Brittany deRonde/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
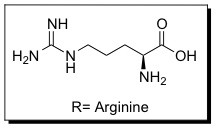
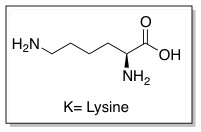
Cell penetrating peptides (CPPs) are proteins with the ability to cross cellular membranes and facilitate the uptake of various cargo, such as small molecules, siRNA, and small DNA fragments. Such cargo can be associated via covalent or non-covalent interactions. Tat is considered a CPP because it contains a protein transduction domain (PTD). PTDs are cation-rich sequences found in proteins, usually containing Lysine or Arginine. | Cell penetrating peptides (CPPs) are proteins with the ability to cross cellular membranes and facilitate the uptake of various cargo, such as small molecules, siRNA, and small DNA fragments. Such cargo can be associated via covalent or non-covalent interactions. Tat is considered a CPP because it contains a protein transduction domain (PTD). PTDs are cation-rich sequences found in proteins, usually containing Lysine or Arginine. | ||
| - | [[Image:Arginine1.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Arginine1.jpg]] [[Image:Lysine1.jpg]] |
It is believed that these sequences enable favorable interactions with cellular membranes that enable them to enter cells. The PTD sequence in Tat is YGRKKRRQRRR (amino acid residues 47-57), which is Arginine-rich. This 11 amino-acid sequence is now referred to as the TAT peptide, and has be shown to have improved cellular uptake compared to Tat. | It is believed that these sequences enable favorable interactions with cellular membranes that enable them to enter cells. The PTD sequence in Tat is YGRKKRRQRRR (amino acid residues 47-57), which is Arginine-rich. This 11 amino-acid sequence is now referred to as the TAT peptide, and has be shown to have improved cellular uptake compared to Tat. | ||
Revision as of 20:05, 15 December 2011
One of the CBI Molecules being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst and on display at the Molecular Playground.
HIV Tat, or simply Tat, is a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) gene that regulates transcription of HIV dsRNA. Tat, which stands for trans-activator of transcription, contains 86 amino acid residues in its sequence.
|
Cell penetrating peptides (CPPs) are proteins with the ability to cross cellular membranes and facilitate the uptake of various cargo, such as small molecules, siRNA, and small DNA fragments. Such cargo can be associated via covalent or non-covalent interactions. Tat is considered a CPP because it contains a protein transduction domain (PTD). PTDs are cation-rich sequences found in proteins, usually containing Lysine or Arginine.
It is believed that these sequences enable favorable interactions with cellular membranes that enable them to enter cells. The PTD sequence in Tat is YGRKKRRQRRR (amino acid residues 47-57), which is Arginine-rich. This 11 amino-acid sequence is now referred to as the TAT peptide, and has be shown to have improved cellular uptake compared to Tat.