DOPA decarboxylase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
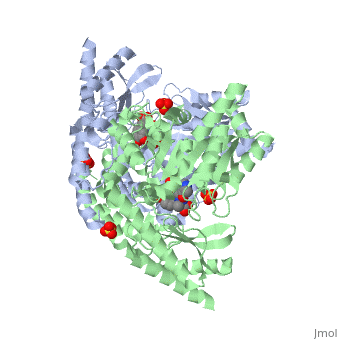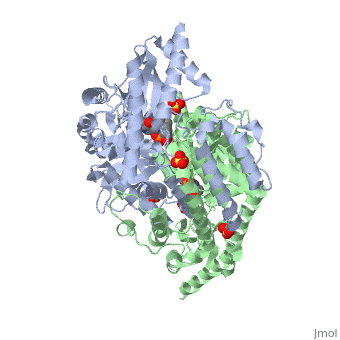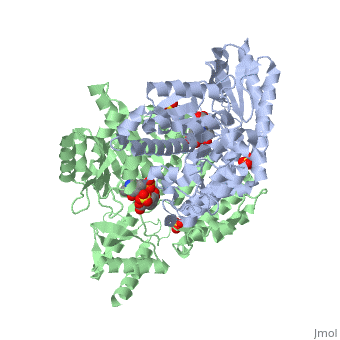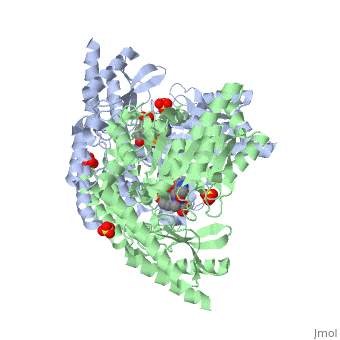
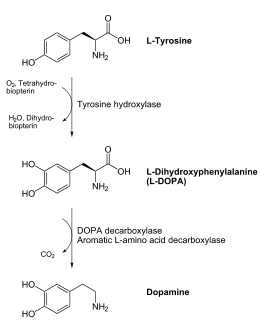
| - | {{STRUCTURE_1js3 | PDB=1js3 | SCENE= }}'''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DOPA_decarboxylase]''' (DDC, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, tryptophan decarboxylase, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, AAAD) is an approximately 52 kDa protein that belongs to the aspartate aminotransferase family (fold type 1) of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyridoxal_phosphate]-dependent enzymes. The catalytically active form of the enzyme exists as a homodimer, typical of this class of enzymes. | + | {{STRUCTURE_1js3 | PDB=1js3 | SCENE= }}'''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DOPA_decarboxylase ''DOPA decarboxylase'']''' (DDC, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, tryptophan decarboxylase, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, AAAD) is an approximately 52 kDa protein that belongs to the aspartate aminotransferase family (fold type 1) of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyridoxal_phosphate ''PLP'']-dependent enzymes. The catalytically active form of the enzyme exists as a homodimer, typical of this class of enzymes. DOPA decarboxylase is responsible for the synthesis of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dopamine ''dopamine''] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serotoninn ''serotonin''] from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/L-dopa ''L-DOPA''] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/L-5-Hydroxytryptophan ''L-5;hydroxytryptophan''], respectively. Due to its role in neurotransmitter synthesis, DOPA decarboxylase has been implicated in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parkinson%27s_disease ''Parkinson's disease''], a disease thought to be the result of the degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. Currently, treatment for the disease is aimed at DOPA decarboxylase inhibition, which would allow greater amounts of exogenously administered L-DOPA to reach the brain. |
[[Image:dopa.png]] | [[Image:dopa.png]] | ||
Revision as of 23:14, 3 May 2011
Introduction
| |||||||||
| 1js3, resolution 2.25Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , | ||||||||
| Activity: | Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase, with EC number 4.1.1.28 | ||||||||
| Related: | 1js6 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
DOPA decarboxylase (DDC, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, tryptophan decarboxylase, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, AAAD) is an approximately 52 kDa protein that belongs to the aspartate aminotransferase family (fold type 1) of PLP-dependent enzymes. The catalytically active form of the enzyme exists as a homodimer, typical of this class of enzymes. DOPA decarboxylase is responsible for the synthesis of dopamine and serotonin from L-DOPA and L-5;hydroxytryptophan, respectively. Due to its role in neurotransmitter synthesis, DOPA decarboxylase has been implicated in Parkinson's disease, a disease thought to be the result of the degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. Currently, treatment for the disease is aimed at DOPA decarboxylase inhibition, which would allow greater amounts of exogenously administered L-DOPA to reach the brain.
Structure
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Brittany Todd, Michal Harel, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky, Brian Hernandez