This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
A-ATP Synthase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | |||
<StructureSection load=1e79 size='500' side='right' caption='F1-ATP synthase motor domain', ([[1e79]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load=1e79 size='500' side='right' caption='F1-ATP synthase motor domain', ([[1e79]])' scene=''> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 11: | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:F_ATPsynthase.gif | thumb]] |
replace with image on desktop | replace with image on desktop | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
Revision as of 06:10, 28 November 2011
| |||||||||||
replace with image on desktop
Structure
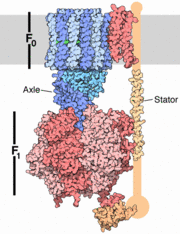
A-ATP synthase ATP synthase is composed of two parts A1 and A0 which are composed of at least nine subunits A3B3C:D:E:F:H2:a:cx that function as a pair of rotary motors connected by central and peripheral stalk(s) [1].This structure is similar to the known structure of F ATP synthase. The A0 domain is the hydrophobic membrane embedded ion-translocating sector that uses the H+ gradient to power ATP synthase in domain A1. A1 is catalytic and water soluble containing A and B subunits. These subunits are comparable to F-ATP synthase ATP synthase alpha/beta subunits. The A subunit of A1 is catalytic and the B subunit is regulatory, with a substrate-binding site on each.
| |||||||||||
| |||||||
| Transition state, 1e79 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , , , , | ||||||
| Activity: | H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase, with EC number 3.6.3.14 | ||||||
| Related: | 1bmf, 1cow, 1e1q, 1e1r, 1efr, 1nbm, 1qo1
| ||||||
| |||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
Contents |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Muller V, Lemker T, Lingl A, Weidner C, Coskun U, Gruber G. Bioenergetics of archaea: ATP synthesis under harsh environmental conditions. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2005;10(2-4):167-80. PMID:16645313 doi:10.1159/000091563
- ↑ Schafer IB, Bailer SM, Duser MG, Borsch M, Bernal RA, Stock D, Gruber G. Crystal structure of the archaeal A1Ao ATP synthase subunit B from Methanosarcina mazei Go1: Implications of nucleotide-binding differences in the major A1Ao subunits A and B. J Mol Biol. 2006 May 5;358(3):725-40. Epub 2006 Mar 10. PMID:16563431 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.02.057
- ↑ Gonzalez JM, Masuchi Y, Robb FT, Ammerman JW, Maeder DL, Yanagibayashi M, Tamaoka J, Kato C. Pyrococcus horikoshii sp. nov., a hyperthermophilic archaeon isolated from a hydrothermal vent at the Okinawa Trough. Extremophiles. 1998 May;2(2):123-30. PMID:9672687
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Manimekalai MS, Kumar A, Jeyakanthan J, Gruber G. The Transition-Like State and P(i) Entrance into the Catalytic A Subunit of the Biological Engine A-ATP Synthase. J Mol Biol. 2011 Mar 16. PMID:21396943 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.03.010
- ↑ Priya R, Kumar A, Manimekalai MS, Gruber G. Conserved Glycine Residues in the P-Loop of ATP Synthases Form a Doorframe for Nucleotide Entrance. J Mol Biol. 2011 Sep 8. PMID:21925186 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.08.045
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Kaitlin Chase MacCulloch, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky