We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Group:MUZIC:XIN
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
[[Image:Xin.jpg]] | [[Image:Xin.jpg]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | == Function == | ||
| - | <ref>PMID:19773341</ref> | ||
== Interactions with other proteins/Function Function == | == Interactions with other proteins/Function Function == | ||
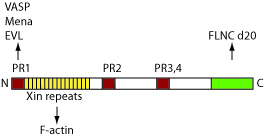
| - | Xin and Mena/VASP colocalize with filamin c in [intercalated discs][http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intercalated_disc](ICD, structure at the end of the myocytes that transduce force from the myofibrils via the cell membranes to the extracelluar matrix and neighboring cells) in the adult heart. | + | Xin and Mena/VASP colocalize with filamin c in [intercalated discs][http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intercalated_disc](ICD, structure at the end of the myocytes that transduce force from the myofibrils via the cell membranes to the extracelluar matrix and neighboring cells) in the adult heart <ref>PMID:19773341</ref>. |
Xin directly binds the EVH1 domain proteins Mena and VASP <ref name="pmid16631741">. | Xin directly binds the EVH1 domain proteins Mena and VASP <ref name="pmid16631741">. | ||
Revision as of 23:56, 11 July 2011
Xin actin-binding repeat-containing protein 1 (Alternative name: Cardiomyopathy-associated protein 1) is coded by the gene (Synonyms:CMYA1, XIN) and has an actin-binding domain (ABD). It crosslinks actin filaments and participates in anchoring of membrane proteins. Intraexogic splicing leads to a least three different isoforms.
Sequence Annotation
Interactions with other proteins/Function Function
Xin and Mena/VASP colocalize with filamin c in [intercalated discs][1](ICD, structure at the end of the myocytes that transduce force from the myofibrils via the cell membranes to the extracelluar matrix and neighboring cells) in the adult heart [1].
Xin directly binds the EVH1 domain proteins Mena and VASP [2]