Ann Taylor sandbox 117
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Succinyl-AAPR-trypsin acyl-enzyme== | ==Succinyl-AAPR-trypsin acyl-enzyme== | ||
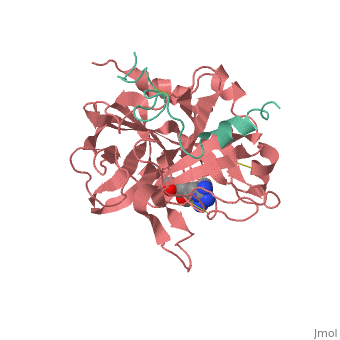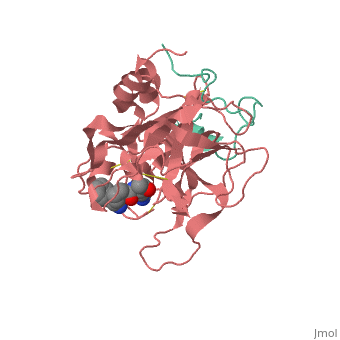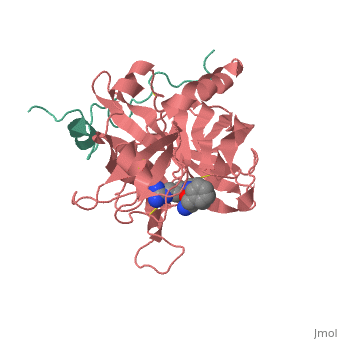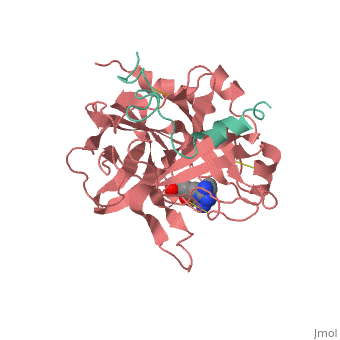
| - | Structures of trypsin acyl-enzymes are used to reconstruct events in the catalytic cycle of serine protease. The structural comparisons provide insight into active site adjustments involved in catalysis. The motions of the catalytic serine and histidine residues coordinated with translation of the substrate reaction center are seen to favor the forward reaction. The structures also clarify how the hydrolytic water attacks in the deacylation reaction. | + | Structures of trypsin acyl-enzymes are used to reconstruct events in the catalytic cycle of serine protease. The structural comparisons provide insight into active site adjustments involved in catalysis. <scene name='Ann_Taylor_sandbox_117/2age/1'>2AGE</scene> The motions of the catalytic serine and histidine residues coordinated with translation of the substrate reaction center are seen to favor the forward reaction. The structures also clarify how the hydrolytic water attacks in the deacylation reaction. |
<applet load="1ppb" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="left" spinBox="true" | <applet load="1ppb" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="left" spinBox="true" | ||
Revision as of 03:03, 21 February 2011
Contents |
Succinyl-AAPR-trypsin acyl-enzyme
Structures of trypsin acyl-enzymes are used to reconstruct events in the catalytic cycle of serine protease. The structural comparisons provide insight into active site adjustments involved in catalysis. The motions of the catalytic serine and histidine residues coordinated with translation of the substrate reaction center are seen to favor the forward reaction. The structures also clarify how the hydrolytic water attacks in the deacylation reaction.
|
Serine proteases, or proteinases, so called due to the presence of a serine residue in the active site, are a class of enzymes that catalyse the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in proteins.
Thrombin
Thrombin is a "trypsin-like" serine protease. Its structure (PDB code 1ppb) is shown here with a peptide chloroketone inhibitor (PPACK). The thrombin A chain (cleaved N terminal fragement) is shown in cyan and the B chain is shown in red. The is made up of a catalytic triad of Ser195, His57 and Asp102, backed up by Ser214. The peptide chloroketone inhibitor (PPACK) is shown in purple. A closeup shows the at which the sidechain of Asp194 makes a salt link with the N-terminus at residue 16, newly formed when the A chain is cleaved in the zymogen-to-enzyme activation process. The specificity pocket is on one side of the throat of the domain 2 beta barrel, and the activation site is close next to it.
The B chain consists of . As is true for all of the "trypsin-like" serine proteases, each of the two thrombin domains consists mainly of a 6-stranded, antiparallel beta barrel. The specificity pocket (here filled with the Lys sidechain of the PPACK inhibitor) is in one side of the throat of the domain 2beta barrel, and the activation site is close next to it.
|
Trypsin-BPTI complex
The trypsin backbone is shown in pink and the trypsin inhibitor, BPTI, in yellow (PDB code 2ptc). The residues [Ser195-His57-Asp102-Ser214] are shown in green, the disulfide bond between residues 14-38 is shown in yellow and the Lys 15 sidechain at the specificity site in pink.
Content Donators
- Content for this page has been included and adapted with permission from Jane S. and David C. Richardson's http://kinemage.biochem.duke.edu/
Replace the PDB id (use lowercase!) after the STRUCTURE_ and after PDB= to load
and display another structure.
| |||||||||
| 2age, resolution 1.15Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | |||||||||
| Non-Standard Residues: | |||||||||
| Activity: | Trypsin, with EC number 3.4.21.4 | ||||||||
| Related: | 2agg, 2agi, 2ah4
| ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, RCSB | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||