Copper Amine Oxidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
== Reaction == | == Reaction == | ||
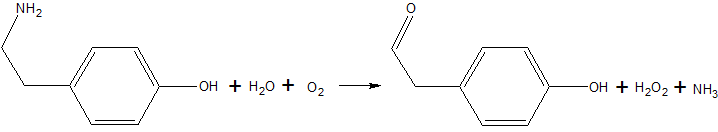
| - | Copper amine oxidase catalyzes the oxidation of a primary amine to an aldehyde, yielding hydrogen peroxide and free ammonia. An example of this is the oxidation of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tyramine | + | Copper amine oxidase catalyzes the oxidation of a primary amine to an aldehyde, yielding hydrogen peroxide and free ammonia. An example of this is the oxidation of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tyramine tyramine]: |
[[Image:Tyramine oxidation.png|The oxidation of tyramine.]] | [[Image:Tyramine oxidation.png|The oxidation of tyramine.]] | ||
Revision as of 03:28, 13 March 2011
| This Sandbox is Reserved from January 10, 2010, through April 10, 2011 for use in BCMB 307-Proteins course taught by Andrea Gorrell at the University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, BC, Canada. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
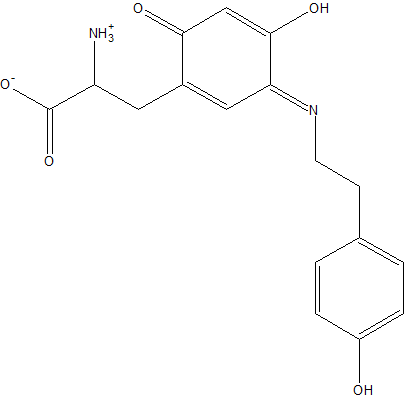
2d1w is a copper amine oxidase found in Arthrobacter globiformis.
Contents |
Structure
Ligand
A closeup of the Cu2+ .
Modified Residue
Reaction
Copper amine oxidase catalyzes the oxidation of a primary amine to an aldehyde, yielding hydrogen peroxide and free ammonia. An example of this is the oxidation of tyramine:
References
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Raymond Lyle, Alexander Berchansky, OCA, Jaime Prilusky