Cyclooxygenase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ==About this structure (1,2)== | ||
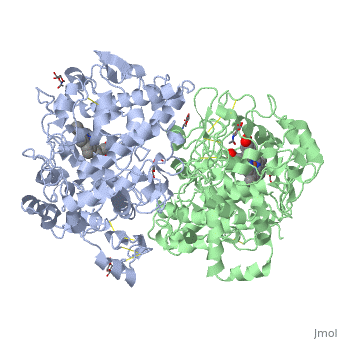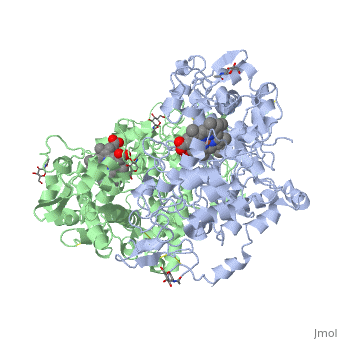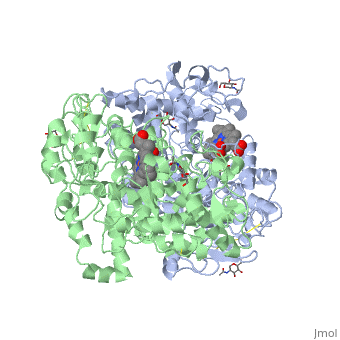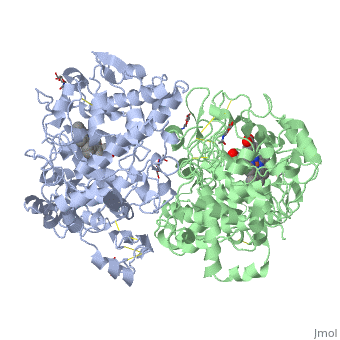
| + | PGHSs are bifunctional homodimers. Both COX-1 and COX-2 are membrane-bound enzymes and are present on the lumenal surfaces of the endoplasmic reticulum and of the inner and outer membranes of the nuclear envelope. However, recently, it has been demonstrated in cultured endothelial cells and fibroblasts that a fraction of COX-2 protein is localized to plasma membrane in caveolae-like structures (3). The primary structure of nascent COX-2 is of 604 amino acids and then it is processed into a mature form by removal of signal peptides giving a protein of 587 amino acids. PGHS-2 is variably glycosylated at two to four sites, leading to the formation of doublets or sometimes triplets on SDS-PAGE. Murine PGHS-2 peptide is presumed to be <scene name='SandboxUAM/Mynewscene/1'>N-glycosilated</scene> three times at Asn56, Asn130, and Asn396(NUEVA). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The COX monomer consists of three structural domains: the N-terminal EGF domain, a membrane binding domain (MBD) and a large C-terminal globular catalytic domain containing the heme binding site. The C-terminal segments beyond Pro583 (35 amino acids in COX-2) have not been resolved crystallographically. Collectively, these domains are made up of 25 alpha helices, seven 310 helices, four beta sheets as well as five disulfide bonds which contribute to the interface binding of the two individual monomers to complete the enzyme. | ||
| + | |||
<Structure load='5cox' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Unhibited mouse cyclooxygenase' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | <Structure load='5cox' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Unhibited mouse cyclooxygenase' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
==NSAIDs== | ==NSAIDs== | ||
| Line 76: | Line 81: | ||
<ref group="xtra">PMID: 8901870</ref><references group="xtra"/> | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 8901870</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
<ref group="xtra">PMID: 8967954</ref><references group="xtra"/> | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 8967954</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 18482003</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 7945196</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 12471036</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 11389100</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 16959971</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 15994313</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 10766797</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 12535526</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 12826679</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 17848513</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 15872218</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID: 17507659</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
Revision as of 14:40, 7 December 2010
About this structure (1,2)
PGHSs are bifunctional homodimers. Both COX-1 and COX-2 are membrane-bound enzymes and are present on the lumenal surfaces of the endoplasmic reticulum and of the inner and outer membranes of the nuclear envelope. However, recently, it has been demonstrated in cultured endothelial cells and fibroblasts that a fraction of COX-2 protein is localized to plasma membrane in caveolae-like structures (3). The primary structure of nascent COX-2 is of 604 amino acids and then it is processed into a mature form by removal of signal peptides giving a protein of 587 amino acids. PGHS-2 is variably glycosylated at two to four sites, leading to the formation of doublets or sometimes triplets on SDS-PAGE. Murine PGHS-2 peptide is presumed to be three times at Asn56, Asn130, and Asn396(NUEVA).
