Naproxen
From Proteopedia
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
dizziness, drowsiness, ringing in the ears, hearing problems. More severe symptoms such as blisters, changes in vision, rash, hives, difficulty breathing, flu-like symptoms, bloody urine, and stomach pain are also known to occur.<ref>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0000526/</ref> | dizziness, drowsiness, ringing in the ears, hearing problems. More severe symptoms such as blisters, changes in vision, rash, hives, difficulty breathing, flu-like symptoms, bloody urine, and stomach pain are also known to occur.<ref>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0000526/</ref> | ||
| - | ==Background Information== | ||
| - | |||
==Chemical Properties== | ==Chemical Properties== | ||
IUPAC:(+)-(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoic acid | IUPAC:(+)-(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoic acid | ||
| Line 39: | Line 37: | ||
==Administration== | ==Administration== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:Naproxen.jpg]] | ||
| - | |||
Prescription naproxen comes in tablet form as an extended-release, delayed-release, or liquid suspension pill that can be taken by mouth. Due to side effects is is commonly advised that it is taken with a full glass of water, taking the tablet with milk or food has also been known to prevent nausea, a common side effect. | Prescription naproxen comes in tablet form as an extended-release, delayed-release, or liquid suspension pill that can be taken by mouth. Due to side effects is is commonly advised that it is taken with a full glass of water, taking the tablet with milk or food has also been known to prevent nausea, a common side effect. | ||
Pills should always be taken whole, never crushed, chewed, or split. | Pills should always be taken whole, never crushed, chewed, or split. | ||
| + | [[Image:Naproxen.jpg|thumb]] | ||
==COX-1 & COX-2 Inhibitor== | ==COX-1 & COX-2 Inhibitor== | ||
Revision as of 20:39, 8 March 2011
| Please do NOT make changes to this Sandbox. Sandboxes 30-60 are reserved for use by Biochemistry 410 & 412 at Messiah College taught by Dr. Hannah Tims during Fall 2012 and Spring 2013. |
Contents |
Naproxen
Naproxen Sodium is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that can be prescribed to relieve swelling, stiffness, tenderness, or pain that can be caused by:[1]
- osteoarthritis
- rheumatoid arthritis
- juvenile arthritis
- ankylosing spondylitis
- bursitis
- tendinitis
- gouty arthritis
Readily available over the counter, naproxen is also used to treat:[2]
- headaches
- menstrual pain
- common colds
- toothaches
- muscle ache
- back pain
"Naproxen and naproxen sodium are marketed under various trade names, including: Aleve, Anaprox, Antalgin, Feminax Ultra, Flanax, Inza, Midol Extended Relief, Miranax, Nalgesin, Naposin, Naprelan, Naprogesic, Naprosyn, Narocin, Proxen, Synflex and Xenobid."[3] Like other NSAID medications naproxen is known to cause ulcers, bleeding, or holes in the lining of the stomach and intestines and should always be taken with a glass of water.
Some of naproxen's side effects, are and are not limited too: constipation, diarrhea, sores in mouth, excessive thirst, headache, dizziness, drowsiness, ringing in the ears, hearing problems. More severe symptoms such as blisters, changes in vision, rash, hives, difficulty breathing, flu-like symptoms, bloody urine, and stomach pain are also known to occur.[4]
Chemical Properties
IUPAC:(+)-(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoic acid
Molecular Weight:230.250 g/mol
Chemical Formula: C14O3H14
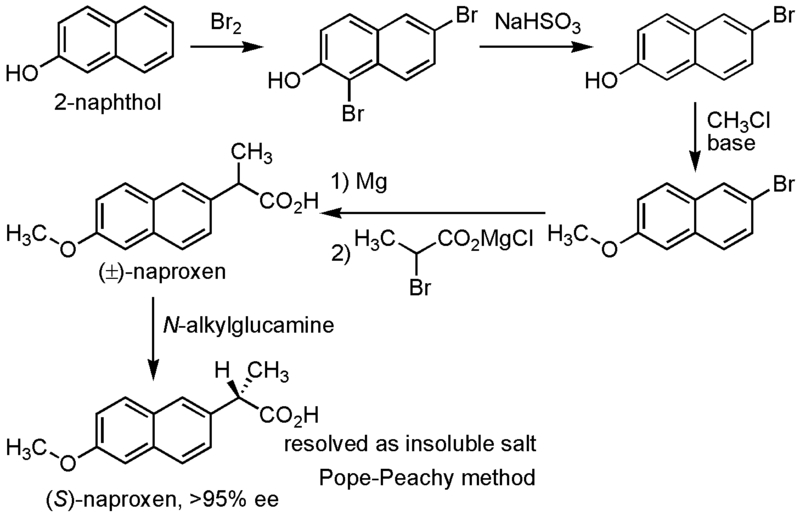
Synthesis
Administration
Prescription naproxen comes in tablet form as an extended-release, delayed-release, or liquid suspension pill that can be taken by mouth. Due to side effects is is commonly advised that it is taken with a full glass of water, taking the tablet with milk or food has also been known to prevent nausea, a common side effect. Pills should always be taken whole, never crushed, chewed, or split.
COX-1 & COX-2 Inhibitor
Cyclooxygenase abbreviated as COX
Naproxen In Vivo
|