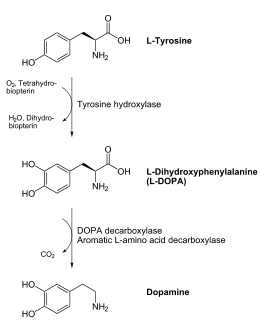
DOPA decarboxylase (DDC, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, tryptophan decarboxylase, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, AAAD) is an approximately 104 kDa protein that belongs to the
aspartate aminotransferase family (fold type 1) of
PLP-dependent (vitamin B6-dependent) enzymes. The catalytically active form of the enzyme exists as a homodimer, typical of this class of enzymes.
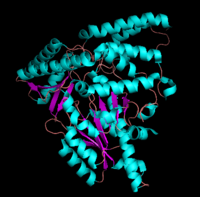
[1] The homodimeric form of the enzyme purified from
sus scrofa is shown in complex with the inhibitor
carbidopa to the right.
DOPA decarboxylase is responsible for the synthesis of dopamine and serotonin from L-DOPA and L-5-hydroxytryptophan, respectively. Due to its role in dopamine biosynthesis, DOPA decarboxylase has been implicated in Parkinson's disease, a disease thought to be the result of the degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. In fact, decarboxylation of L-DOPA by DOPA decarboxylase is the controlling step for the formation of dopamine in patients with Parkinson's [2] Currently, treatment for the disease is aimed at DOPA decarboxylase inhibition. Since dopamine cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, it cannot be used to directly treat Parkinson's disease. Thus, exogenously administered L-DOPA is the primary treatment for patients suffering from this neurodegenerative disease. Unfortunately, DOPA decarboxylase rapidly converts L-DOPA to dopamine in the blood stream, with only a small percentage reaching the brain. By inhibiting the enzyme, greater amounts of exogenously administered L-DOPA can reach the brain, where it can then be converted to dopamine. [3]
PLP-Dependent Enzymes
Overview
Pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (PLP), the biologically active phosphorylated derivative of vitamin B6, is a versatile and abundant cofactor to a variety of enzymes in all organisms. Almost all PLP-dependet enzymes function in pathways associated with amino compounds, primarily amino acid metabolism. These enzymes carry out many types of reactions, including transaminations,
decarboxylations', racemizations, and deaminations (amongst others). PLP is considered to be the most versatile cofactor, thus imparting a wide range of functions on PLP-dependent enzymes. This versatility stems from the fact that PLP can covalently bind the substrate and then act as an electrophilic catalyst. And although these enzymes have wide range of function, there exist only five structural classes: the aspartate amino transferase family, the tryptophan synthase β family, the alanine racemase family, the D-amino acid family, and the glycogen phosphorylase family. [4] [1] 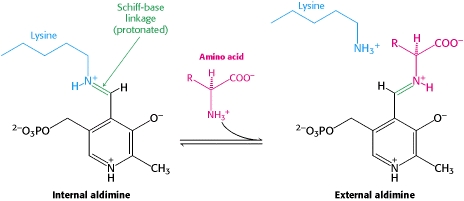
The PLP is bound covalently to lysine residues in a Schiff base linkage (aldimine). In this form, it reacts with many free amino acids to replace the Schiff base to the lysine of the enzyme with a Schiff base to the amino acid substrate.
The Aspartate Aminotransferase Family
Aspartate Aminotransferase
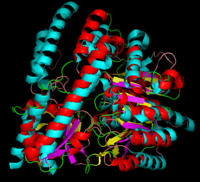
DOPA decarboxylase superimposed on aspartate aminotransferase
DOPA Decarboxylase
Primary Structure
The amino acid sequence of a proteins polypeptide chain is referred to as its primary structure. Each polypeptide chain of DOPA decarboxylase is composed of 486 amino acids that ultimately encode the three-dimensional structure of the protein.
