We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Phl p 2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{STRUCTURE_3kle | PDB=2vxq | SCENE= }} | {{STRUCTURE_3kle | PDB=2vxq | SCENE= }} | ||
==Immune system== | ==Immune system== | ||
| - | The immune system is the body's way of protecting itself from foreign and potentially harmful microbes such as viruses and bacteria. When an unknown substance enters the body the immune system responds with a cascade of reactions which begin with identification of the microbe and hopefully ends with the neutralization of the pathogen. | + | The immune system is the body's way of protecting itself from foreign and potentially harmful microbes such as viruses and bacteria. When an unknown substance enters the body the immune system responds with a cascade of reactions which begin with identification of the microbe and hopefully ends with the neutralization of the pathogen. The identification and recognition of a pathogen however is a tricky process as the immune system must be able to differentiate between its own cells and foreign ones. |
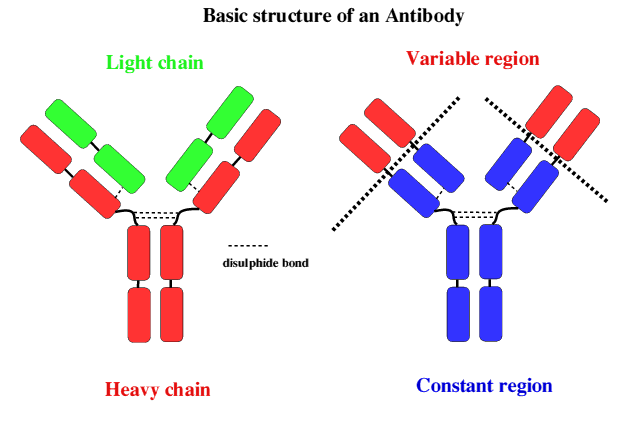
==Antibodies== | ==Antibodies== | ||
[[Image:Antibody_basic_structure.gif]] | [[Image:Antibody_basic_structure.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 16:56, 2 December 2010
Contents |
Immune system
The immune system is the body's way of protecting itself from foreign and potentially harmful microbes such as viruses and bacteria. When an unknown substance enters the body the immune system responds with a cascade of reactions which begin with identification of the microbe and hopefully ends with the neutralization of the pathogen. The identification and recognition of a pathogen however is a tricky process as the immune system must be able to differentiate between its own cells and foreign ones.
Antibodies
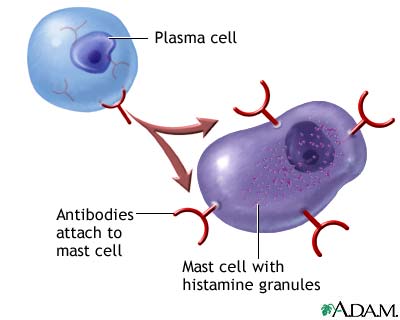
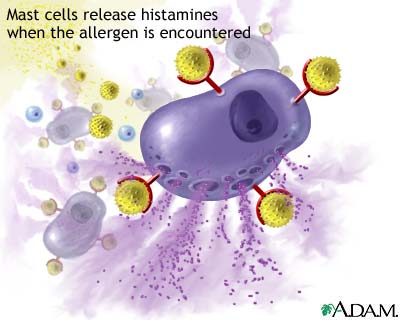
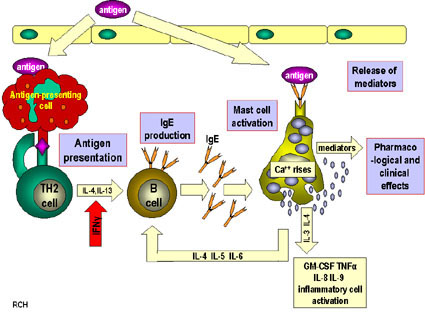
Type I Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity mechanism
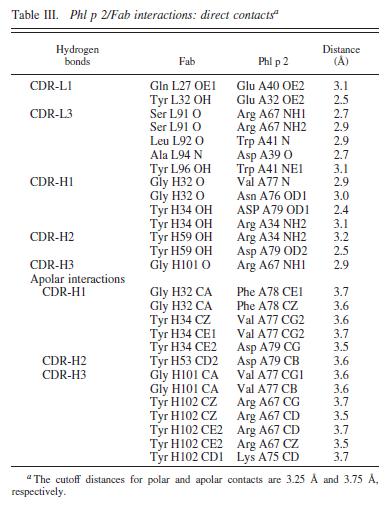
Phl p 2 and huMab2