This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Colicin E2
From Proteopedia
(→Synthesis and release) |
(→Killing Activities) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Killing Activities== | ==Killing Activities== | ||
| + | Colicin E2 kills its target cell, after leaving behind the immunity protein at the cell surface, with its [[DNase Activity]] found in its C terminal cytotoxic domain. | ||
Revision as of 16:33, 25 February 2011
Colicin E2 is a type of Colicin, a bacteriocin made by E. coli which acts against other nearby E. coli to kill them with its DNase activity; it digests the host genome, leading to its death.
Synthesis and release
The ColE2 operon is encoded on a plasmid in E. coli, alongside its Colicin Immunity Protein, Imm. This protects the colicinogenic cell from the cytotoxic activity of the colicin.
Mechanism of uptake
| |||||||||
| 2ysu, resolution 3.50Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, RCSB | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
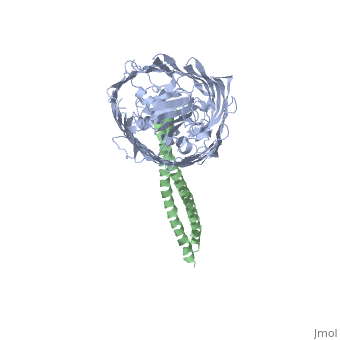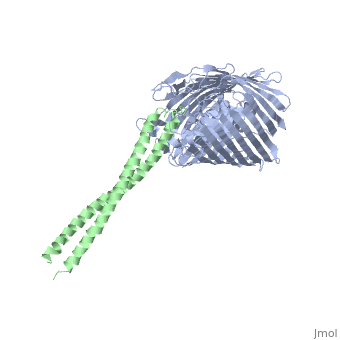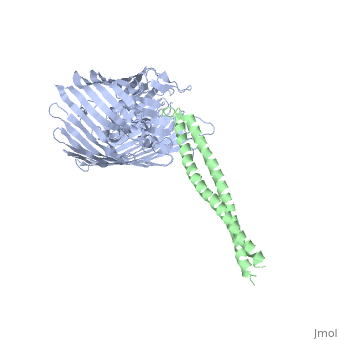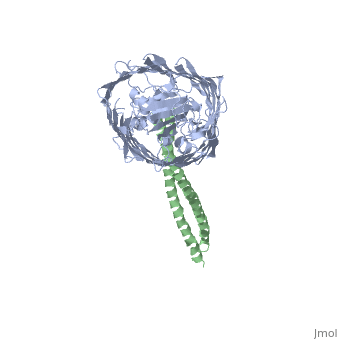
Colicin E2 binds to the BtuB receptor on the target E. coli cell to begin its translocation across the membrane. This structure shows the binding between (blue) and the (green).
Killing Activities
Colicin E2 kills its target cell, after leaving behind the immunity protein at the cell surface, with its DNase Activity found in its C terminal cytotoxic domain.