Ton
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
The Ton proteins are involved in the uptake of vitamin B12 and chelated-iron into the cell<ref>PMID: 17347522</ref>, and the system as a whole is known to be an energy-transducing system. Each of the three proteins involved have their separate role<ref name='Held'>PMID: 12193634</ref>. For more information, see the respective pages for TonB, ExbB and ExbD. | The Ton proteins are involved in the uptake of vitamin B12 and chelated-iron into the cell<ref>PMID: 17347522</ref>, and the system as a whole is known to be an energy-transducing system. Each of the three proteins involved have their separate role<ref name='Held'>PMID: 12193634</ref>. For more information, see the respective pages for TonB, ExbB and ExbD. | ||
| - | The Ton system can be exploited by group B Colicins {see [[Colicin]] for more details) which include: | + | The Ton system can be exploited by group B Colicins {see [[Colicin]] for more details) which include<ref name="Cascales">PMID: 17347522</ref><ref>PMID: 124727</ref>: |
*[[Colicin 5]] | *[[Colicin 5]] | ||
*[[Colicin 6]] | *[[Colicin 6]] | ||
Revision as of 17:57, 25 April 2011
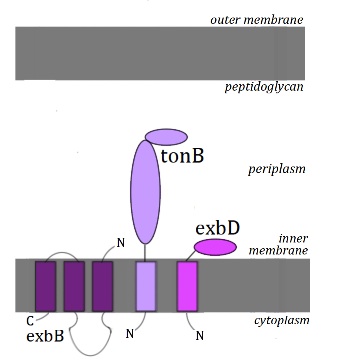
The Ton System[1]
Contents |
Structure
The Ton system comprises of the triumvirate TonB/ExbB/ExbD inner membrane complex.
Function
The Ton proteins are involved in the uptake of vitamin B12 and chelated-iron into the cell[2], and the system as a whole is known to be an energy-transducing system. Each of the three proteins involved have their separate role[3]. For more information, see the respective pages for TonB, ExbB and ExbD.
The Ton system can be exploited by group B Colicins {see Colicin for more details) which include[4][5]:
- Colicin 5
- Colicin 6
- Colicin 7
- Colicin 8
- Colicin 9
- Colicin 10
- Colicin Ia
- Colicin Ib
- Colicin B
- Colicin D
- Colicin M
- Colicin V
- Colicin Js
- Colicin Y
Interaction of Ton proteins
Like in the Tol complex, the Ton system proteins interact with each other[6]:
- the transmembrane domain of TonB interacts with both ExbB and ExbD, which contribute to the stability of the protein and support the TonB-dependent active transport across the outer membrane.
- ExbB and ExbD interact with each other, which has been suggested to play a part in the mechanism of energy transduction
References
- ↑ Witty M, Sanz C, Shah A, Grossmann JG, Mizuguchi K, Perham RN, Luisi B. Structure of the periplasmic domain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa TolA: evidence for an evolutionary relationship with the TonB transporter protein. EMBO J. 2002 Aug 15;21(16):4207-18. PMID:12169623
- ↑ Cascales E, Buchanan SK, Duche D, Kleanthous C, Lloubes R, Postle K, Riley M, Slatin S, Cavard D. Colicin biology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007 Mar;71(1):158-229. PMID:17347522 doi:10.1128/MMBR.00036-06
- ↑ Held KG, Postle K. ExbB and ExbD do not function independently in TonB-dependent energy transduction. J Bacteriol. 2002 Sep;184(18):5170-3. PMID:12193634
- ↑ Cascales E, Buchanan SK, Duche D, Kleanthous C, Lloubes R, Postle K, Riley M, Slatin S, Cavard D. Colicin biology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007 Mar;71(1):158-229. PMID:17347522 doi:10.1128/MMBR.00036-06
- ↑ Davies JK, Reeves P. Genetics of resistance to colicins in Escherichia coli K-12: cross-resistance among colicins of group B. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):96-101. PMID:124727
- ↑ Higgs PI, Myers PS, Postle K. Interactions in the TonB-dependent energy transduction complex: ExbB and ExbD form homomultimers. J Bacteriol. 1998 Nov;180(22):6031-8. PMID:9811664
