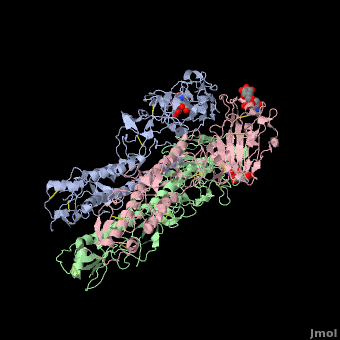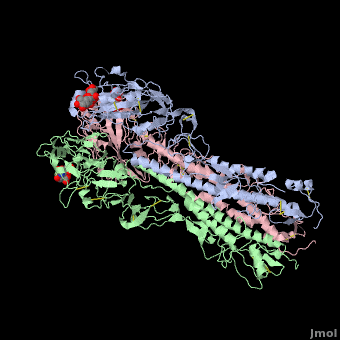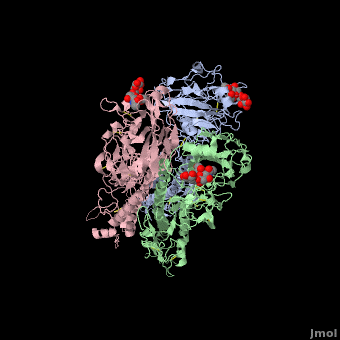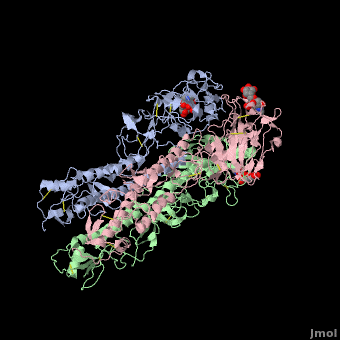
Hemagglutinin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
The <scene name='SAndbox_159/Ha2/2'>HA2 subunit</scene> (221 amino acids) has a hair spin structure composed by two antiparallel alpha-helixes. One of these belongs to the longest alpha-helixes in globular protein: it is 50 angstrom long. The hydrophobic N-terminus part of HA2, called fusion peptide, is close to a protease’s cleavage site: this protease is implied in the virus’ entry in the host cell. | The <scene name='SAndbox_159/Ha2/2'>HA2 subunit</scene> (221 amino acids) has a hair spin structure composed by two antiparallel alpha-helixes. One of these belongs to the longest alpha-helixes in globular protein: it is 50 angstrom long. The hydrophobic N-terminus part of HA2, called fusion peptide, is close to a protease’s cleavage site: this protease is implied in the virus’ entry in the host cell. | ||
| - | HA1 and HA2 are bound each other by a disulfide bind. The three long alpha-helixes (of the three HA2) are coiled-coil to form a central region of 40 Angström, and thank to the hydrophobic amino acids and those which form salt bridges bound, we obtain a HA stabilized. | + | HA1 and HA2 are bound each other by a disulfide bind. The three long alpha-helixes (of the three HA2) are coiled-coil to form a central region of 40 Angström, and thank to the hydrophobic amino acids and those which form salt bridges bound, we obtain a HA stabilized.<ref>PMID: 3304138</ref> |
==2WRE== | ==2WRE== | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
<scene name='SAndbox_159/Amino_acids_in_the_stability/1'>(Cys 97, Pro 99, Cis139, Pro 147, Tyr 195, Arg 229).</scene>(*) | <scene name='SAndbox_159/Amino_acids_in_the_stability/1'>(Cys 97, Pro 99, Cis139, Pro 147, Tyr 195, Arg 229).</scene>(*) | ||
The Sia-1-Gal-2 glycosidic bond adopts a cis conformation. Extensive hydrogen bond direction are settled between avian and Gal-2 of the receptor: two water molecules (Wat-1 and Wat-2) have a significant role in mediating these interactions(see fig.1). | The Sia-1-Gal-2 glycosidic bond adopts a cis conformation. Extensive hydrogen bond direction are settled between avian and Gal-2 of the receptor: two water molecules (Wat-1 and Wat-2) have a significant role in mediating these interactions(see fig.1). | ||
| - | The site chain of Lys-222 and the main chain carbonyl at 225 are linked by Wat-1 to the 3'OH of Gal-2. Gln-226 and Asn 186 form hydrogen bonds with the hydroxyl groups of 4'C of Gal-2 and 9'C of Sia-1. | + | The site chain of Lys-222 and the main chain carbonyl at 225 are linked by Wat-1 to the 3'OH of Gal-2. Gln-226 and Asn 186 form hydrogen bonds with the hydroxyl groups of 4'C of Gal-2 and 9'C of Sia-1.<ref>Cell Binding protein in Avian Influenza; Jack Cerchiara,'06 and Brendan Holsberry, 07;http://biology.kenyon.edu/BMB/Chime2/2005/Cerchiara-Holsberry/FRAMES/start.htm</ref> |
==Oligosaccharides== | ==Oligosaccharides== | ||
| - | Some <scene name='SAndbox_159/Asparagines/1'>Asparagines</scene> of HA1 (8, 22, 38, 81, 165, 285)(*) have oligosaccharides chains attached to them. The seventh oligasaccharide is linked to an Aspargine of HA2 (484). All of them are complex oligosaccharides and are on the lateral surfaces of the molecule, except for site and 165. No precise functions have been assigned to them, even if the oligosaccharide at 165 seems to allow the stabilisation of oligomeric contact between globular units at the top of the protein's structure. | + | Some <scene name='SAndbox_159/Asparagines/1'>Asparagines</scene> of HA1 (8, 22, 38, 81, 165, 285)(*) have oligosaccharides chains attached to them. The seventh oligasaccharide is linked to an Aspargine of HA2 (484). All of them are complex oligosaccharides and are on the lateral surfaces of the molecule, except for site and 165. No precise functions have been assigned to them, even if the oligosaccharide at 165 seems to allow the stabilisation of oligomeric contact between globular units at the top of the protein's structure. |
==Antigenic variability== | ==Antigenic variability== | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | == | + | ==References== |
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| - | |||
| - | - Hemagglutinin (HA) - Cell Binding protein in Avian Influenza; Jack Cerchiara,'06 and Brendan Holsberry, 07;http://biology.kenyon.edu/BMB/Chime2/2005/Cerchiara-Holsberry/FRAMES/start.htm | ||
| - | |||
| - | - The structure and function of the hemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus; Wiley DC, Skehel JJ. | ||
| - | Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:365-94. PMID: 3304138 | ||
| - | |||
| - | <references/> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ---- | ||
Revision as of 12:01, 12 December 2010
| |||||||||||
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Influenza
References
- ↑ Gottschalk A. Chemistry of virus receptors. The Viruses. 1959;3:51–61.
- ↑ Wiley DC, Skehel JJ. The structure and function of the hemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:365-94. PMID:3304138 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002053
- ↑ Liu J, Stevens DJ, Haire LF, Walker PA, Coombs PJ, Russell RJ, Gamblin SJ, Skehel JJ. Structures of receptor complexes formed by hemagglutinins from the Asian Influenza pandemic of 1957. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Oct 6;106(40):17175-80. Epub 2009 Sep 28. PMID:19805083
- ↑ Cell Binding protein in Avian Influenza; Jack Cerchiara,'06 and Brendan Holsberry, 07;http://biology.kenyon.edu/BMB/Chime2/2005/Cerchiara-Holsberry/FRAMES/start.htm
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Julien Madouasse, Michal Harel, David Canner, Mark Hoelzer, Ann Taylor, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Marius Mihasan