Sandbox20
From Proteopedia
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
Tus binds to a conserved cytosine residue which is not base paired. The interactions between residues of the Tus protein and this unpaired cytosine nucleotide are <scene name='Sandbox20/Tus/9'>shown by clicking here</scene>. | Tus binds to a conserved cytosine residue which is not base paired. The interactions between residues of the Tus protein and this unpaired cytosine nucleotide are <scene name='Sandbox20/Tus/9'>shown by clicking here</scene>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | <Structure load='2EWJ' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='The DNA-binding site of Tus' scene='andbox20/Tus/9' /> | ||
Revision as of 01:15, 28 April 2011
Contents |
Introduction
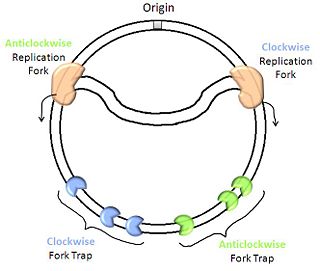
Replication Termination in E. coli and B. subtilis
Replication forks proceed from the origin of the circular chromosome in opposite directions, creating a characteristic theta structure . Although the use of two active polymerase complexes is clearly faster than one, this mechanism generates difficulty when it comes to terminating replication. Among other factors, the presence of DNA-associated proteins causes the two replication complexes to proceed at different rates, and they therefore do not necessarily meet directly opposite the origin. However, the position of termination is not random, and is defined by the presence of termination sites which associate protein factors capable of halting the advance of the replication fork from only one direction. From their positions within the chromosome and their directionality, you can see that this occurs only once the complex has traversed more than half of the total DNA.
The Proteins
RTP
|
This is the area for text about RTP
Tus
|
This is the area for text about Tus
Tus binds to a conserved cytosine residue which is not base paired. The interactions between residues of the Tus protein and this unpaired cytosine nucleotide are .