Also known as T-Cap or Titin Cap protein.
It is a small protein of 19kDa, 167 amino acids. It is predominantly expressed in striated muscle. It is a structural protein of the muscle; it is associated to the Z-disc in the sarcomere. It acts as multifunctional protein linking titin and other proteins implicated in sarcomere structure and signalling pathways.
Gene regulation and expression
It is encoded by the Tcap gene, in mice (Mus musculus) and humans (Homo sapiens).
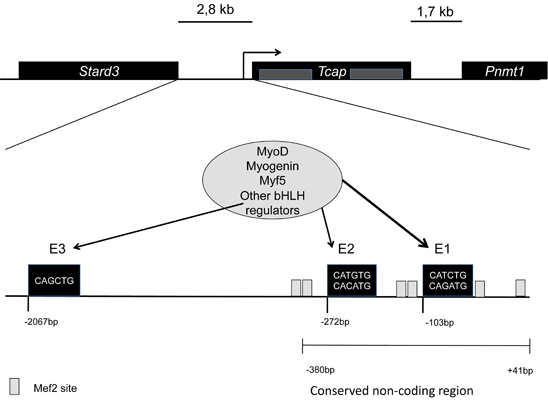
In mice it is located in chromosome 11, in humans in the long arm of chromosome 17. Tcap is encoded by two exons, and has non-conserved intragenic sequences. The gene is flanked by two other genes, namely Stard3 upstream separated by 2,8kb, and Pnmt1 downstream separated by 1,7kb. It has three conserved E-box elements at -103bp (E1), -272bp (E2), and -2067bp (E3).
For the full activation of the gene the regulation of E1 is highly important. MyoD plays an important role in this regulation all through development, while myogenin mainly during late differentiation into myoblasts. [1]
At the transcriptional level it is thought that there is only one isoform of Tcap, and it is one of the most abundant transcripts in skeletal muscle [2]. It does not have different levels of expression in different types of skeletal muscle; levels of expression of Tcap are lower in neonatal compared to adult striated muscle. The transcript is accumulated in a linear pattern similar to that of the myosin heavy chain [3]. In these same studies it was reported that denervation leads to decrease in the expression of Tcap, suggesting that locomotor activity is a potential regulator of its maintenance.
“Tcap” gene product, the protein Telethonin
Telethonin protein is found mostly in skeletal and cardiac muscle. It is one of the major components of the sarcomere, it is localized to the Z-disc. It was also reported a nuclear localization.[4] [5]
Studies on telethonin structure by Zou et al. [6] report that it is made up of five stranded antiparallel β-sheets extended by two wing-shaped β-hairpin motifs (A-B, C-D). These two motifs are related by an approximate two-fold symmetry, which generates an almost perfect palindromic arrangement.
The structure of telethonin was determined using X-ray crystallography [7],[8] . The shape and architecture of the complex of titin/telethonin was studied by small-angle- X-ray scattering (SAXS) and then compared to the crystallographic models. They also used in-vitro experiments to follow the formation of the complex in non-myogenic Cos1 cells, in order to understand if the assemblage is possible [9]
This symmetry of telethonin permits its interaction with titin. Both are assembled in an antiparallel (titin:telethonin). Titin N-terminal domains Z1 and Z2 (two Ig like repeats) interact with the C-terminal region of telethonin (residues 1-53). Telethonin mediates in the antiparallel assembly of the two Z1Z2domains.
In early differentiating myocytes titin C-terminal and telethonin co-localize and titin kinase is close to telethonin C-terminal, and it is phosphorylated. This phosphorylation is involved in the reorganization of the cytoskeleton during myofibrillogenesis. [10] This co-localization is not seen in adult myofibrils, titin kinase is reported to localize in the M-band [11]; It was also informed that telethonin interacts with other proteins including: Potassium channel β-subunit of the slow activating component of the delayed rectifier potassium current (IKs) channel (minK) [12], ankyrin1, and Z-disc proteins FATZ,/Myozenin-1/ Calsarcin-3 [13], and Ankrd2.[14]
Telethonin interacts with minK’s cytoplasmic domain. MinK binds specifically to the sixteen C-terminal residues of telethonin. This suggest a that minK, telethonin ant titin form a complex that links myofibrils to the sarcolemma. Phosphorilation of telethonin in Ser157 is a negative regulation for this interaction. This interaction occurs in cardiac myofibrils, it has been reported that minK is not expressed in skeletal muscle.[15],
Telethonin interacts with FATZ/Myozenin-1/Calsarcin-3 N-terminal between residues 78-125. It might be an association as mechanosensing and stretch-associated signalling machinery. [16]
The interaction between Ankrd2 and telethonin has been proposed as a sensor of muscle stress/stretch and a starting point for the transmission of the mechanical signal to the nucleus regulating gene expression. [17]
Telethonin is also involved in signalling processes that regulate muscle development. A feed back loop is formed with MRFs (MyoD, myogenin, Myf5) regulating Tcap gene expression; telethonin interacts with myostatin, inhibiting it. So it regulates MyoD through the Myostatin – Smad3 pathway. [18].
