User:Brian Hernandez/DOPA Decarboxylase
From Proteopedia
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
==='''Inhibitor Binding'''=== | ==='''Inhibitor Binding'''=== | ||
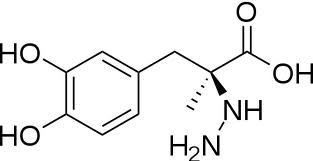
The inhibitor '''carbiDOPA''' binds to the enzyme by forming a hydrazone linkage with the PLP cofactor through its hydrazine moiety <ref name=Burkhard>PMID: 11685243 </ref>. | The inhibitor '''carbiDOPA''' binds to the enzyme by forming a hydrazone linkage with the PLP cofactor through its hydrazine moiety <ref name=Burkhard>PMID: 11685243 </ref>. | ||
| + | [[Image:carbidopa.jpeg]] | ||
Revision as of 05:21, 29 November 2011
| |||||||||||
DDC and Parkinson's Disease
Treatment
Parkinson's disease, a neurological disorder, can be characterized by tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. With it's possible relation to degenerative dopamine-producing cells in the brain, administration of L-DOPA can increase the amount of synthesized dopamine in the nerve cell; direct treatment with dopamine is not sufficient as dopamine itself cannot pass the blood-brain barrier. However, only a small percentage of the dose actually reaches the nervous system, with the remaining majority being rapidly converted to dopamine in the blood stream. This dopamine-rich blood causes side effects of nausea, daytime sleepiness, orthostatic hypotension, involuntary movements, decreased appetite, insomnia, and cramping. Addition of a DDC inhibitor would block peripheral conversion to dopamine and allow a greater percentage of L-DOPA to reach the brain, causing an increase in brain dopamine levels, and diminishing the side effects of dopamine-rich blood.
Inhibitor Binding
The inhibitor carbiDOPA binds to the enzyme by forming a hydrazone linkage with the PLP cofactor through its hydrazine moiety [1].