This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox89220
From Proteopedia
(→Structure) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<Structure load='2amy' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Phosphomannose mutase 2' scene='PMM2' /> | <Structure load='2amy' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Phosphomannose mutase 2' scene='PMM2' /> | ||
<scene name='Sandbox89220/2amy/5'>Phosphomannose mutase 2</scene> | <scene name='Sandbox89220/2amy/5'>Phosphomannose mutase 2</scene> | ||
| + | <scene name='Sandbox89220/2amy/6'>PMM2</scene> | ||
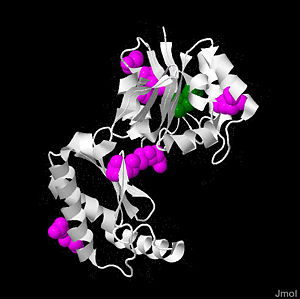
PMM2 is a 246 amino acid long protein, with 2 identical subunits working as independent domains, hence it’s also known as a homodimeric protein. In addition, it’s classified as the member of HAD (haloacid dehydrolase) superfamily due to the fact that it had 4 different types of motifs, each of which is highly conserved across the vertebrates’ lineages during evolutions. Similar to other members in HAD superfamily, the two domains are separately recognized as core and cap domain. The core domain (residues 1 – 90, and 198-262)of PMM2 displays the characteristic 4 motifs of HAD superfamily that contribute to the catalytic ability of the active sites in the protein. Motif 1 has Asp as nucleophile which serves as the mediator for the phosphoryl group transfer, the second Asp, on the other hand, acts as in the general acid-base reaction. While motif 1 provides the nucleophilic and general acid-base reactions, motif 2 in the protein which usually contains Thr or Ser helps in positioning or binding on the substrates’ phosphoryl group. In addition, motif 3 has the typical Lys or Arg residues while motif 4 has the acidic residues (Asp and Glu) that bind magnesium cofactor. The cap domain of PMM2 is smaller, functioning as the regulator for the access of the substrate into the active site of the core domain and at the same time contains the primary and secondary substrate specificity loops that recognize only specific substrate. | PMM2 is a 246 amino acid long protein, with 2 identical subunits working as independent domains, hence it’s also known as a homodimeric protein. In addition, it’s classified as the member of HAD (haloacid dehydrolase) superfamily due to the fact that it had 4 different types of motifs, each of which is highly conserved across the vertebrates’ lineages during evolutions. Similar to other members in HAD superfamily, the two domains are separately recognized as core and cap domain. The core domain (residues 1 – 90, and 198-262)of PMM2 displays the characteristic 4 motifs of HAD superfamily that contribute to the catalytic ability of the active sites in the protein. Motif 1 has Asp as nucleophile which serves as the mediator for the phosphoryl group transfer, the second Asp, on the other hand, acts as in the general acid-base reaction. While motif 1 provides the nucleophilic and general acid-base reactions, motif 2 in the protein which usually contains Thr or Ser helps in positioning or binding on the substrates’ phosphoryl group. In addition, motif 3 has the typical Lys or Arg residues while motif 4 has the acidic residues (Asp and Glu) that bind magnesium cofactor. The cap domain of PMM2 is smaller, functioning as the regulator for the access of the substrate into the active site of the core domain and at the same time contains the primary and secondary substrate specificity loops that recognize only specific substrate. | ||
Revision as of 03:35, 19 April 2011
Contents |
Phosphomannose mutase 2
Background
How does PMM2 work?
Structure
|
PMM2 is a 246 amino acid long protein, with 2 identical subunits working as independent domains, hence it’s also known as a homodimeric protein. In addition, it’s classified as the member of HAD (haloacid dehydrolase) superfamily due to the fact that it had 4 different types of motifs, each of which is highly conserved across the vertebrates’ lineages during evolutions. Similar to other members in HAD superfamily, the two domains are separately recognized as core and cap domain. The core domain (residues 1 – 90, and 198-262)of PMM2 displays the characteristic 4 motifs of HAD superfamily that contribute to the catalytic ability of the active sites in the protein. Motif 1 has Asp as nucleophile which serves as the mediator for the phosphoryl group transfer, the second Asp, on the other hand, acts as in the general acid-base reaction. While motif 1 provides the nucleophilic and general acid-base reactions, motif 2 in the protein which usually contains Thr or Ser helps in positioning or binding on the substrates’ phosphoryl group. In addition, motif 3 has the typical Lys or Arg residues while motif 4 has the acidic residues (Asp and Glu) that bind magnesium cofactor. The cap domain of PMM2 is smaller, functioning as the regulator for the access of the substrate into the active site of the core domain and at the same time contains the primary and secondary substrate specificity loops that recognize only specific substrate.
