This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Tol
From Proteopedia
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
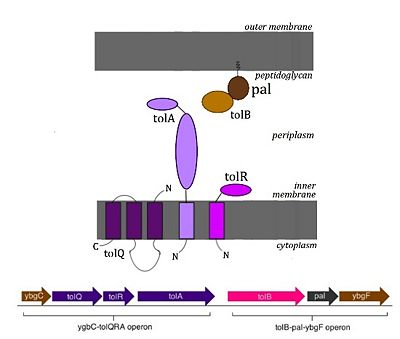
The Tol system, also known as Tol-Pal, is a multi-protein complex found in the cell envelope of many gram-negative bacteria. It contains 7 proteins ([[TolQ]], [[TolR]], [[TolA]], [[TolB]], [[Pal]], [[YbgF]], [[YbgC]]), whose respective genes are organized into two operons as seen in the diagram. | The Tol system, also known as Tol-Pal, is a multi-protein complex found in the cell envelope of many gram-negative bacteria. It contains 7 proteins ([[TolQ]], [[TolR]], [[TolA]], [[TolB]], [[Pal]], [[YbgF]], [[YbgC]]), whose respective genes are organized into two operons as seen in the diagram. | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==Function== | ||
| - | As of yet, the cellular role of the Tol protein is unclear. However, the system components are thought to be involved in the maintenance of the outer membrane as mutations of Tol proteins result in cells which leak the contents of the periplasm, as well as a hypersensitivity to some detergents, antibiotics and other agents.<ref>PMID: 8955385</ref>. It is also thought to play a role in anchoring the outer membrane to the peptidoglycan layer through the interactions that occur between TolB, Pal, Lpp and OmpA<ref name='Bouveret'>PMID 7744736</ref>, as well as the regulation of porin activity due to the interactions seen between TolB and TolA<ref>PMID: 9393690</ref>. | ||
===Interaction of Tol proteins=== | ===Interaction of Tol proteins=== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 15: | ||
* TolA also interacts with both YbgF and TolB | * TolA also interacts with both YbgF and TolB | ||
* TolB has the ability to dimerize | * TolB has the ability to dimerize | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Function== | ||
| + | As of yet, the cellular role of the Tol protein is unclear. However, the system components are thought to be involved in the maintenance of the outer membrane as mutations of Tol proteins result in cells which leak the contents of the periplasm, as well as a hypersensitivity to some detergents, antibiotics and other agents.<ref>PMID: 8955385</ref>. It is also thought to play a role in anchoring the outer membrane to the peptidoglycan layer through the interactions that occur between TolB, Pal, Lpp and OmpA<ref name='Bouveret'>PMID 7744736</ref>, as well as the regulation of porin activity due to the interactions seen between TolB and TolA<ref>PMID: 9393690</ref>. | ||
===Interaction of Tol with Colicins=== | ===Interaction of Tol with Colicins=== | ||
Revision as of 08:21, 23 April 2011
Contents |
Structure
The Tol system, also known as Tol-Pal, is a multi-protein complex found in the cell envelope of many gram-negative bacteria. It contains 7 proteins (TolQ, TolR, TolA, TolB, Pal, YbgF, YbgC), whose respective genes are organized into two operons as seen in the diagram.
Interaction of Tol proteins
It was first suggested in 1994 that the Tol proteins interact to form a multiprotein complex of precise stoichiometry by Guihard et al, who showed that the level of Tol proteins at certain sites in the cell increases at a similar ratio with respect to one another when purified Colicin A is added to the whole cell.[4]
Cross-linking experiments show that[5]:
- the TolQ transmembrane domain interacts with the first TolQ transmembrane domain
- the C-terminal and central domains of TolR are involved in its dimerization and this dimer interacts with the third transmembrane domain of TolQ
- the C-terminal domain of TolR is also involved in the interaction with TolA
More recent experiments[6] show that these interactions also occur:
- TolA also interacts with both YbgF and TolB
- TolB has the ability to dimerize
Function
As of yet, the cellular role of the Tol protein is unclear. However, the system components are thought to be involved in the maintenance of the outer membrane as mutations of Tol proteins result in cells which leak the contents of the periplasm, as well as a hypersensitivity to some detergents, antibiotics and other agents.[7]. It is also thought to play a role in anchoring the outer membrane to the peptidoglycan layer through the interactions that occur between TolB, Pal, Lpp and OmpA[8], as well as the regulation of porin activity due to the interactions seen between TolB and TolA[9].