Secondary Structure
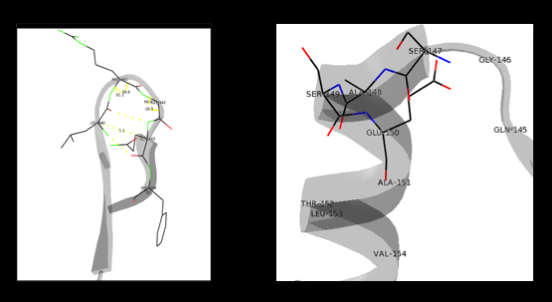
The formation of secondary structural elements (like α helices and β sheets) arise in response to the hydrophobic effect and the need to neutralize main-chain polar groups by hydrogen bonding. Each polypeptide chain of DOPA decarboxylase is composed of a seven-stranded mixed , a four-stranded anti-parallel , several , and other, lesser known, secondary structural elements (like loops and the extended strand). Another common secondary structure is the β-turn, or reverse turn. Depicted below is an example of a Type 1 β-turn of DOPA decarboxylase. This β-turn is comprised of residues Leu-440, Arg-441, Gly-442, and Gln-443. The distance between Cαi and Cαi+3 is 5.1Å, within the acceptable limit of 7Å. As in most β-turns, there is a hydrogen bond between the C=O of Leu-440 and the NH of Gln-443. The phi and psi angles of residues i+1 (Arg-441) and i+2 (Gly-442) are indicated in the diagram.
The α helix is characterized by main chain hydrogen bonds between the C=O of residue n and the NH of residue n+4. All residues in the helix participate in this type of hydrogen bonding except the first NH groups and the last C=O groups at the ends of the helix. Helix-capping motifs are specific hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions found at the ends of helices. Seven distinct capping motifs have been identified; three at the N-terminus and four at the C-terminus [5] . Shown above is the capping-box motif found at the end of the helix composed of residues 147-171. This form of special capping satisfies two of the four non hydrogen-bonded helix N-terminal amides. The side-chain capping apparent here is typical at the N-terminus.
Tertiary Structure
This level of protein structure refers to the overall three-dimensional shape the polypeptide chain creates. Domains are the fundamental units that generate the tertiary structure, and DOPA decarboxylase is composed of three distinct domains.
The contains the PLP-binding site, and consists of a seven-stranded mixed β sheet that is surrounded by eight α helices, resulting in a typical α/β fold, the most regular and common of the protein structures (recall that α helices and β strands typically alternate in this fold, generating an outer layer of α helices and an inner layer of β sheets). This particular fold falls into the class of open twisted parallel or mixed β sheet with α helices on both sides of the sheet. The small is comprised of a four-stranded anti-parallel β sheet that has three α helices packed against the face opposite to the large domain. Although the aforementioned domains exist in all members of this family of PLP-dependent enzymes, including bacterial ornithine decarboxylase (OrnDC) and dialkylglycine decarboxylase (DGD), the is unique to DOPA decarboxylase, and is a representative case of domain swapping. This domain is composed of two parallel helices linked by an extended strand, which essentially lies like a flap over the second subunit. As well, residues from the N-terminal domain and the small domain form a short
Quaternary Structure
The level of protein structure exists solely in multisubunit complexes. DOPA decarboxylase is a homodimeric enzyme with the active site located near the monomer-monomer interface, thus highlighting the importance of this level of protein structure to the enzymes function. Furthermore, since the N-terminal domain of one monomer packs on top of the other monomer, resulting in an extended dimer interface, this level of tertiary structure is most likely stable only in the dimeric form of the enzyme.
Function
The Active Site
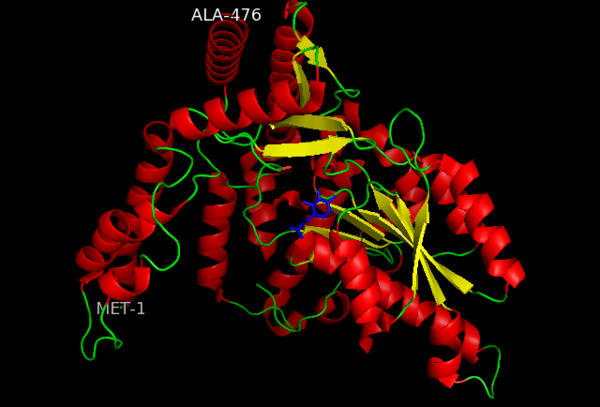
The active site of DOPA decarboxylase is located in a cleft at the between the two subunits of the dimer, like all PLP-dependent enzymes of the aspartate aminotransferase family. Since it is at the interface, residues from both domains and both subunits are involved in cofactor binding, although the active site is composed of residues mainly from one monomer. The is composed of several key residues, including Lys-303, Asp-271, His-192, Thr-82, Ile-101, and Phe-103. serves to bind PLP via a Schiff base linkage in the absence on substrate.