There is an interaction with MDM2 N-terminal. MDM2 is capable of redirecting telethonin to the nucleus. Telethonin is inhibited by MDM2 in a dose dependent manner. In cells MDM2 is involved in the regulation of proteasomal turnover of telethonin. [19]
Pathologies associated with telethonin
Different mutations in telethonin have been associated with several myopathies. Mutations can lead to limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2G (LGMD2G) [20], to hypertrophic cardiopathy., [21], and dilated cardiomyopathy.
Two mutations found in the Tcap gene cause a deletion of the telethonin C-terminal region, losing the site which can be phosphorylated, for example by titin kinase [22], leading to disruption of the sarcomeric structure; as was observed in a few brazilian families with LGMD2G.
Defects in the MLP-Tcap association are linked to human dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure (Knöll 2002). Mutations that affect ability of MLP to interact with telethonin result in the loss of telethonin binding, facilitating its mislocalization from the complex with titin, leading to defects in the Z-disc and progression of dilated cardiomyopathy. Knöll et al. conclude that genetic mutations causing a incorrect interaction of telethonin with MLP can lead to a development of human dilated cardiomyopathy through modifications in the conformation and function of titin.
It was reported that in 10 cases of neurogenic atrophy there was a decreased staining for telethonin in type II fibers, and in early stages of fiber atrophy, [23] indicating a selective downregulation of telethonin. These observations can be related to in vivo studies done in rats, in which after short term denervation (two days), Tcap transcript is reduced by about 50% in skeletal muscle. [24].
References
- ↑ Zhang S, Londhe P, Zhang M, Davie JK. Transcriptional analysis of the titin cap gene. Mol Genet Genomics. 2011 Mar;285(3):261-72. Epub 2011 Feb 9. PMID:21305318 doi:10.1007/s00438-011-0603-6
- ↑ Valle G, Faulkner G, De Antoni A, Pacchioni B, Pallavicini A, Pandolfo D, Tiso N, Toppo S, Trevisan S, Lanfranchi G. Telethonin, a novel sarcomeric protein of heart and skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1997 Sep 29;415(2):163-8. PMID:9350988
- ↑ Mason P, Bayol S, Loughna PT. The novel sarcomeric protein telethonin exhibits developmental and functional regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Apr 21;257(3):699-703. PMID:10208846 doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.0531
- ↑ Vainzof M, Moreira ES, Suzuki OT, Faulkner G, Valle G, Beggs AH, Carpen O, Ribeiro AF, Zanoteli E, Gurgel-Gianneti J, Tsanaclis AM, Silva HC, Passos-Bueno MR, Zatz M. Telethonin protein expression in neuromuscular disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Oct 9;1588(1):33-40. PMID:12379311
- ↑ Tian LF, Li HY, Jin BF, Pan X, Man JH, Zhang PJ, Li WH, Liang B, Liu H, Zhao J, Gong WL, Zhou T, Zhang XM. MDM2 interacts with and downregulates a sarcomeric protein, TCAP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Jun 23;345(1):355-61. Epub 2006 May 2. PMID:16678796 doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.04.108
- ↑ Zou P, Pinotsis N, Lange S, Song YH, Popov A, Mavridis I, Mayans OM, Gautel M, Wilmanns M. Palindromic assembly of the giant muscle protein titin in the sarcomeric Z-disk. Nature. 2006 Jan 12;439(7073):229-33. PMID:16407954 doi:10.1038/nature04343
- ↑ Zou P, Gautel M, Geerlof A, Wilmanns M, Koch MH, Svergun DI. Solution scattering suggests cross-linking function of telethonin in the complex with titin. J Biol Chem. 2003 Jan 24;278(4):2636-44. Epub 2002 Nov 20. PMID:12446666 doi:10.1074/jbc.M210217200
- ↑ Zou P, Pinotsis N, Lange S, Song YH, Popov A, Mavridis I, Mayans OM, Gautel M, Wilmanns M. Palindromic assembly of the giant muscle protein titin in the sarcomeric Z-disk. Nature. 2006 Jan 12;439(7073):229-33. PMID:16407954 doi:10.1038/nature04343
- ↑ Pinotsis N, Petoukhov M, Lange S, Svergun D, Zou P, Gautel M, Wilmanns M. Evidence for a dimeric assembly of two titin/telethonin complexes induced by the telethonin C-terminus. J Struct Biol. 2006 Aug;155(2):239-50. Epub 2006 Apr 27. PMID:16713295 doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2006.03.028
- ↑ Mayans O, van der Ven PF, Wilm M, Mues A, Young P, Furst DO, Wilmanns M, Gautel M. Structural basis for activation of the titin kinase domain during myofibrillogenesis. Nature. 1998 Oct 29;395(6705):863-9. PMID:9804419 doi:10.1038/27603
