User:Meili Yang/sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
Meili Yang (Talk | contribs)
(New page: Bacterial chemotaxis receptor One of the CBI Molecules being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Ch...)
Next diff →
Revision as of 22:06, 9 December 2010
One of the CBI Molecules being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst and on display at the Molecular Playground.
The bacterial chemotaxis receptors are transmembrane receptors with a simple signalling pathway which has elements relevant to the general understanding of signal recognition and transduction across membranes, how signals are relayed between molecules in a pathway, and how adaptation to a persistent signal is achieved.
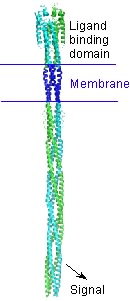
Bacterial chemotaxis receptors are composed of a ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain consisting of two helices TM1 and TM2, and a cytoplasmic domain. All known bacterial chemotaxis receptors have a highly conserved cytoplasmic domain, which unites signals from different ligand domains into a single signalling pathway to flagella motors.
|
Cytoplasmic domain
The spinning protein () ) is the ligand binding domain of the aspartate receptor with the aspartate ligand bound (LKT).
Molecular Playground banner: A bacterial chemotaxis receptor protein used by bacteria to "smell" their environment.