The COX monomer consists of three structural domains: the N-terminal EGF domain, a membrane binding domain (MBD) and a large C-terminal globular catalytic domain containing the heme binding site. The C-terminal segments beyond Pro583 (35 amino acids in COX-2) have not been resolved crystallographically. Collectively, these domains are made up of 25 alpha helices, seven 310 helices, four beta sheets as well as five disulfide bonds which contribute to the interface binding of the two individual monomers to complete the enzyme.
|
NSAIDs
| Drug | Coefficient of selectivity (IC50Cox-1/IC50Cox-2) |
|---|---|
| Ketorolac | |
| Naproxen | |
| Ibuprofen | |
| Indometacin | |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | |
| Diclofenac | |
| Valdecoxib | |
| Etoricoxib | |
| Pharmacologic group | Drug |
|---|---|
| Salicylates | Acetylsalicylic acid |
| Propionic | Naproxen |
| Ibuprofen | |
| Para-aminophenols | Paracetamol |
| Indolacetic | Indometacin |
| Pirrolacetic | Ketorolac |
| Phenilacetic | Diclofenac |
| Piranoidacetic | Etodolac |
| Anthranilic | Mefenamic acid |
| Nicotinic | Clonixin |
| Sulfonanilides | Nimesulide |
Reference
- Ghosh N, Chaki R, Mandal V, Mandal SC. COX-2 as a target for cancer chemotherapy. Pharmacol Rep. 2010 Mar-Apr;62(2):233-44. PMID:20508278
- Smith WL, DeWitt DL, Garavito RM. Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:145-82. PMID:10966456 doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.145
- Rang HP, Dale MM, Ritter JM, Flower RJ. 2008. Pharmacology. Elsevier. 6th edition. 844 p.
- Smith WL, Langenbach R. Why there are two cyclooxygenase isozymes. J Clin Invest. 2001 Jun;107(12):1491-5. PMID:11413152 doi:10.1172/JCI13271
- Chandrasekharan NV, Dai H, Roos KL, Evanson NK, Tomsik J, Elton TS, Simmons DL. COX-3, a cyclooxygenase-1 variant inhibited by acetaminophen and other analgesic/antipyretic drugs: cloning, structure, and expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 15;99(21):13926-31. Epub 2002 Sep 19. PMID:12242329 doi:10.1073/pnas.162468699
- Garavito RM, Mulichak AM. The structure of mammalian cyclooxygenases. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003;32:183-206. Epub 2003 Feb 5. PMID:12574066 doi:10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.141906
- Perrone G, Zagami M, Altomare V, Battista C, Morini S, Rabitti C. COX-2 localization within plasma membrane caveolae-like structures in human lobular intraepithelial neoplasia of the breast. Virchows Arch. 2007 Dec;451(6):1039-45. Epub 2007 Sep 13. PMID:17851687 doi:10.1007/s00428-007-0506-4
- Spencer AG, Thuresson E, Otto JC, Song I, Smith T, DeWitt DL, Garavito RM, Smith WL. The membrane binding domains of prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthases 1 and 2. Peptide mapping and mutational analysis. J Biol Chem. 1999 Nov 12;274(46):32936-42. PMID:10551860
- Luong C, Miller A, Barnett J, Chow J, Ramesha C, Browner MF. Flexibility of the NSAID binding site in the structure of human cyclooxygenase-2. Nat Struct Biol. 1996 Nov;3(11):927-33. PMID:8901870
- Kurumbail RG, Stevens AM, Gierse JK, McDonald JJ, Stegeman RA, Pak JY, Gildehaus D, Miyashiro JM, Penning TD, Seibert K, Isakson PC, Stallings WC. Structural basis for selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 by anti-inflammatory agents. Nature. 1996 Dec 19-26;384(6610):644-8. PMID:8967954 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/384644a0
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Cristina Murga, Michal Harel, David Canner, María Laura Saiz Álvarez, Alexander Berchansky