We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Brian Hernandez/DOPA Decarboxylase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
==='''The Active Site'''=== | ==='''The Active Site'''=== | ||
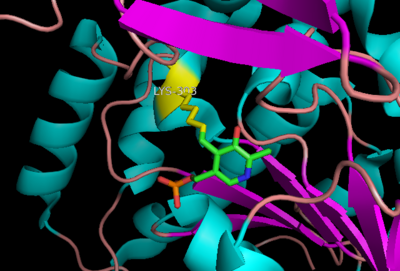
| - | DDC's active site is located in a <scene name='DOPA_decarboxylase/Dimer_interface/2'>cleft</scene> between the two monomer subunits, but is composed mainly of residues from one monomer.The <scene name='DOPA_decarboxylase/Active_site/1'>active site</scene> is composed of several key residues, including Lys-303, Asp-271, His-192, Thr-82, Ile-101, and Phe-103. In the ligand free form, PLP binds to Lys 303 via a Schiff base linkage. A [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_bridge_(protein) salt bridge] forms between the carboxylate group of Asp 271 and the protonated pyridine nitrogen of PLP yielding a strong '''electron sink''' capable of stabilizing the carbanionic intermediates. The only two active site residues from the adjacent monomer, Ile-101 and Phe-103, are part of the substrate binding pocket. | + | DDC's active site is located in a <scene name='DOPA_decarboxylase/Dimer_interface/2'>cleft</scene> between the two monomer subunits, but is composed mainly of residues from one monomer.The <scene name='DOPA_decarboxylase/Active_site/1'>active site</scene> is composed of several key residues, including Lys-303, Asp-271, His-192, Thr-82, Ile-101, and Phe-103. In the ligand free form, PLP binds to Lys 303 via a '''Schiff base linkage'''. A [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_bridge_(protein) salt bridge] forms between the carboxylate group of Asp 271 and the protonated pyridine nitrogen of PLP yielding a strong '''electron sink''' capable of stabilizing the carbanionic intermediates. The only two active site residues from the adjacent monomer, Ile-101 and Phe-103, are part of the substrate binding pocket. |
[[image:plp bound.png|thumb|center|400px|'''Schiff base linkage of PLP to Lys303 in the active site''']] | [[image:plp bound.png|thumb|center|400px|'''Schiff base linkage of PLP to Lys303 in the active site''']] | ||
Revision as of 07:06, 29 November 2011
| |||||||||||
3D structures of DOPA decarboxylase
| |||||||||
| 1js3, resolution 2.25Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , | ||||||||
| Activity: | Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase, with EC number 4.1.1.28 | ||||||||
| Related: | 1js6 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
3k40 – DDC – Drosophila melanogaster
1js3 – pDDC + inhibitor – pig
1js6 - pDDC
3rbf, 3rbl – hDDC – human
3rch – hDDC + vitamin B6 phosphate + pyridoxal phosphate
References
- ↑ Christenson JG, Dairman W, Udenfriend S. On the identity of DOPA decarboxylase and 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase (immunological titration-aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase-serotonin-dopamine-norepinephrine). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):343-7. PMID:4536745
- ↑ Schneider G, Kack H, Lindqvist Y. The manifold of vitamin B6 dependent enzymes. Structure. 2000 Jan 15;8(1):R1-6. PMID:10673430
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Burkhard P, Dominici P, Borri-Voltattorni C, Jansonius JN, Malashkevich VN. Structural insight into Parkinson's disease treatment from drug-inhibited DOPA decarboxylase. Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Nov;8(11):963-7. PMID:11685243 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsb1101-963
- ↑ Ishii S, Mizuguchi H, Nishino J, Hayashi H, Kagamiyama H. Functionally important residues of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase probed by sequence alignment and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biochem. 1996 Aug;120(2):369-76. PMID:8889823