- ↑ Mayans O, van der Ven PF, Wilm M, Mues A, Young P, Furst DO, Wilmanns M, Gautel M. Structural basis for activation of the titin kinase domain during myofibrillogenesis. Nature. 1998 Oct 29;395(6705):863-9. PMID:9804419 doi:10.1038/27603
- ↑ Furukawa T, Ono Y, Tsuchiya H, Katayama Y, Bang ML, Labeit D, Labeit S, Inagaki N, Gregorio CC. Specific interaction of the potassium channel beta-subunit minK with the sarcomeric protein T-cap suggests a T-tubule-myofibril linking system. J Mol Biol. 2001 Nov 2;313(4):775-84. PMID:11697903 doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5053
- ↑ Frey N, Olson EN. Calsarcin-3, a novel skeletal muscle-specific member of the calsarcin family, interacts with multiple Z-disc proteins. J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 19;277(16):13998-4004. Epub 2002 Feb 12. PMID:11842093 doi:10.1074/jbc.M200712200
- ↑ Kojic S, Medeot E, Guccione E, Krmac H, Zara I, Martinelli V, Valle G, Faulkner G. The Ankrd2 protein, a link between the sarcomere and the nucleus in skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 2004 May 28;339(2):313-25. PMID:15136035 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.03.071
- ↑ Furukawa T, Ono Y, Tsuchiya H, Katayama Y, Bang ML, Labeit D, Labeit S, Inagaki N, Gregorio CC. Specific interaction of the potassium channel beta-subunit minK with the sarcomeric protein T-cap suggests a T-tubule-myofibril linking system. J Mol Biol. 2001 Nov 2;313(4):775-84. PMID:11697903 doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5053
- ↑ Frey N, Olson EN. Calsarcin-3, a novel skeletal muscle-specific member of the calsarcin family, interacts with multiple Z-disc proteins. J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 19;277(16):13998-4004. Epub 2002 Feb 12. PMID:11842093 doi:10.1074/jbc.M200712200
- ↑ Kojic S, Medeot E, Guccione E, Krmac H, Zara I, Martinelli V, Valle G, Faulkner G. The Ankrd2 protein, a link between the sarcomere and the nucleus in skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 2004 May 28;339(2):313-25. PMID:15136035 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.03.071
- ↑ Markert CD, Ning J, Staley JT, Heinzke L, Childers CK, Ferreira JA, Brown M, Stoker A, Okamura C, Childers MK. TCAP knockdown by RNA interference inhibits myoblast differentiation in cultured skeletal muscle cells. Neuromuscul Disord. 2008 May;18(5):413-22. Epub 2008 Apr 28. PMID:18440815 doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2008.03.010
- ↑ Tian LF, Li HY, Jin BF, Pan X, Man JH, Zhang PJ, Li WH, Liang B, Liu H, Zhao J, Gong WL, Zhou T, Zhang XM. MDM2 interacts with and downregulates a sarcomeric protein, TCAP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Jun 23;345(1):355-61. Epub 2006 May 2. PMID:16678796 doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.04.108
- ↑ Moreira ES, Wiltshire TJ, Faulkner G, Nilforoushan A, Vainzof M, Suzuki OT, Valle G, Reeves R, Zatz M, Passos-Bueno MR, Jenne DE. Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2G is caused by mutations in the gene encoding the sarcomeric protein telethonin. Nat Genet. 2000 Feb;24(2):163-6. PMID:10655062 doi:10.1038/72822
- ↑ Knoll R, Hoshijima M, Hoffman HM, Person V, Lorenzen-Schmidt I, Bang ML, Hayashi T, Shiga N, Yasukawa H, Schaper W, McKenna W, Yokoyama M, Schork NJ, Omens JH, McCulloch AD, Kimura A, Gregorio CC, Poller W, Schaper J, Schultheiss HP, Chien KR. The cardiac mechanical stretch sensor machinery involves a Z disc complex that is defective in a subset of human dilated cardiomyopathy. Cell. 2002 Dec 27;111(7):943-55. PMID:12507422
- ↑ Moreira ES, Wiltshire TJ, Faulkner G, Nilforoushan A, Vainzof M, Suzuki OT, Valle G, Reeves R, Zatz M, Passos-Bueno MR, Jenne DE. Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2G is caused by mutations in the gene encoding the sarcomeric protein telethonin. Nat Genet. 2000 Feb;24(2):163-6. PMID:10655062 doi:10.1038/72822
- ↑ Schroder R, Reimann J, Iakovenko A, Mues A, Bonnemann CG, Matten J, Gautel M. Early and selective disappearance of telethonin protein from the sarcomere in neurogenic atrophy. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2001;22(3):259-64. PMID:11763198
- ↑ Mason P, Bayol S, Loughna PT. The novel sarcomeric protein telethonin exhibits developmental and functional regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Apr 21;257(3):699-703. PMID:10208846 doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.0531
| |



