This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
ToxT
From Proteopedia
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Structural Features== | ==Structural Features== | ||
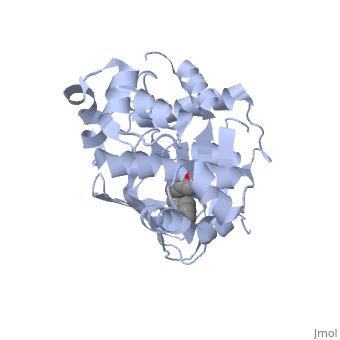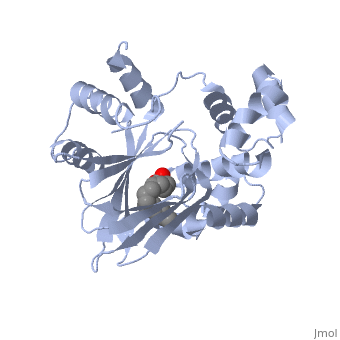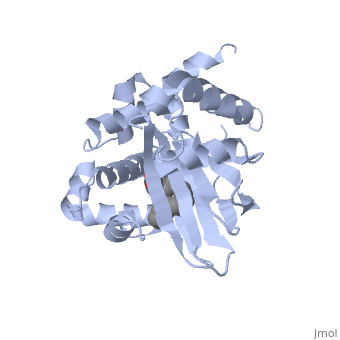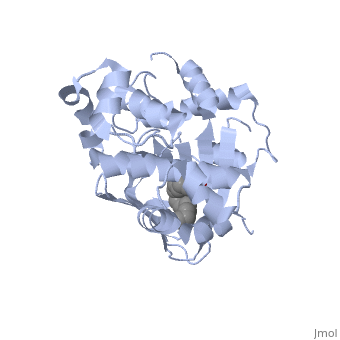
ToxT belongs to a family of transcriptional regulators known as AraC.<ref name="structure">PMID: 20133655</ref> The AraC family is defined by a 100 amino acid region of sequence similarity that forms a DNA-binding domain with two helix-turn-helix motifs. <ref name="arac">PMID: 11282467</ref> | ToxT belongs to a family of transcriptional regulators known as AraC.<ref name="structure">PMID: 20133655</ref> The AraC family is defined by a 100 amino acid region of sequence similarity that forms a DNA-binding domain with two helix-turn-helix motifs. <ref name="arac">PMID: 11282467</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 23:29, 26 November 2011
|
Introduction
ToxT is a molecule at the end of a transcriptional cascade that autoregulates the transcription of the primary virulence factors of Vibrio cholerae[1] and itself. These two factors, cholera toxin (CT)[2] and the toxin co-regulated pilus (TCP), are instrumental in causing the disease cholera[3]. This is an intestinal infection resulting in massive water loss in the affected individual, causing extreme dehydration.[4]
Structural Features
ToxT belongs to a family of transcriptional regulators known as AraC.[1] The AraC family is defined by a 100 amino acid region of sequence similarity that forms a DNA-binding domain with two helix-turn-helix motifs. [2]
References
- ↑ Lowden MJ, Skorupski K, Pellegrini M, Chiorazzo MG, Taylor RK, Kull FJ. Structure of Vibrio cholerae ToxT reveals a mechanism for fatty acid regulation of virulence genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 16;107(7):2860-5. Epub 2010 Feb 1. PMID:20133655
- ↑ Martin RG, Rosner JL. The AraC transcriptional activators. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2001 Apr;4(2):132-7. PMID:11282467
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Ingrid Youngworth, Yang Yang, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky