This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
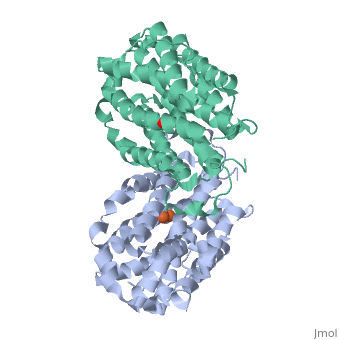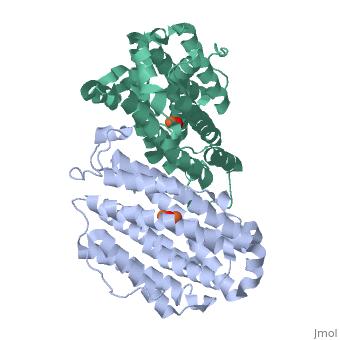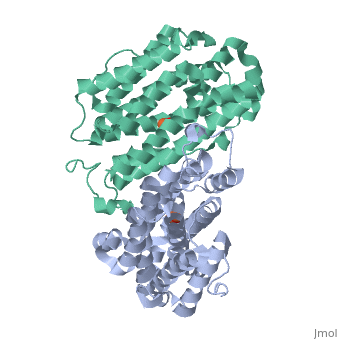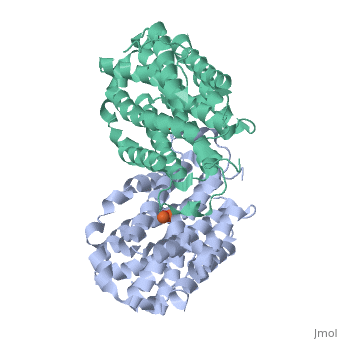
Mouse Ribonucleotide Reductase R2
From Proteopedia
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Activity Within DNA Synthesis== | ==Activity Within DNA Synthesis== | ||
| - | Ribonucleotide reductase is essential in the formation of new deoxyribonucleotides. These are essential for the repair and replication of DNA with organisms. This reaction is highly regulated, which is important; since levels of deoxyribonucleotides must be correct to lower chances of cell death or genetic abnormalities. With mice and humans, the two subunits are coded for by genes located on different chromosomes. The R2 subunit determines the activity of the enzyme, since its levels vary while the levels of the R1 subunit are quite constant. DNA damage induces transcription of the R1 gene only. The transcription of R2 is induced by p53 during the S phase of the cell. One interesting fact about this gene is that the human ribonucleotide reductase R2 promoter can activate transcription of the human R2 gene in a mouse cell. The human R2 gene can be expressed in a functional R2 protein within a mouse cell. The same is true for a mouse R2 gene in a human cell. This illustrates close relatedness of the genes. <ref>http://www.jbc.org/cgi/content/full/279/11/10796</ref> | + | Ribonucleotide reductase is essential in the formation of new deoxyribonucleotides. These are essential for the repair and replication of DNA with organisms. This reaction is highly regulated, which is important; since levels of deoxyribonucleotides must be correct to lower chances of cell death or genetic abnormalities. With mice and humans, the two subunits are coded for by genes located on different chromosomes. The R2 subunit determines the activity of the enzyme, since its levels vary while the levels of the R1 subunit are quite constant. DNA damage induces transcription of the R1 gene only. The transcription of R2 is induced by [[p53]] during the S phase of the cell. One interesting fact about this gene is that the human ribonucleotide reductase R2 promoter can activate transcription of the human R2 gene in a mouse cell. The human R2 gene can be expressed in a functional R2 protein within a mouse cell. The same is true for a mouse R2 gene in a human cell. This illustrates close relatedness of the genes. <ref>http://www.jbc.org/cgi/content/full/279/11/10796</ref> |
==Structual Properties== | ==Structual Properties== | ||
Revision as of 03:32, 6 March 2012
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ http://www.jbc.org/cgi/content/full/281/36/26022
- ↑ http://www.jbc.org/cgi/content/full/279/11/10796
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/
BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool, National Center for Biotechnology Information
Gräslund A, Narváez AJ, Thelander L, Voevodskaya N. 2006 "The Involvement of Arg265 of Mouse Ribonucleotide Reductase R2 Protein in Proton Transfer and Catalysis." J. Biol. Chem., 281(36): 26022-26028.
Björklund S, Chabes AL, Thelander L. 2004 "S Phase-specific Transcription of the Mouse Ribonucleotide Reductase R2 Gene Requires Both a Proximal Repressive E2F-binding Site and an Upstream Promoter Activating Region." J. Biol. Chem., 279(11): 10796-10807.
PDBSum: European Bioinformatics Institution