Group:MUZIC:Nebulin
From Proteopedia

| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1ark' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='1ark' size='300' side='right' caption='NMR structure of the SH3 domain of Nebulin' scene='User:Marie-Cecile_Pelissier/Workbench/Nebulin/Overall/2'> |
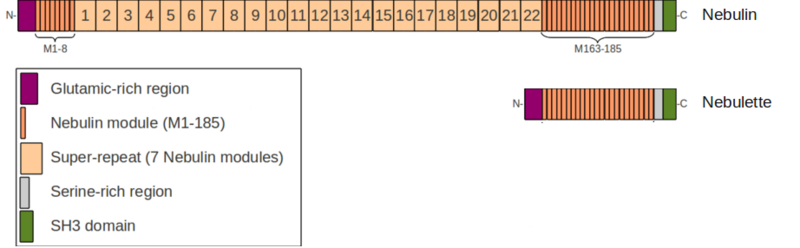
Nebulin (UniProt ID: P20929 [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P20929]) is a very large filamentous protein (600-900 kDa) <ref>PMID 6547565</ref> tightly associated to the thin filament of the muscle sarcomere throughout its length. Nebulin is mostly found within the sarcomeres of skeletal muscles but was also identified at a low level in cardiac muscle cells <ref>PMID 12729758</ref>. However, the sarcomeres of cardiac muscles predominantly contain a Nebulin-like protein called Nebulette (UniProt ID: O76041 [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O76041]) which is a "short version" of Nebulin (100 kDa), highly similar to its C-terminal part <ref>PMID 8581976</ref>. | Nebulin (UniProt ID: P20929 [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P20929]) is a very large filamentous protein (600-900 kDa) <ref>PMID 6547565</ref> tightly associated to the thin filament of the muscle sarcomere throughout its length. Nebulin is mostly found within the sarcomeres of skeletal muscles but was also identified at a low level in cardiac muscle cells <ref>PMID 12729758</ref>. However, the sarcomeres of cardiac muscles predominantly contain a Nebulin-like protein called Nebulette (UniProt ID: O76041 [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O76041]) which is a "short version" of Nebulin (100 kDa), highly similar to its C-terminal part <ref>PMID 8581976</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 13:22, 30 November 2011
Contents |
Introduction
| |||||||||||
Function and related diseases
The Nebulin protein is involved in the structural integrity of the sarcomeres and is linked to many signalling pathways crucial for the maintenance of the sarcomere. The main fucntions of Nebulin are [4]:
- To define and regulate the length of the thin filaments of actin (molecular ruler);
- To maintain the alignment of adjacent myofibrills (linker of adjacent Z-disks);
- To regulate muscle contraction (regulator of cross-bridge cycles).
Mutations in the Nebulin encoding gene are the most common cause of Nemaline myopathy (NM), a non-dystrophic congenital muscle disorder characterised by muscle weakness.
Domains and interactions
Glutamic rich region
Nebulin modules
The Nebulin modules are 35 residues long modules for which no structural information is available.
- Tropomodulin: The N-terminal modules bind Tropomodulin at the pointed end of the thin filament of Actin.
- Actin: Each Nebulin module is able to bind to a monomer of F-Actin in a way that would control the length of the thin filament of Actin.
- Tropomyosin/Troponin: The central super-repeats of 7 Neb modules binds 1 Tropomyosin/Troponin complex.
- Myosin and Myosin Binding Protein C: The central super-repeats were also shown to bind Myosin in a way that would regulate the actomyosin activity.
- Calmodulin: The N-terminal and C-terminal super-repeats can bind Calmodulin in a Calcium-independant manner.
- CapZ: The C-terminal modules can bind the barbed end capping protein CapZ.
- Desmin: The C-terminal modules located close to the Z-disk bind Desmin, which is likely to play a role in the alignment of adjacent myofibrills.
- Alpha-Actinin: The C-terminal modules located within the Z-disk bind α-Actinin
Serine rich region
The Ser-rich region has no homology to known structural motifs. The Serine residues can be phosphorylated by GSK3-β in a way that modulates some of the Nebulin interactions.
SH3 domain
The SH3 domain is the only domain of Nebulin for which a 3D structure is available. The Nebulin SH3 domain adopts a β-Barrel . It interacts with Proline-rich motif of its binding partners.
- Titin: The SH3 domain of Nebulin binds to Pro-rich motifs located within the elastic PEVK region of Titin.
- Myopalladin: The SH3 domain also binds the central region of Myopalladin, which allows its targeting to the Z-disk
- N-WASP: The SH3 domain binds the N-WASP protein during early stages of myofibrillogenesis, this interaction promoting nucleation of the thin filament of Actin.
References
- ↑ Wang K. Cytoskeletal matrix in striated muscle: the role of titin, nebulin and intermediate filaments. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;170:285-305. PMID:6547565
- ↑ Kazmierski ST, Antin PB, Witt CC, Huebner N, McElhinny AS, Labeit S, Gregorio CC. The complete mouse nebulin gene sequence and the identification of cardiac nebulin. J Mol Biol. 2003 May 9;328(4):835-46. PMID:12729758
- ↑ Moncman CL, Wang K. Nebulette: a 107 kD nebulin-like protein in cardiac muscle. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1995;32(3):205-25. PMID:8581976 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cm.970320305
- ↑ Ottenheijm CA, Granzier H. Lifting the nebula: novel insights into skeletal muscle contractility. Physiology (Bethesda). 2010 Oct;25(5):304-10. PMID:20940435 doi:10.1152/physiol.00016.2010
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Marie-Cecile Pelissier, Michal Harel, Jaime Prilusky, Nikos Pinotsis