Matrix metalloproteinase
From Proteopedia
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
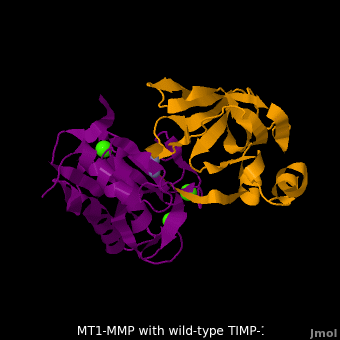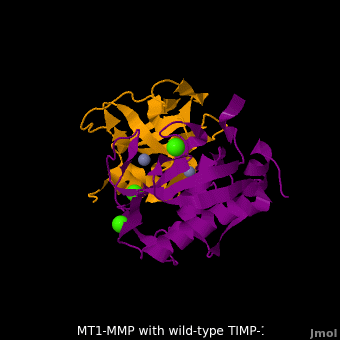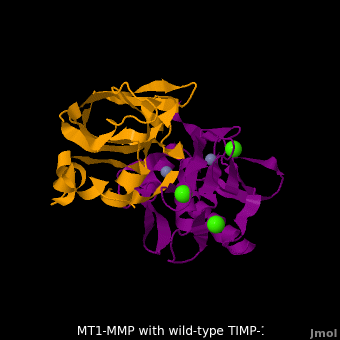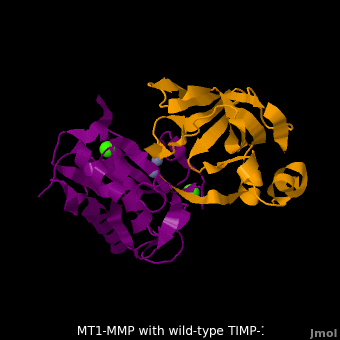
<scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/9'>Membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP)</scene> <font color='darkmagenta'><b>(darkmagenta)</b></font> also forms complex with <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/11'>wild-type TIMP-1</scene> ([[2j0t]], <font color='orange'><b>colored orange</b></font>), producing <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/12'>similar hydrogen bond network in the WT TIMP-1 binding interface</scene> as well as <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/13'>in the case with MT3-MMP</scene>. This network of hydrogen bonds stabilizes the CD and EF loops that compose the binding interface. Importantly, the <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/14'>hydrogen bond between Cys1 and Ser68 may position the amino and carboxyl groups of Cys1 to effectively coordinate the Zn2+ ion</scene>. However, this MT1-MMP-WT-TIMP-1 complex is not tight-binding. MT1-MMP is unique since even though it exhibits high structural homology to all MMPs, it is not inhibited by TIMP-1, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv3/1'>but is inhibited by the structural homologous TIMP-2</scene> ([[1bqq]]). <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/15'>The single point mutation T98L</scene> (mutant TIMP-1 is colored in <span style="color:yellow;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">yellow</span> with <font color='red'><b>T98L shown in red</b></font>) transformed TIMP-1 into a high affinity inhibitor of MT1-MMP ([[3ma2]]). WT-TIMP-1, WT-TIMP-2, and TIMP-1 T98L mutant have kinetic dissociation binding constant (K<sub>D</sub>) 1.53 x 10<sup>-6</sup>, 5.61 x 10<sup>-8</sup>, and 8.70 x 10<sup>-8</sup>, respectively. So, K<sub>D</sub> of WT-TIMP-2 is 2 orders of magnitude smaller than that of WT-TIMP-1, indicating the weak affinity between MT1-MMP and WT-TIMP-1. The TIMP-1 T98L mutant regained high-affinity binding to MT1-MMP, resulting in a 2 order of magnitude decrease in K<sub>D</sub>, similar to the case for WT-TIMP-2, the ''in vivo'' inhibitor of MT1-MMP. The overall structures of the complexes of <font color='darkmagenta'><b>MT1-MMP</b></font>-<font color='orange'><b>WT-TIMP-1</b></font> and <font color='violet'><b>MT1-MMP</b></font>-<span style="color:yellow;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">mutant-T98L-TIMP-1</span> are <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/17'>relatively similar</scene>. Even the structure of <font color='magenta'><b>MT3-MMP</b></font>-<font color='orange'><b>WT-TIMP-1</b></font> is <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/18'>similar to those of MT1-MMP-TIMP-1s</scene> (with <font color='orange'><b>wild-type</b></font> and <span style="color:yellow;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">TIMP-1 T98L mutant</span>). <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv4/1'>Leu98 is pointing toward MT1-MMP residues Pro259 and Phe260, establishing a strong hydrophobic core</scene>, which is situated near the MT1-MMP <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv4/3'>catalytic Zn2+ ion surrounded by His239, His243, and His249</scene>. So, this T98L replacement may stabilize the entire area by establishing a strong hydrophobic core upon binding to the enzyme. However, it seems unlikely that these additional bonds could | <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/9'>Membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP)</scene> <font color='darkmagenta'><b>(darkmagenta)</b></font> also forms complex with <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/11'>wild-type TIMP-1</scene> ([[2j0t]], <font color='orange'><b>colored orange</b></font>), producing <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/12'>similar hydrogen bond network in the WT TIMP-1 binding interface</scene> as well as <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/13'>in the case with MT3-MMP</scene>. This network of hydrogen bonds stabilizes the CD and EF loops that compose the binding interface. Importantly, the <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/14'>hydrogen bond between Cys1 and Ser68 may position the amino and carboxyl groups of Cys1 to effectively coordinate the Zn2+ ion</scene>. However, this MT1-MMP-WT-TIMP-1 complex is not tight-binding. MT1-MMP is unique since even though it exhibits high structural homology to all MMPs, it is not inhibited by TIMP-1, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv3/1'>but is inhibited by the structural homologous TIMP-2</scene> ([[1bqq]]). <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/15'>The single point mutation T98L</scene> (mutant TIMP-1 is colored in <span style="color:yellow;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">yellow</span> with <font color='red'><b>T98L shown in red</b></font>) transformed TIMP-1 into a high affinity inhibitor of MT1-MMP ([[3ma2]]). WT-TIMP-1, WT-TIMP-2, and TIMP-1 T98L mutant have kinetic dissociation binding constant (K<sub>D</sub>) 1.53 x 10<sup>-6</sup>, 5.61 x 10<sup>-8</sup>, and 8.70 x 10<sup>-8</sup>, respectively. So, K<sub>D</sub> of WT-TIMP-2 is 2 orders of magnitude smaller than that of WT-TIMP-1, indicating the weak affinity between MT1-MMP and WT-TIMP-1. The TIMP-1 T98L mutant regained high-affinity binding to MT1-MMP, resulting in a 2 order of magnitude decrease in K<sub>D</sub>, similar to the case for WT-TIMP-2, the ''in vivo'' inhibitor of MT1-MMP. The overall structures of the complexes of <font color='darkmagenta'><b>MT1-MMP</b></font>-<font color='orange'><b>WT-TIMP-1</b></font> and <font color='violet'><b>MT1-MMP</b></font>-<span style="color:yellow;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">mutant-T98L-TIMP-1</span> are <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/17'>relatively similar</scene>. Even the structure of <font color='magenta'><b>MT3-MMP</b></font>-<font color='orange'><b>WT-TIMP-1</b></font> is <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/18'>similar to those of MT1-MMP-TIMP-1s</scene> (with <font color='orange'><b>wild-type</b></font> and <span style="color:yellow;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">TIMP-1 T98L mutant</span>). <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv4/1'>Leu98 is pointing toward MT1-MMP residues Pro259 and Phe260, establishing a strong hydrophobic core</scene>, which is situated near the MT1-MMP <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv4/3'>catalytic Zn2+ ion surrounded by His239, His243, and His249</scene>. So, this T98L replacement may stabilize the entire area by establishing a strong hydrophobic core upon binding to the enzyme. However, it seems unlikely that these additional bonds could | ||
account for the entire binding effect between MT1-MMP and TIMP-1. Statistical analysis of the <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/15'>key hydrogen bond</scene> stabilities in the TIMP-1 T98L mutant reveals that the hydrogen bonds network in mutant form is significantly more stable than that in WT-TIMP-1. Mutations that enhance hydrogen | account for the entire binding effect between MT1-MMP and TIMP-1. Statistical analysis of the <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/15'>key hydrogen bond</scene> stabilities in the TIMP-1 T98L mutant reveals that the hydrogen bonds network in mutant form is significantly more stable than that in WT-TIMP-1. Mutations that enhance hydrogen | ||
| - | bond stability contribute to the stability of the bound-like, less flexible, conformation of TIMP-1, which eventually results in increasing binding affinity for MT1-MMP. Thus, mutation affected the instrinsic dynamics of the inhibitor rather than its structure, thereby facilitating the interaction. | + | bond stability contribute to the stability of the bound-like, less flexible, conformation of TIMP-1, which eventually results in increasing binding affinity for MT1-MMP. Thus, mutation affected the instrinsic dynamics of the inhibitor rather than its structure, thereby facilitating the interaction <ref name="Grossman">PMID:20545310</ref>. |
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
[[2k72]] – hMMP residues 254-290 - NMR<BR /> | [[2k72]] – hMMP residues 254-290 - NMR<BR /> | ||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Revision as of 09:42, 14 July 2011
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) are Zinc-dependent endopeptidases. MMP degrades extracellular matrix proteins. MMPs are produced by 28 different genes and are classified according to their protein substrates. They are inhibited by proteases called tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase (TIMP). The pro-MMP contains a pro-peptide which must be removed to render the MMP active. The images at the left and at the right correspond to one representative MMP, i.e. the crystal structure of human pro MMP1 (1su3).
