Sandbox 35
From Proteopedia
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| - | This protease belongs to an extended family of aminopeptidases, dipeptidyl peptidases, endopeptidases, and other enzymes having both exo- and endo-peptidase activity. The inactivated zymogen with N-terminal propeptide regions - | + | This protease belongs to an extended family of aminopeptidases, dipeptidyl peptidases, endopeptidases, and other enzymes having both exo- and endo-peptidase activity. The inactivated zymogen with N-terminal propeptide regions - stabilizing in alkaline environments and enabling proper folding - is activated through removal of the propeptide regions <ref>PMID: 7845226</ref><ref>PMID: 12188906</ref>. |
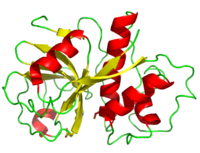
<StructureSection load='9pap' size='500' side='right' caption='Structure of Papain (PDB entry [[9PAP]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='9pap' size='500' side='right' caption='Structure of Papain (PDB entry [[9PAP]])' scene=''> | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| - | + | Papain's polypeptide chain consists of 212 amino acid residues which upon folding form a groove containing the active site between its two domains. | |
<scene name='Sandbox_35/Secondary_structure_papain/2'>secondary structure</scene> | <scene name='Sandbox_35/Secondary_structure_papain/2'>secondary structure</scene> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
===Distribution of Residues=== | ===Distribution of Residues=== | ||
| - | <scene name='Sandbox_35/Papain_acid_and_basic_residues/1'>acidic and basic residues</scene> | + | Papain has a scattered distribution of <scene name='Sandbox_35/Papain_acid_and_basic_residues/1'>acidic and basic residues</scene>, but can be seen to have more basic residues than acidic shedding light into the application of its use as a digestive supplement. <ref>[http://www.webmd.com/vitamins-supplements/ingredientmono-69-PAPAIN.aspx?activeIngredientId=69&activeIngredientName=PAPAIN] WebMD</ref> Its <scene name='Sandbox_35/Hydrophobicity_papain/3'>polar and non-polar residues</scene> build on this picture with <scene name='Sandbox_35/Papain_polar/1'>polar residues</scene> resting more on the outside and <scene name='Sandbox_35/Nonpolar_papain/2'>non-polar residues</scene> sequestering near the center. Observations have revealed that the proteins atomic positions are more ordered going from the center out <ref>PMID: 6502713 </ref> |
| - | + | ||
| - | <scene name='Sandbox_35/Hydrophobicity_papain/3'>polar and non-polar | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | <scene name='Sandbox_35/Papain_polar/1'>polar residues</scene> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | <scene name='Sandbox_35/Nonpolar_papain/2'>non-polar residues</scene> | + | |
===Ligands interactions=== | ===Ligands interactions=== | ||
Revision as of 21:51, 13 November 2011
| Please do NOT make changes to this Sandbox. Sandboxes 30-60 are reserved for use by Biochemistry 410 & 412 at Messiah College taught by Dr. Hannah Tims during Fall 2012 and Spring 2013. |
Contents |
Papain
Introduction
DID YOU KNOW?
. Meat tenderizer. Old time home remedy for insect, jellyfish, and stingray stings[1]. Who would have thought that a sulfhydryl protease from the latex of the papaya fruit, Carica papaya and Vasconcellea cundinamarcensis would have such a practical application beyond proteopedia?
This protease belongs to an extended family of aminopeptidases, dipeptidyl peptidases, endopeptidases, and other enzymes having both exo- and endo-peptidase activity. The inactivated zymogen with N-terminal propeptide regions - stabilizing in alkaline environments and enabling proper folding - is activated through removal of the propeptide regions [2][3].
| |||||||||||
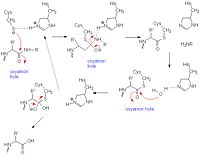
Catalytic Mechanism
References
- ↑ [1] Ameridan International
- ↑ Rawlings ND, Barrett AJ. Families of cysteine peptidases. Methods Enzymol. 1994;244:461-86. PMID:7845226
- ↑ Yamamoto Y, Kurata M, Watabe S, Murakami R, Takahashi SY. Novel cysteine proteinase inhibitors homologous to the proregions of cysteine proteinases. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2002 Apr;3(2):231-8. PMID:12188906
- ↑ [2]9PAP PDB
- ↑ Wang J, Xiang YF, Lim C. The double catalytic triad, Cys25-His159-Asp158 and Cys25-His159-Asn175, in papain catalysis: role of Asp158 and Asn175. Protein Eng. 1994 Jan;7(1):75-82. PMID:8140097
- ↑ [3] WebMD
- ↑ Kamphuis IG, Kalk KH, Swarte MB, Drenth J. Structure of papain refined at 1.65 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 25;179(2):233-56. PMID:6502713
- ↑ [4] University of Maine
http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2PAD
• Show the secondary structures.
• Compare the distribution of polar residues to that of nonpolar residues.
• Highlight the active site.
• If you can find a PDB file of the enzyme that contains a pseudo-substrate (may be inhibitor), highlight it.
• Show the contacts or attractions that are present between the pseudo-substrate and the protein, and if the enzyme has multiple subunits, show the contacts between the subunits.
• Identify any other ligands that are present in the structure and the types of contacts that are present between them and the protein
http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Sandbox_55#cite_note-18 Table of contents Pictures References (cross links)