This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Glycolysis
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
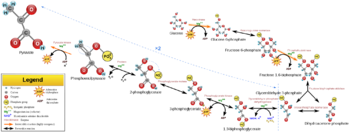
[[Glycolysis]] is a critical process in the [[Carbohydrate Metabolism|metabolism of carbohydrates]]. By utilizing various enzymes, glucose is converted into pyruvate. The free energy released during this process in the form of ATP and NADH subsequently powers nearly countless catalytic reactions in the cell. | [[Glycolysis]] is a critical process in the [[Carbohydrate Metabolism|metabolism of carbohydrates]]. By utilizing various enzymes, glucose is converted into pyruvate. The free energy released during this process in the form of ATP and NADH subsequently powers nearly countless catalytic reactions in the cell. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
Articles in Proteopedia concerning [[Glycolysis]] include: | Articles in Proteopedia concerning [[Glycolysis]] include: | ||
Revision as of 12:38, 18 December 2010
Glycolysis is a critical process in the metabolism of carbohydrates. By utilizing various enzymes, glucose is converted into pyruvate. The free energy released during this process in the form of ATP and NADH subsequently powers nearly countless catalytic reactions in the cell.
Articles in Proteopedia concerning Glycolysis include:
- Alcohol dehydrogenase
- Aldolase
- Enolase
- Fructose Bisphosphate Aldolase
- Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
- Glycolysis Enzymes
- Hexokinase Structure & Mechanism
- Hexokinase Type 1
- Lactate Dehydrogenase
- Lactate Dehydrogenase Structure & Mechanism
- Phosphofructokinase
- Phosphofructokinase Structure & Mechanism
- Phosphoglucose Isomerase Structure & Mechanism
- Phosphoglycerate Kinase (PGK)
- Phosphoglycerate Mutase
- Pyruvate decarboxylase
- Pyruvate Kinase
- Triose Phosphate Isomerase
- Triose Phosphate Isomerase Structure & Mechanism
To view automatically seeded indices concerning Glycolysis See:
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
David Canner, Alexander Berchansky, Karsten Theis, Jaime Prilusky