MT1-MMP-TIMP-1 complex
| |||||||||||
3D structures of matrix metalloproteinase
MMP1 interstitial collagenase
1su3 – pro-hMMP – human
MMP2 gelatinase-A
1qib - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant)
1rtg - hMMP hemopexin-like domain
1ks0 – hMMP first fibronectin type II domain – NMR
1cxw - hMMP second fibronectin type II domain – NMR
1j7m - hMMP third fibronectin type II domain (mutant) – NMR
1eak – pro-hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + peptide inhibitor
1hov, 1eub - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor– NMR
1gxd – pro-hMMP (mutant) + TIMP-2
MMP3 stromelysin 1
1qia, 1qic, 1cqr, 1slm - hMMP catalytic domain
3ohl, 3oho, 1g49, 1ciz, 1b8y, 1caq, 1usn, 2usn, 1ums, 1umt – hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
1uea - hMMP catalytic domain + TIMP-1
1oo9 - hMMP catalytic domain + TIMP-1 N terminal
2jt5, 2jt6, 2jnp, 3usn, 1sln - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor – NMR
MMP7 matrilysin
2y6c, 2y6d – hMMP residues 95-298 + inhibitor
MMP8 neutrophil collagenase
3dng, 3dpe, 3dpf, 1zp5, 1jh1, 1jj9, 1i76, 1a85, 1mmb – hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
1i73 - hMMP catalytic domain + peptide inhibitor
MMP9 gelatinase-B
1l6j - pro-hMMP
1gkc - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
2ovx, 2ovz, 2ow0, 2ow1, 2ow2, 1gkd - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + inhibitor
MMP10 stromelysin 2
1q3a - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant)
MMP11 stromelysin 3
1hv5 - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
MMP12 macrophage
3ba0, 2oxu - hMMP
2krj, 2k9c - hMMP catalytic domain – NMR
1jk3 - hMMP catalytic domain
2poj - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) - NMR
2jxy - hMMP hemopexin-like domain - NMR
3n2u, 3n2v, 2wo8, 2wo9, 2woa, 1utt, 1utz, 1ros – hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
3lk8, 3lik, 3lil, 3lir, 3ljg, 3nx7, 3lka, 3ehx, 3ehy, 3f15, 3f16, 3f17, 3f18, 3f19, 3f1a, 1y93, 1rmz, 1os2, 1os9 - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + inhibitor
2k2g, 2z2d - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor - NMR
2w0d, 1ycm, 1z3j - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + inhibitor - NMR
MMP13 collagenase 3
1cxv - MMP catalytic domain - mouse
2yig, 3ljz, 3kec, 3kej, 3kek, 3kry, 3i7g, 3i7i, 3elm, 2pjt, 2ozr, 1xuc, 1xud, 1xur, 1you – hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
MMP14 Membrane T1
3ma2 – hMMP residues 112-292 + TIMP-1 (mutant)
1buv, 1bqq - hMMP + TIMP-2
3c7x – hMMP hemopexin-like domain
MMP16 Membrane T3
1rm8 - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
MMP20 enamelysin
2jsd - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor - NMR
MMP23 CA-MMP
2k72 – hMMP residues 254-290 - NMR
References
- ↑ Grossman M, Tworowski D, Dym O, Lee MH, Levy Y, Murphy G, Sagi I. Intrinsic protein flexibility of endogenous protease inhibitor TIMP-1 controls its binding interface and effects its function. Biochemistry. 2010 Jun 14. PMID:20545310 doi:10.1021/bi902141x