional information, see: Membrane Channels & Pumps
- Glutamate Receptor on the cover of Nature
- Glutamate receptor Wikipedia entry
- Glutamate Receptors page at the MRC Centre for Synaptic Plasticity at the University of Bristol
Page started with original page seeded by OCA on Wed Dec 16 11:24:54 2009 for 3kg2.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Wayne Decatur, Alexander Berchansky, Michal Harel, David Canner, Nikki Hunter
Categories: Rattus norvegicus | Gouaux, E. | Rosconi, M P. | Sobolevsky, A I. | Alternative splicing | Cell membrane | Glycoprotein | Ion channel | Ion transport | Membrane | Membrane protein | Postsynaptic cell membrane | Receptor | Rna editing | Synapse | Tetramer | Transmembrane | Transport | Neuron | Neurotransmitter | Potassium Channels | RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month | Streptomyces lividans | Cabral, J M. | Chait, B T. | Cohen, S L. | Doyle, D A. | Gulbis, J M. | Kuo, A. | Mackinnon, R. | Pfuetzner, R A. | Integral membrane protein | Potassium channel