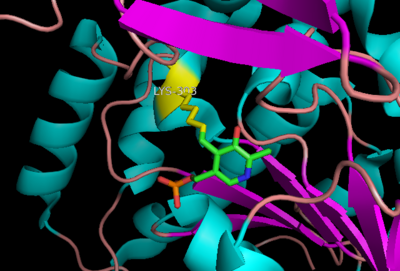
Schiff base linkage of PLP to Lys303 in the active site
As well, a salt bridge exists between the carboxyl group of and the protonated pyridine nitrogen of PLP to further stabilize intermediate. Essentially, a salt bridge combines hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions (two common types non-covalent interactions). This interaction serves to provide an electron sink that can stabilize the carbanionic intermediates [6] . PLP is further anchored to the protein by an extended hydrogen bond network, as shown below.
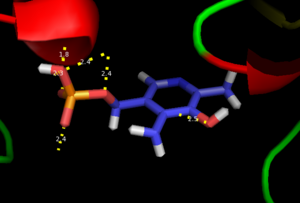
H-bonding network of PLP in the active site
The only two active site residues from the adjacent monomer, Ile-101 and Phe-103, are part of the substrate binding pocket.
Inhibitor Binding
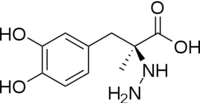
The inhibitor binds to the enzyme by forming a hydrazone linkage with PLP through its hydrazine moiety. The catechol ring of carbiDOPA is deeply buried in the active site cleft and is stabilized by with Ile-101 and Phe-103. The 4' hydroxyl group of the catechol ring participates in hydrogen bonding with , further stabilizing the inhibitor in the active site cleft. PLP is further involved in substrate binding by forming a hydrogen bond to the 3' of the catechol ring. , a highly conserved residue of PLP-dependent decarboxylases
[7] hydrogen bonds to the carboxylate group of carbiDOPA.
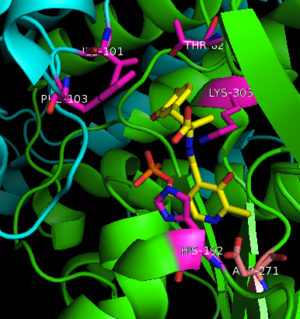
Key interactions between the active site residues, PLP, and carbiDOPA
Flexible Loop
In all three crystal structures of DOPA decarboxylase solved to date, residues 328-339 are invisible in the electron density map. This is because these amino acids form a short mobile loop that is believed to be important to the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme [7]. During catalysis, this loop is proposed to lose its flexibility and extend toward the active site, both occluding the active site from solvent during catalysis and possibly even taking part in the catalytic mechanism. The mobile loop is found in other PLP-depended enzymes, such as glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase. The idea that this flexible loop plays an important role in catalysis is supported by the fact that it contains several highly conserved residues, Tyr-332 and Lys-334. The conformational change that occurs is thought to be a result of loop residues directly interacting with the inhbitor.
Classification
DOPA decarboxylase is classified in the following manner using SCOP:
- Class: alpha and beta proteins (α/β)
- Fold: PLP-dependent transferase-like
- Superfamily: PLP-dependent transferases
- Family: Pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylase
- Domain: DOPA decarboxylase
DOPA decarboxylase is classified in the following manner using CATH:
- Class: alpha beta
- Architecture: 3-layer sandwich
- Topology: Aspartate aminotransferase
- Class: alpha beta
- Architecture: alpha-beta complex
- Topology: Aspartate aminotransferase
- Class: mainly alpha
- Architecture: up-down bundle
- Topology: dopa decarboxylase