Sandbox Reserved 384
From Proteopedia
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | <!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
| - | *[[User:LoganBrushart/Sandbox 384]] | + | *[[User:LoganBrushart/Sandbox reserved 384]] |
<Structure load='2qkh' size='400' frame='true' align='right' caption='Glucose-dependant insulinotropic polypeptide receptor, [[2qkh]]' scene='' /> | <Structure load='2qkh' size='400' frame='true' align='right' caption='Glucose-dependant insulinotropic polypeptide receptor, [[2qkh]]' scene='' /> | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
--> | --> | ||
| - | == | + | ==Background== |
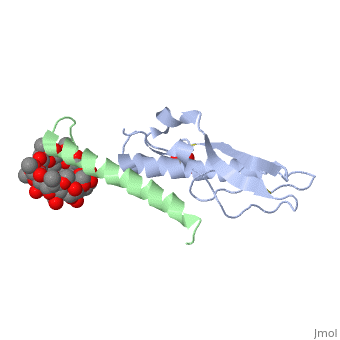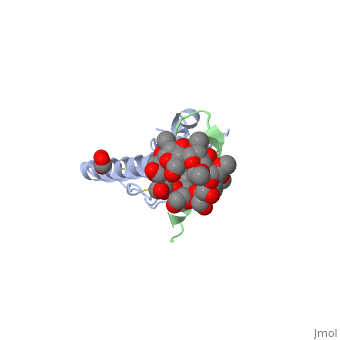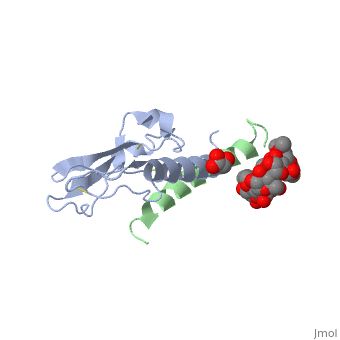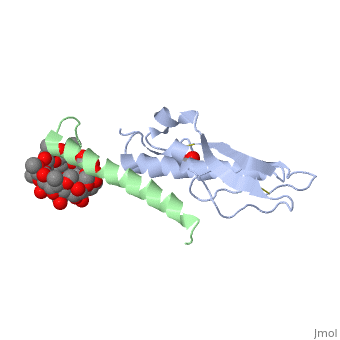
| - | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) is a transmembrane protein which is responsible for boosting glucose-induced insulin production. The transcription of this protein is positively controlled by glucose molecules, GIPR is expressed in higher levels when glucose is in higher concentration. The receptor | + | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) is a transmembrane protein which is responsible for boosting glucose-induced insulin production. The transcription of this protein is positively controlled by glucose molecules, GIPR is expressed in higher levels when glucose is in higher concentration. The receptor is a multispan membrane bound protein (shown in blue) consisting of an alpha helix, half twist helices, and beta sheets binded in several locations with disulfide bonds within itself. The ligand which binds to GIPR is Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) also known as Gastric inhibitory polypeptide(shown in green). GIP is an alpha helical endogenous polypeptide hormone which is released upon the ingestion of food, specifically the carbohydrate glucose. |
| + | [[Image:F3.small.jpg |left| ]] | ||
| + | ===Molecular Function=== | ||
| + | The prupose of the receptor is to bind Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) in the presence of Glucose. This causes a chain reaction that increases secretion of insulin molecules.It binds to GIPR though hydrophobic interactions and causes the release of G protein-coupled receptors which in turn causes an enzymatic cascade resulting in the increase secretion of insulin. | ||
| + | |||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
[[2qkh]] | [[2qkh]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:F3.small.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 18:54, 30 November 2011
| This Sandbox is Reserved from September 14, 2021, through May 31, 2022, for use in the class Introduction to Biochemistry taught by User:John Means at the University of Rio Grande, Rio Grande, OH, USA. This reservation includes 5 reserved sandboxes (Sandbox Reserved 1590 through Sandbox Reserved 1594). |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing. For an example of a student Proteopedia page, please see Photosystem II, Tetanospasmin, or Guanine riboswitch. |
|
Background
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) is a transmembrane protein which is responsible for boosting glucose-induced insulin production. The transcription of this protein is positively controlled by glucose molecules, GIPR is expressed in higher levels when glucose is in higher concentration. The receptor is a multispan membrane bound protein (shown in blue) consisting of an alpha helix, half twist helices, and beta sheets binded in several locations with disulfide bonds within itself. The ligand which binds to GIPR is Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) also known as Gastric inhibitory polypeptide(shown in green). GIP is an alpha helical endogenous polypeptide hormone which is released upon the ingestion of food, specifically the carbohydrate glucose.
Molecular Function
The prupose of the receptor is to bind Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) in the presence of Glucose. This causes a chain reaction that increases secretion of insulin molecules.It binds to GIPR though hydrophobic interactions and causes the release of G protein-coupled receptors which in turn causes an enzymatic cascade resulting in the increase secretion of insulin.