Sandbox Reserved 483
From Proteopedia
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
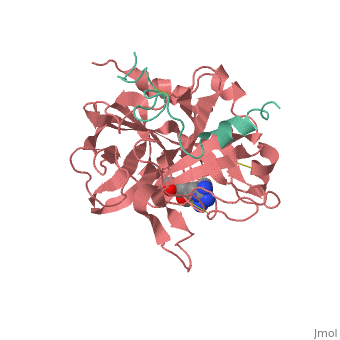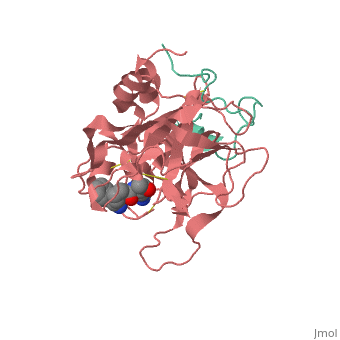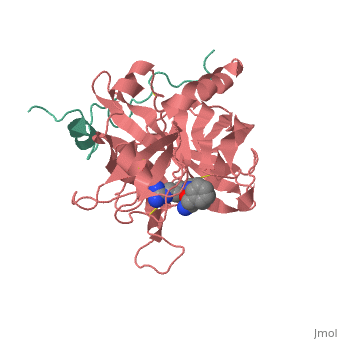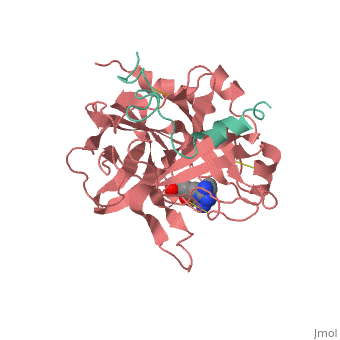
<Structure load='<Structure load='1ppb' size='600' frame='true' align='right' caption='Thrombin (Factor IIa)' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | <Structure load='<Structure load='1ppb' size='600' frame='true' align='right' caption='Thrombin (Factor IIa)' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
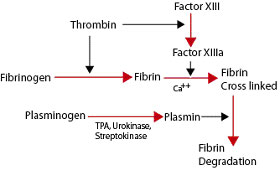
| - | Thrombin is a Trypsin like Serine protease (1). It uses the serine amino acid to specifically cleave fibrinogen into fibrin (3).This forms a blood clot which stops blood from leaking out of the blood circulatory system in case of a rupture. It also catalyzes the activation of factor XIII which stabilizes the fibrin network (3). | + | Thrombin is a Trypsin like Serine protease (1). It uses the serine amino acid to specifically cleave fibrinogen into fibrin (3).This forms a blood clot which stops blood from leaking out of the blood circulatory system in case of a rupture. It also catalyzes the activation of factor XIII which stabilizes the fibrin network (3). It additionally aids in inflammatory responses by activating neutrophils and platelet (2). |
'''Structure''' | '''Structure''' | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | The thrombin molecular structure can be divided into two chains. The first chain (chain A) has 36 residues and is non-essential for proteolytic activities. The second chain (chain B) has a total of 259 amino acid residues and is derived from the carboxyl terminal sequence of prothrombin (2). | + | The thrombin molecular structure can be divided into two chains. The first chain (chain A) has 36 residues and is non-essential for proteolytic activities. The second chain (chain B) has a total of 259 amino acid residues and is derived from the carboxyl terminal sequence of prothrombin (2). With the B chain containing 3 active site amino acids, His57, Asp102, and Ser195 (2). |
Revision as of 00:25, 2 May 2012
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 13/03/2012, through 01/06/2012 for use in the course "Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Robert B. Rose at the North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 451 through Sandbox Reserved 500. | ||||||
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing For more help, look at this link: http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Help:Getting_Started_in_Proteopedia Thrombin (Factor IIa)Introduction
Thrombin is a Trypsin like Serine protease (1). It uses the serine amino acid to specifically cleave fibrinogen into fibrin (3).This forms a blood clot which stops blood from leaking out of the blood circulatory system in case of a rupture. It also catalyzes the activation of factor XIII which stabilizes the fibrin network (3). It additionally aids in inflammatory responses by activating neutrophils and platelet (2). Structure The thrombin molecular structure can be divided into two chains. The first chain (chain A) has 36 residues and is non-essential for proteolytic activities. The second chain (chain B) has a total of 259 amino acid residues and is derived from the carboxyl terminal sequence of prothrombin (2). With the B chain containing 3 active site amino acids, His57, Asp102, and Ser195 (2).
Applications References Source 1: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/101/motm.do?momID=25 Source 2: http://serpins.med.unc.edu/~fcc/ResearchPicts2006/Thrombin.html Source 3: Widmaier, Eric P., Hershel Raff, Kevin T. Strang, and Arthur J. Vander. "Cardiovascular Physiology." Vander's Human Physiology: The Mechanisms of Body Function. Boston: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2008. 423-27. Print. Source 5: http://www.pdb.org/pdb/101/motm_disscussed_entry.do?id=1ppb |