We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Plectin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
--> | --> | ||
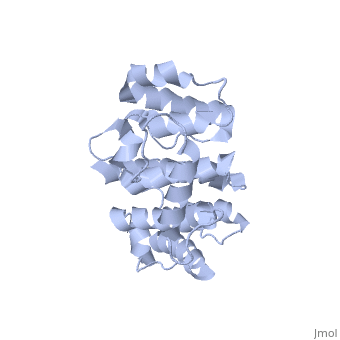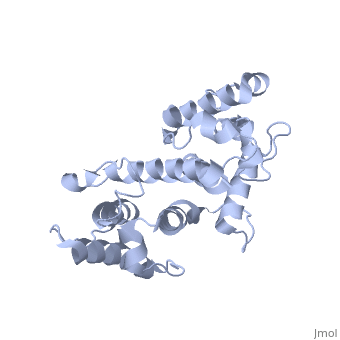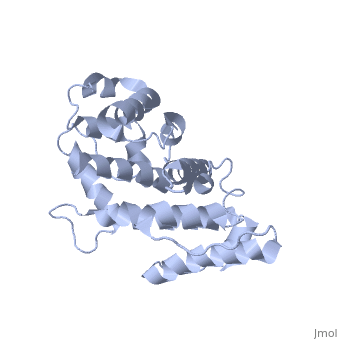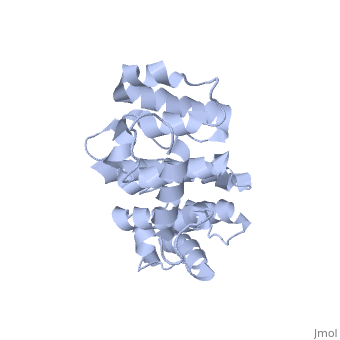
| - | Plectin, a universal and functionally versatile cytolinker protein, can be divided in three main sections; a central coiled-coil rod domain, N and C-terminal globular region and exhibits a dumbbell like structure | + | Plectin, a universal and functionally versatile cytolinker protein, can be divided in three main sections; a central coiled-coil rod domain, N and C-terminal globular region and exhibits a dumbbell like structure <ref>PMID:3430617</ref>. C-terminal region is composed of 6 homologous repeating domains, and this region has a role in binding to intermediate filaments such as vimentin and cytokeratin (2). N-terminal globular region contains actin binding domain (ABD) comprising two calponin homology (CH) domains and N-terminal arm, which varies among isoforms (3). |
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 13:18, 23 June 2011
|
Plectin, a universal and functionally versatile cytolinker protein, can be divided in three main sections; a central coiled-coil rod domain, N and C-terminal globular region and exhibits a dumbbell like structure [1]. C-terminal region is composed of 6 homologous repeating domains, and this region has a role in binding to intermediate filaments such as vimentin and cytokeratin (2). N-terminal globular region contains actin binding domain (ABD) comprising two calponin homology (CH) domains and N-terminal arm, which varies among isoforms (3).
- ↑ Foisner R, Wiche G. Structure and hydrodynamic properties of plectin molecules. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):515-31. PMID:3430617