Sandbox Reserved 484
From Proteopedia
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
[[Image:CTSBFig1.jpg | thumb]] | [[Image:CTSBFig1.jpg | thumb]] | ||
| - | Cathepsin B is a very complex protein which is a part of the super family of papain-like cysteine proteases. These papain-like cysteine proteases are abundant in nature and can be found in baculovirus, eubacteria, yeast, plants, and animals. They are synthesized as inactive pro-enzymes with N-terminal pro-peptide regions. The pro-peptide plays an important role as an inhibitor of enzymatic activity. A number of cysteine proteases are located within lysosomes and they have very specific functions in endo and exopeptidase activity. Cathepsin B is synthesized as a pre-proenzyme of 339 amino acid residues and it can act as an endopeptidase. Its activity is inhibited by a2-macroglobulin. The most crucial functions of Cathepsin B are that it is implicated in the turnover of proteins and carries out different roles in maintaining the normal metabolism of cells. Cathepsin B is found in humans and other mammals and it is encoded by a single gene and this gene exhibits a high degree of sequence homology to other cysteine proteases of the papain super family. However, in parasitic helmiths and free-living nematodes, the cathepsin B genes can be seen as large multigene families instead of just one single gene shown in humans and mammals. The function of this cathepsin B gene has not been verified for sure, but research is showing that cathepsin B could be involved in induction of protective immunity. In diseases, such as cancer and arthritis, Cathepsin B gene shows up regulation and in Alzheimer’s disease down regulation is shown. | + | Cathepsin B is a very complex protein which is a part of the super family of papain-like cysteine proteases[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Papain]. These papain-like cysteine proteases are abundant in nature and can be found in baculovirus, eubacteria, yeast, plants, and animals. They are synthesized as inactive pro-enzymes with N-terminal pro-peptide regions. The pro-peptide plays an important role as an inhibitor of enzymatic activity. A number of cysteine proteases are located within lysosomes and they have very specific functions in endo and exopeptidase activity. Cathepsin B is synthesized as a pre-proenzyme of 339 amino acid residues and it can act as an endopeptidase. Its activity is inhibited by a2-macroglobulin. The most crucial functions of Cathepsin B are that it is implicated in the turnover of proteins and carries out different roles in maintaining the normal metabolism of cells. Cathepsin B is found in humans and other mammals and it is encoded by a single gene and this gene exhibits a high degree of sequence homology to other cysteine proteases of the papain super family. However, in parasitic helmiths and free-living nematodes, the cathepsin B genes can be seen as large multigene families instead of just one single gene shown in humans and mammals. The function of this cathepsin B gene has not been verified for sure, but research is showing that cathepsin B could be involved in induction of protective immunity. In diseases, such as cancer and arthritis, Cathepsin B gene shows up regulation and in Alzheimer’s disease down regulation is shown. |
Revision as of 18:44, 1 May 2012
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 13/03/2012, through 01/06/2012 for use in the course "Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Robert B. Rose at the North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 451 through Sandbox Reserved 500. | |||||||
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing For more help, look at this link: http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Help:Getting_Started_in_Proteopedia
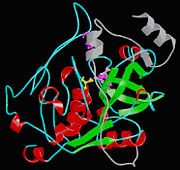
Cathepsin BCathepsin B is a very complex protein which is a part of the super family of papain-like cysteine proteases[1]. These papain-like cysteine proteases are abundant in nature and can be found in baculovirus, eubacteria, yeast, plants, and animals. They are synthesized as inactive pro-enzymes with N-terminal pro-peptide regions. The pro-peptide plays an important role as an inhibitor of enzymatic activity. A number of cysteine proteases are located within lysosomes and they have very specific functions in endo and exopeptidase activity. Cathepsin B is synthesized as a pre-proenzyme of 339 amino acid residues and it can act as an endopeptidase. Its activity is inhibited by a2-macroglobulin. The most crucial functions of Cathepsin B are that it is implicated in the turnover of proteins and carries out different roles in maintaining the normal metabolism of cells. Cathepsin B is found in humans and other mammals and it is encoded by a single gene and this gene exhibits a high degree of sequence homology to other cysteine proteases of the papain super family. However, in parasitic helmiths and free-living nematodes, the cathepsin B genes can be seen as large multigene families instead of just one single gene shown in humans and mammals. The function of this cathepsin B gene has not been verified for sure, but research is showing that cathepsin B could be involved in induction of protective immunity. In diseases, such as cancer and arthritis, Cathepsin B gene shows up regulation and in Alzheimer’s disease down regulation is shown.
Structure
The structure of cathepsin B. FunctionMechanism of ActionMedical Implications or Possible ApplicationReferences |