User:Logan Brushart
From Proteopedia
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
The second man died. | The second man died. | ||
===About The Receptor=== | ===About The Receptor=== | ||
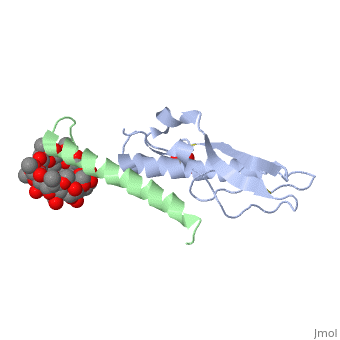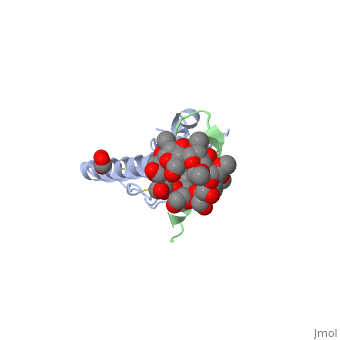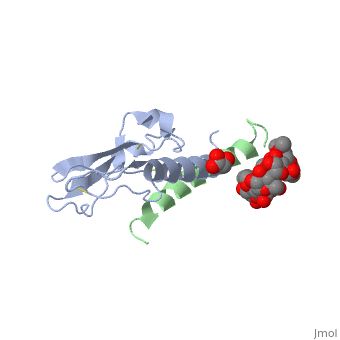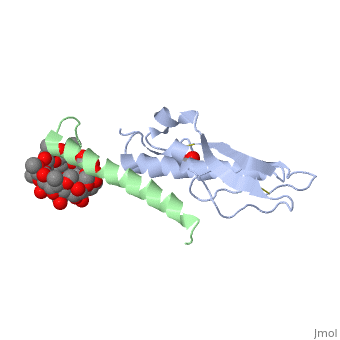
| - | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) is a transmembrane protein which is responsible for boosting glucose-induced insulin production. The transcription of this protein is positively controlled by glucose molecules, GIPR is expressed in higher levels when glucose is in higher concentration. The receptor in a multispan membrane bound protein (shown in blue) consisting of an alpha helix, half twist helices, and beta sheets binded in several locations with disulfide bonds within itself. The ligand which binds to GIPR is Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) also know as Gastric inhibitory polypeptide(shown in green). GIP is an alpha helical endogenous polypeptide hormone which is released upon the ingestion of food, specifically the carbohydrate glucose. It binds to GIPR though hydrophobic interactions and causes the release of G protein-coupled receptors which in turn | + | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) is a transmembrane protein which is responsible for boosting glucose-induced insulin production. The transcription of this protein is positively controlled by glucose molecules, GIPR is expressed in higher levels when glucose is in higher concentration. The receptor in a multispan membrane bound protein (shown in blue) consisting of an alpha helix, half twist helices, and beta sheets binded in several locations with disulfide bonds within itself. The ligand which binds to GIPR is Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) also know as Gastric inhibitory polypeptide(shown in green). GIP is an alpha helical endogenous polypeptide hormone which is released upon the ingestion of food, specifically the carbohydrate glucose. It binds to GIPR though hydrophobic interactions and causes the release of G protein-coupled receptors which in turn causes an enzymatic cascade resulting in the increase secretion of insulin. |
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
[[2qkh]] | [[2qkh]] | ||
Revision as of 02:12, 30 November 2011
|
Background
two men walk into a bar. The first man says to the bartender "I'll have some H2O." The second man says "That sounds good, I'll have some H2O too." The second man died.
About The Receptor
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) is a transmembrane protein which is responsible for boosting glucose-induced insulin production. The transcription of this protein is positively controlled by glucose molecules, GIPR is expressed in higher levels when glucose is in higher concentration. The receptor in a multispan membrane bound protein (shown in blue) consisting of an alpha helix, half twist helices, and beta sheets binded in several locations with disulfide bonds within itself. The ligand which binds to GIPR is Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) also know as Gastric inhibitory polypeptide(shown in green). GIP is an alpha helical endogenous polypeptide hormone which is released upon the ingestion of food, specifically the carbohydrate glucose. It binds to GIPR though hydrophobic interactions and causes the release of G protein-coupled receptors which in turn causes an enzymatic cascade resulting in the increase secretion of insulin.