DOPA decarboxylase
From Proteopedia
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===Structure=== | ===Structure=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 23:34, 3 May 2011
Introduction
| |||||||||
| 1js3, resolution 2.25Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , | ||||||||
| Activity: | Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase, with EC number 4.1.1.28 | ||||||||
| Related: | 1js6 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
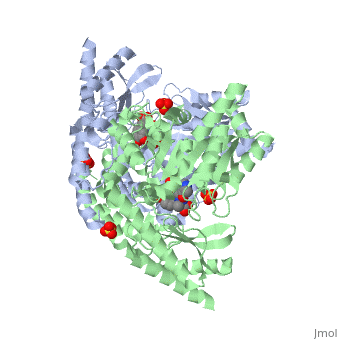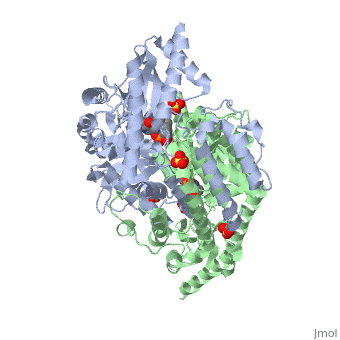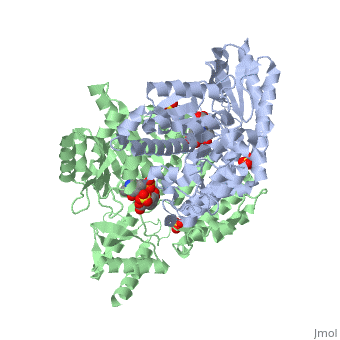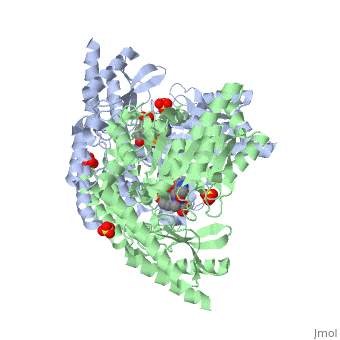
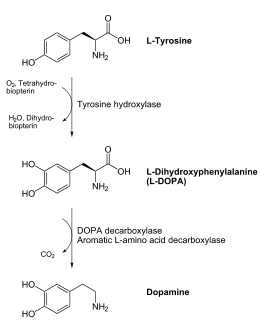
DOPA decarboxylase (DDC, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, tryptophan decarboxylase, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, AAAD) is an approximately 52 kDa protein that belongs to the aspartate aminotransferase family (fold type 1) of PLP-dependent enzymes. The catalytically active form of the enzyme exists as a homodimer, typical of this class of enzymes.[1] The homodimeric form of the enzyme purified from sus scrofa is shown in complex with the inhibitor carbidopa to the right. DOPA decarboxylase is responsible for the synthesis of dopamine and serotonin from L-DOPA and L-5;hydroxytryptophan, respectively. Due to its role in neurotransmitter synthesis, DOPA decarboxylase has been implicated in Parkinson's disease, a disease thought to be the result of the degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. Currently, treatment for the disease is aimed at DOPA decarboxylase inhibition, which would allow greater amounts of exogenously administered L-DOPA to reach the brain.
Structure
References
- ↑ Schneider G, Kack H, Lindqvist Y. The manifold of vitamin B6 dependent enzymes. Structure. 2000 Jan 15;8(1):R1-6. PMID:10673430
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Brittany Todd, Michal Harel, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky, Brian Hernandez