Interaction of Tol with Colicins
|
The Tol-Pal system is used by group A colicins in order to translocate across the outer membrane, targeting mainly the inner membrane component TolA as well as TolQ and TolR. The colicins set up a translocon, constituting of the outer membrane receptor, translocator proteins and one or more periplasmic translocator proteins. The colicins recruit the Tol proteins using a Tol binding antigen, or epitope, which is embedded in the IUTD (Intrinsically Unstructured Translocation domain) found on the N-terminal (T-) domain of the colicin[10].
A yeast two-hybrid screen was carried out in order to determine the interactions between colicins and the Tol-Pal system during the import of colicin.[6] The screen showed that TolB dimerizes, and its amino terminal domain (D1) interacts with the periplasmic, C-terminal domain of TolA (TolAIII), whilst the central domain of TolA (TolAII) interacts with YbgF. It is the interaction between TolAIII and D1 that forms a "trans-envelope complex" which brings the inner and outer membranes closer together allowing for the uptake of colicin A. The N-terminal of the group A colicins then interact with TolA and also sometimes TolB during translocation into the inner membrane.
The structure shows the interaction between TolB and the of Colicin E9.
Regulation
It has been shown that the regulation of Tol genes is linked to the cell envelope stability.[11] In studies with E. coli, the tol-pal genes have been induced by RcsC in response to cell envelope stress.[12] RcsC is a transmembrane sensor kinase, and along with the cytoplasmic response regulator RcsB, makes up the RcsBC regulatory system.[13] RcsBC is involved in the regulation of cps genes which code for the biosynthsis machinery of a major component for the capsula, cholanic acid.
References
- ↑ Witty M, Sanz C, Shah A, Grossmann JG, Mizuguchi K, Perham RN, Luisi B. Structure of the periplasmic domain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa TolA: evidence for an evolutionary relationship with the TonB transporter protein. EMBO J. 2002 Aug 15;21(16):4207-18. PMID:12169623
- ↑ http://ecoliwiki.net/colipedia/index.php/tolA:Expression
- ↑ http://ecoliwiki.net/colipedia/index.php/tolB:Expression
- ↑ Guihard G, Boulanger P, Benedetti H, Lloubes R, Besnard M, Letellier L. Colicin A and the Tol proteins involved in its translocation are preferentially located in the contact sites between the inner and outer membranes of Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):5874-80. PMID:8119930
- ↑ Journet L, Rigal A, Lazdunski C, Benedetti H. Role of TolR N-terminal, central, and C-terminal domains in dimerization and interaction with TolA and tolQ. J Bacteriol. 1999 Aug;181(15):4476-84. PMID:10419942
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Walburger A, Lazdunski C, Corda Y. The Tol/Pal system function requires an interaction between the C-terminal domain of TolA and the N-terminal domain of TolB. Mol Microbiol. 2002 May;44(3):695-708. PMID:11994151
- ↑ Dennis JJ, Lafontaine ER, Sokol PA. Identification and characterization of the tolQRA genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1996 Dec;178(24):7059-68. PMID:8955385
- ↑ Bouveret E, Derouiche R, Rigal A, Lloubes R, Lazdunski C, Benedetti H. Peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein-TolB interaction. A possible key to explaining the formation of contact sites between the inner and outer membranes of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 12;270(19):11071-7. PMID:7744736
- ↑ Rigal A, Bouveret E, Lloubes R, Lazdunski C, Benedetti H. The TolB protein interacts with the porins of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1997 Dec;179(23):7274-9. PMID:9393690
- ↑ Kleanthous C. Swimming against the tide: progress and challenges in our understanding of colicin translocation. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010 Dec;8(12):843-8. Epub 2010 Nov 9. PMID:21060316 doi:10.1038/nrmicro2454
- ↑ Cascales E, Buchanan SK, Duche D, Kleanthous C, Lloubes R, Postle K, Riley M, Slatin S, Cavard D. Colicin biology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007 Mar;71(1):158-229. PMID:17347522 doi:10.1128/MMBR.00036-06
- ↑ Clavel T, Lazzaroni JC, Vianney A, Portalier R. Expression of the tolQRA genes of Escherichia coli K-12 is controlled by the RcsC sensor protein involved in capsule synthesis. Mol Microbiol. 1996 Jan;19(1):19-25. PMID:8821933
- ↑ Majdalani N, Heck M, Stout V, Gottesman S. Role of RcsF in signaling to the Rcs phosphorelay pathway in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 2005 Oct;187(19):6770-8. PMID:16166540 doi:10.1128/JB.187.19.6770-6778.2005